Inside a Real Fraud Detection Case Study: Leveraging AI and Big Data for Superior Security
In the relentless battle against financial crime, organizations are turning to advanced technologies to safeguard assets and consumer trust. This deep dive presents a compelling fraud detection case study, illustrating how the strategic integration of AI and big data platforms provides an unprecedented advantage. By combining sophisticated machine learning with vast, real-time data streams, businesses can now identify and mitigate fraudulent activities with unparalleled precision and speed, transforming security from a reactive measure into a proactive defense mechanism.
Introduction: The Imperative for Advanced Fraud Detection
The digital age has ushered in an era of unprecedented convenience, but it has also created fertile ground for sophisticated fraudulent schemes. Traditional rule-based systems, once the bedrock of financial security, are increasingly proving inadequate against the cunning and ever-evolving tactics of fraudsters. These legacy systems are often rigid, slow to adapt, and generate a high number of false positives, disrupting legitimate transactions and eroding customer confidence. The sheer volume, velocity, and variety of modern transaction data – the “Big Data” challenge – simply overwhelm manual review processes and static rulesets.
Against this backdrop, the need for a dynamic and intelligent approach to fraud prevention has become paramount. This article explores a practical fraud detection case study, highlighting how a financial institution leveraged a cutting-edge AI Data Platform to overcome these challenges. The objective is to demonstrate the transformative power of a unified data and AI strategy, enabling real-time anomaly detection and predictive analytics to not only identify fraud but also anticipate it, thereby protecting both the institution’s bottom line and its reputation.
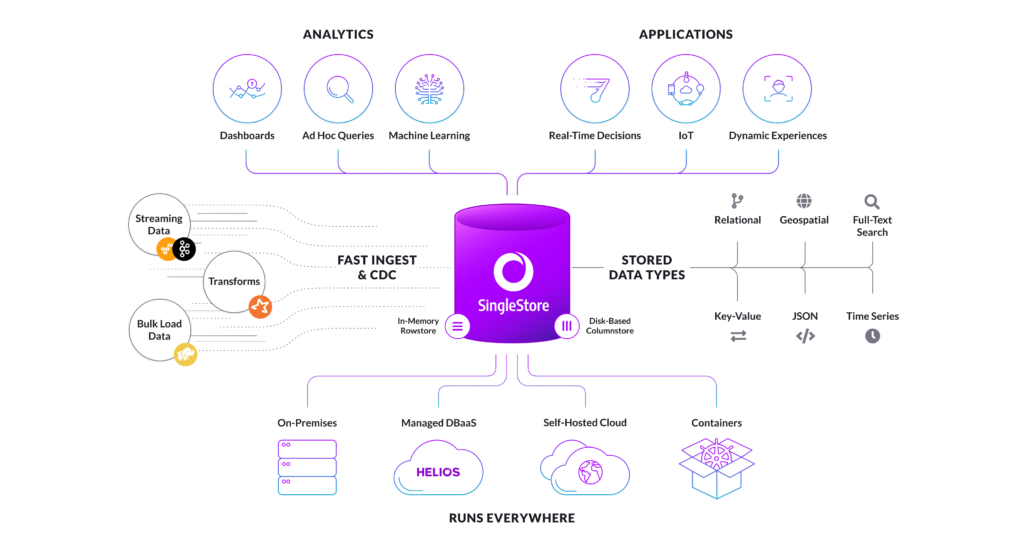
Core Breakdown: Architecting AI-Powered Fraud Detection Platforms
An effective AI-powered fraud detection system is built upon a robust architectural foundation, typically a unified AI Data Platform. This platform is designed to handle immense data volumes, facilitate complex analytical operations, and support the entire machine learning lifecycle, from data ingestion to model deployment and monitoring. For a comprehensive fraud detection case study, understanding these underlying technical components is crucial.
Unified Data & AI Platform with Streaming Architecture
At the heart of modern fraud detection is a streaming architecture capable of ingesting and processing data in real-time. This involves:
- Real-time Data Ingestion: Technologies like Apache Kafka or Amazon Kinesis capture transaction data, user login attempts, behavioral biometrics, and other critical signals as they occur. This ensures that fraudulent activities are flagged milliseconds after they happen, rather than hours or days later.
- Data Transformation and Feature Engineering: Raw data is cleaned, enriched, and transformed into features suitable for machine learning models. This might involve calculating aggregate statistics (e.g., average transaction value over the last hour), deriving velocity features (e.g., number of transactions per minute), or constructing relational features (e.g., how many unique merchants a user interacted with recently).
- Feature Store: A critical component of any scalable AI Data Platform, the Feature Store serves as a centralized repository for curated and versioned features. It ensures consistency between training and serving environments, reduces data duplication, and accelerates the development of new fraud detection models. For instance, features like “customer’s typical spending habits” or “geographic transaction clusters” can be pre-computed and made readily available.
- Model Training and Management: The platform supports the training of various machine learning models—from traditional algorithms like Gradient Boosting Machines (GBM) to deep learning models for sequence analysis. An MLOps framework facilitates experiment tracking, model versioning, and automated retraining, ensuring models remain effective against evolving fraud patterns.
- Real-time Inference Engine: Deployed models make predictions on incoming data streams, identifying anomalies and assigning a fraud probability score to each transaction. This engine needs to be highly scalable and low-latency to provide instantaneous decisions.
- Data Labeling and Feedback Loops: Continuous improvement relies on accurately labeled data. When an alert is generated, human analysts review it. Their feedback (e.g., “confirmed fraud,” “false positive”) is then used to label data, which in turn retrains and refines the models. This iterative process, often supported by specialized data labeling tools, is vital for model performance.
The Power of Real-time Anomaly Detection and Classification Models
In our featured fraud detection case study, the platform employed a hybrid approach combining multiple AI/ML techniques. Anomaly detection models were trained to identify deviations from normal behavioral baselines, flagging unusual transaction sizes, locations, or frequencies. Concurrently, classification models (e.g., Random Forests, Neural Networks) were trained on historical labeled fraud data to predict the likelihood of a transaction being fraudulent based on a wide array of features. The synergy of these models allowed the system to catch subtle indicators of fraud that would be impossible for rule-based systems to detect.
Challenges and Barriers to Adoption
While the benefits are clear, implementing an advanced AI Data Platform for fraud detection is not without its hurdles:
- Data Quality and Integration: Inconsistent data formats, missing values, and disparate data sources can severely impact model performance. Integrating data from legacy systems often requires significant engineering effort.
- Data Drift and Model Decay: Fraudsters are adaptive. Over time, the patterns of fraud change, leading to “data drift” where the distribution of incoming data diverges from the data the model was trained on. This necessitates continuous monitoring and frequent model retraining, a core aspect of robust MLOps.
- Interpretability and Explainability: “Black box” AI models can be difficult to interpret, posing challenges for regulatory compliance and audit trails. Techniques like SHAP or LIME are often employed to provide explainability for model decisions.
- False Positives vs. False Negatives: Striking the right balance is crucial. Too many false positives disrupt legitimate customers, while too many false negatives lead to financial losses. Optimizing models for specific business objectives (e.g., minimizing financial loss while maintaining customer experience) is a continuous challenge.
- Regulatory Compliance and Data Privacy: Handling sensitive financial data requires strict adherence to regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and industry-specific compliance standards, adding complexity to data governance and storage.
Business Value and ROI: A Tangible Impact
Despite the challenges, the return on investment (ROI) from a well-implemented AI Data Platform for fraud detection is substantial:
- Significant Reduction in Financial Losses: Direct impact on the bottom line by preventing successful fraudulent transactions.
- Faster Model Deployment and Iteration: MLOps practices enable rapid deployment of new models and quick adaptation to emerging fraud schemes, ensuring continuous protection.
- Improved Data Quality for AI: Centralized data governance and Feature Stores ensure high-quality, consistent data, leading to more accurate and reliable models.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Fewer false positives mean fewer legitimate transactions are declined, improving customer satisfaction and trust.
- Operational Efficiency: Automating fraud detection reduces the manual workload on human analysts, allowing them to focus on complex cases and strategic initiatives.
- Better Risk Management: Proactive identification of high-risk scenarios and emerging threats strengthens the overall risk posture of the organization.

Comparative Insight: AI Data Platforms vs. Traditional Approaches in Fraud Detection
To fully appreciate the impact of a modern AI Data Platform on fraud detection, it’s essential to compare it against previous generations of technology. Historically, fraud detection relied heavily on rule-based systems and human analysts.
Traditional Rule-Based Systems and Data Warehouses
Legacy systems typically operate on a predefined set of rules, such as “block transactions over $1000 from a new IP address” or “flag more than 5 transactions in 5 minutes.” These systems are:
- Static: They struggle to adapt to new fraud patterns unless rules are manually updated, which is time-consuming and reactive.
- Prone to High False Positives: Overly broad rules can inadvertently block legitimate customer activity. Conversely, rules that are too narrow can miss sophisticated fraud.
- Limited Scalability: Processing vast, real-time data streams efficiently becomes a significant challenge, often leading to batch processing with delays.
- Lack of Predictive Power: They identify fraud after it occurs, rather than predicting potential risks.
- Data Warehouses: While excellent for historical reporting and business intelligence, traditional data warehouses are not optimized for the high-velocity, real-time ingestion and complex analytical workloads required for modern AI-driven fraud detection. Their batch-oriented nature and rigid schemas often create bottlenecks for dynamic feature engineering and model training.
The Evolution to Data Lakes and Beyond
The introduction of data lakes offered more flexibility by storing raw, unstructured data at scale. This was a step forward, allowing for more diverse data sources. However, data lakes alone often lacked:
- Data Governance: Without proper tooling, data lakes can become “data swamps,” making it difficult to find, understand, and trust data.
- Real-time Capabilities: While capable of storing real-time streams, processing and acting on that data in real-time still required significant custom engineering.
- Integrated AI/ML Lifecycle: Data lakes provided the raw material but didn’t inherently offer the integrated tools for MLOps, Feature Stores, or automated model deployment and monitoring.
The Distinct Advantage of AI Data Platforms
In contrast, a dedicated AI Data Platform for fraud detection offers a holistic, integrated solution:
- Adaptive and Proactive: Machine learning models continuously learn from new data, detecting novel fraud patterns and predicting future risks. This adaptability is critical in an evolving threat landscape.
- Real-time Decision Making: Streaming architectures and low-latency inference engines enable instantaneous fraud detection and prevention, minimizing losses.
- Superior Accuracy and Reduced False Positives: Sophisticated algorithms analyze millions of data points and complex relationships, leading to more precise fraud identification and fewer disruptions for legitimate customers.
- End-to-End MLOps: The platform supports the entire machine learning lifecycle, from automated data ingestion and feature engineering (via a Feature Store) to model training, deployment, monitoring, and retraining, ensuring model efficacy over time.
- Robust Data Governance: Features like data lineage, central metadata management, and auditability (as highlighted by “Data Lineage for Model Auditing” in our context) are built-in, addressing compliance requirements and increasing trust in AI decisions.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud-native or hybrid architectures allow the platform to scale dynamically with data volume and computational demands, while offering flexibility in deploying various AI/ML models.
While cloud-native AI/ML services (e.g., AWS SageMaker, Google Vertex AI) offer powerful tools, and specialized Fraud Detection SaaS (e.g., Feedzai, Sift) provide out-of-the-box solutions, a bespoke AI Data Platform often provides greater customization, tighter integration with proprietary data, and full control over the AI/ML pipeline, especially for organizations with unique regulatory requirements or highly specific fraud typologies. This allows the organization in our fraud detection case study to tailor its solution precisely to its needs, differentiating it from generic offerings.

World2Data Verdict: Pioneering the Future of Secure Transactions
The success demonstrated in this fraud detection case study unequivocally illustrates that the future of financial security lies in adaptive, intelligent AI Data Platforms. For organizations navigating the treacherous waters of digital fraud, the imperative is clear: move beyond static defenses and embrace a dynamic, AI-first approach. World2Data.com advocates for the strategic investment in unified data and AI platforms that prioritize real-time processing, robust MLOps capabilities, and centralized Feature Stores. The ability to rapidly iterate on models, ensure data quality for AI, and provide transparent data lineage for auditing is not merely an advantage but a fundamental requirement.
We predict that successful enterprises will increasingly adopt modular yet integrated platforms that allow for seamless integration of new data sources and advanced AI models. This will empower them to not only detect existing fraud but also proactively predict and neutralize emerging threats, thereby securing customer trust and maintaining a resilient financial ecosystem in an increasingly complex digital world. This proactive stance, powered by sophisticated data and AI, is the bedrock of future financial security, transforming every fraud detection case study into a testament to innovation and resilience.