Real-Time Analytics: The Power of Instant Data in 2025
For organizations navigating the complexities of the modern digital landscape, the capacity to process and derive insights from data instantly defines success. Real-Time Analytics offers unparalleled opportunities to respond to events as they unfold, turning raw data into actionable intelligence without delay. This article delves into the transformative power of instant data, exploring its architectural underpinnings, business benefits, and strategic imperatives for the coming years.
Platform Category: Stream Processing, Event Streaming, Real-time Data Warehousing
Core Technology/Architecture: Event-Driven Architecture, Low-Latency Data Processing, Distributed Stream Processing, In-Memory Computing
Key Data Governance Feature: Real-time Data Lineage, Streaming Data Access Control, Data Quality for Event Streams
Primary AI/ML Integration: Real-time ML Inference, Anomaly Detection, Predictive Analytics on Event Streams
Main Competitors/Alternatives: Apache Flink, Apache Kafka, Apache Spark Streaming, ClickHouse, Google Cloud Dataflow, AWS Kinesis
Unlocking Value with Real-Time Analytics in the Modern Enterprise
In 2025, the proliferation of data from IoT devices, web interactions, social media, and transactional systems means that traditional batch processing can no longer keep pace with business demands. Real-Time Analytics transcends the limitations of historical data analysis, providing immediate insights that empower organizations to make instantaneous decisions. This paradigm shift from reactive to proactive operations is not merely an technological upgrade; it’s a fundamental change in how businesses interact with their environment, anticipate customer needs, and mitigate emerging risks.
The objective of this deep dive is to dissect the multifaceted nature of real-time data processing, highlighting its architectural components, the challenges inherent in its implementation, and the significant return on investment it delivers. We will explore how instant data fuels everything from operational efficiency and enhanced customer experiences to driving innovation and securing a definitive competitive edge. Understanding the nuances of Real-Time Analytics is no longer optional; it is a critical imperative for any organization aiming to thrive in the data-driven future.
Core Breakdown: Architecture, Components, and Capabilities of Real-Time Analytics
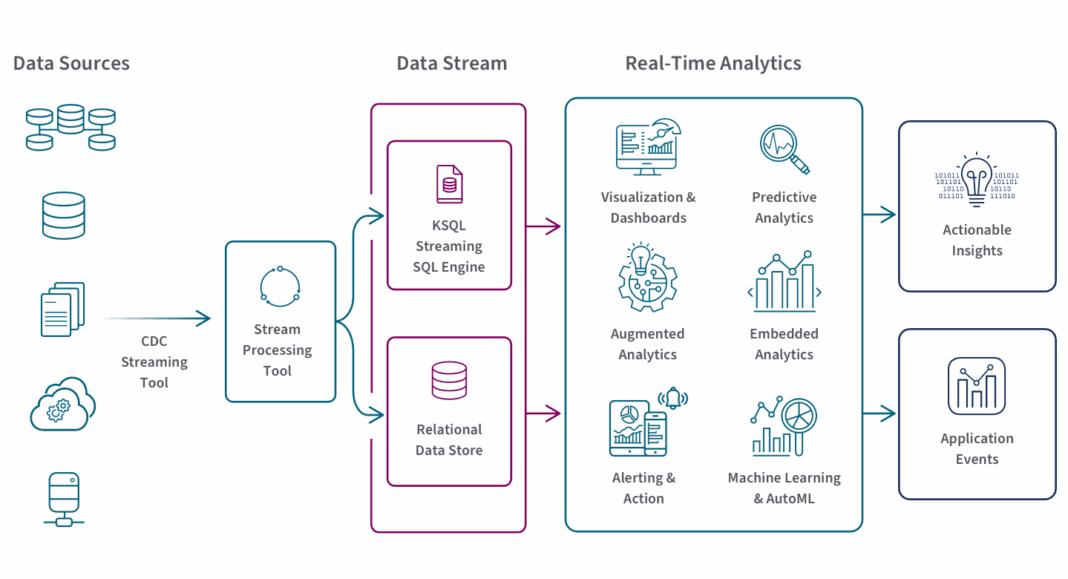
At its heart, a robust Real-Time Analytics platform relies on a sophisticated interplay of specialized technologies designed to handle data streams with minimal latency. The architecture is typically event-driven, meaning that data is processed as a continuous flow of events rather than in discrete batches. This allows for immediate action and insight generation.
Underlying Technologies and Architecture:
- Event-Driven Architecture (EDA): This foundational paradigm treats every action or state change as an “event.” Systems built on EDA process these events as they occur, facilitating rapid propagation and analysis. Technologies like Apache Kafka or AWS Kinesis are central to event streaming, acting as high-throughput, fault-tolerant distributed log systems for publishing and subscribing to event streams.
- Stream Processing Engines: These are the computational workhorses of real-time analytics. Platforms such as Apache Flink, Apache Spark Streaming, and Google Cloud Dataflow excel at ingesting, transforming, and analyzing continuous data streams. They can perform complex aggregations, windowing functions, and stateful computations on data in motion, enabling immediate pattern recognition and anomaly detection.
- Low-Latency Data Processing: This refers to the ability to process data with delays measured in milliseconds. It requires optimized network protocols, efficient serialization formats, and processing engines designed for speed.
- In-Memory Computing: To achieve ultra-low latency, many real-time analytics solutions leverage in-memory databases or data grids. Storing frequently accessed data and computational states directly in RAM significantly reduces I/O bottlenecks associated with disk-based systems, accelerating query responses and analytical operations.
- Real-time Data Warehousing: While traditional data warehouses are designed for historical analysis, real-time data warehousing solutions (like ClickHouse) are optimized for ingesting and querying massive volumes of streaming data with very low latency, often used for operational analytics dashboards.
Key Features for Data Governance and AI/ML Integration:
- Real-time Data Lineage: Crucial for compliance and understanding data flow, real-time data lineage tracks events from source to consumption, providing an audit trail for data transformations and usage within the streaming pipeline.
- Streaming Data Access Control: Implementing granular security policies on data streams ensures that sensitive information is only accessible to authorized users and applications, a vital aspect of data privacy and compliance in real-time environments.
- Data Quality for Event Streams: Maintaining high data quality is paramount. Real-time validation and cleansing mechanisms detect and correct errors, inconsistencies, or missing values as data flows through the system, preventing propagation of bad data into downstream analytics or AI models.
- Real-time ML Inference: Integrating machine learning models directly into streaming pipelines allows for instantaneous predictions and recommendations. For example, fraud detection systems can score transactions in milliseconds, or recommendation engines can suggest products based on current browsing behavior.
- Anomaly Detection: By continuously monitoring data streams, real-time analytics platforms can identify unusual patterns or outliers immediately, triggering alerts for security breaches, operational failures, or sudden shifts in market trends.
- Predictive Analytics on Event Streams: Beyond detection, these capabilities enable systems to forecast future events or behaviors based on the incoming stream of data, such as predicting equipment failure before it occurs or anticipating customer churn.
Challenges and Barriers to Adoption
Despite its immense potential, implementing Real-Time Analytics is not without its hurdles. Organizations often face significant challenges:
- Data Volume, Velocity, and Variety (the 3 Vs): Managing the sheer scale, speed, and diverse formats of incoming real-time data requires robust infrastructure and sophisticated processing capabilities.
- Data Quality and Consistency: Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of data ingested from disparate sources in real-time is a continuous challenge, exacerbated by potential data drift or schema changes.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating real-time analytics components with existing legacy systems, diverse data sources, and downstream applications can be complex and resource-intensive.
- Operational Complexity and MLOps: Deploying, monitoring, and maintaining real-time streaming pipelines and integrated AI/ML models demands specialized skills and robust MLOps practices to handle continuous deployment, model drift detection, and immediate retraining.
- Cost of Infrastructure and Tools: The specialized hardware, software licenses, and cloud services required for high-performance real-time processing can represent a substantial investment.
- Skill Gap: There’s a persistent shortage of data engineers and architects proficient in stream processing, distributed systems, and real-time data governance.
- Security and Regulatory Compliance: Securing data in motion and ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR or CCPA for rapidly moving data streams adds layers of complexity.
Business Value and ROI
Overcoming these challenges unlocks substantial business value, leading to a compelling return on investment (ROI):
- Faster Model Deployment and Iteration: Real-time feedback loops significantly accelerate the deployment of new analytical models and features, allowing businesses to adapt quicker to market changes.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Instant insights empower decision-makers to react proactively to unfolding events, whether it’s optimizing marketing campaigns, adjusting supply chains, or detecting fraud.
- Optimized Operations: From predictive maintenance in manufacturing to dynamic inventory management in retail, real-time data streamlines operations, reduces waste, and boosts efficiency.
- Superior Customer Experience: Personalized recommendations, proactive customer support, and tailored engagements based on current behavior lead to increased satisfaction and loyalty.
- Competitive Advantage: Businesses leveraging instant data can identify emerging trends, launch new products faster, and outmaneuver slower competitors, securing a leading position in dynamic markets.
- Improved Data Quality for AI: Real-time data validation and cleansing ensure that AI/ML models are trained and inferencing on the freshest, most accurate data, leading to more reliable predictions and decisions.

As the above AI Data Platform Architecture Diagram illustrates, Real-Time Analytics forms a crucial foundational layer, feeding cleaned and enriched data streams into various AI/ML components for immediate intelligence generation and model serving. It underpins the entire data lifecycle, from ingestion to real-time inference.
Comparative Insight: Real-Time Analytics vs. Traditional Data Lakes/Warehouses
To truly appreciate the power of Real-Time Analytics, it’s essential to contrast it with the more traditional data processing paradigms: the Data Lake and the Data Warehouse. While these traditional systems have served as cornerstones for business intelligence and historical analysis for decades, they operate on fundamentally different principles and cater to different use cases.
Traditional Data Warehouses are highly structured repositories designed for reporting and historical analysis. Data is typically extracted, transformed, and loaded (ETL) in batches, often daily or weekly. This process involves significant latency, meaning the data analyzed is always historical, not current. Data warehouses excel at complex queries over large volumes of historical data for long-term strategic planning, trend analysis, and regulatory reporting. Their strength lies in data consistency, predefined schemas, and robust data governance for structured data.
Data Lakes emerged to address the limitations of data warehouses in handling unstructured and semi-structured data at scale. They store raw data in its native format, often in large, inexpensive storage systems like HDFS or cloud object storage. Data lakes are flexible and support various analytical workloads, including big data processing, machine learning, and exploratory analysis. However, like data warehouses, they are primarily optimized for batch processing. While they can ingest data quickly, deriving insights typically involves processing pipelines that introduce delays, making them less suitable for immediate decision-making.
In stark contrast, Real-Time Analytics platforms are designed for immediacy. Their primary goal is to process data “in flight,” as it is generated, to deliver insights within milliseconds or seconds. The core differences are profound:
- Latency: Real-Time Analytics (milliseconds to seconds) vs. Data Warehouses/Lakes (minutes to hours or days).
- Data State: Real-Time Analytics focuses on data in motion (streams, events) vs. Data Warehouses/Lakes primarily on data at rest (persisted historical data).
- Use Cases: Real-Time Analytics enables fraud detection, personalized customer interactions, predictive maintenance, dynamic pricing, and operational monitoring. Data Warehouses/Lakes support quarterly reports, annual trend analysis, campaign effectiveness evaluation, and long-term business strategy.
- Data Model: Real-Time Analytics often operates on schema-on-read principles for flexibility with event data, though strong schema governance is increasingly important for data quality. Data Warehouses rely on schema-on-write with rigid structures. Data Lakes are schema-agnostic for raw data.
- Processing Paradigm: Stream processing for Real-Time Analytics vs. Batch processing for Data Warehouses/Lakes.
- Infrastructure: Specialized stream processing engines, in-memory databases, and event brokers for real-time; relational databases, distributed file systems, and MPP architectures for traditional systems.
While distinct, these paradigms are not mutually exclusive. A comprehensive modern data strategy often involves an integrated approach, where Real-Time Analytics platforms feed processed, high-quality data into data lakes or data warehouses for historical archiving, deeper analytical queries, and model training. This hybrid approach leverages the strengths of each system, providing both immediate operational insights and robust historical context for strategic decision-making. The real power lies in orchestrating these systems to create a unified, agile data ecosystem.

The MLOps Workflow Automation diagram highlights how continuous integration, continuous delivery, and continuous monitoring are critical for managing the lifecycle of machine learning models. Real-Time Analytics plays a pivotal role here, providing the low-latency data necessary for real-time inference, model drift detection, and enabling automated model retraining in response to live data changes, thereby operationalizing AI at speed and scale.
World2Data Verdict: The Imperative for Real-Time Agility
The future of business, particularly by 2025, is inextricably linked to the ability to leverage data instantly. Real-Time Analytics is no longer a luxury for pioneering tech companies but a fundamental requirement for competitive advantage across virtually every industry. World2Data.com asserts that organizations failing to integrate robust real-time analytical capabilities into their core strategy will find themselves increasingly marginalized by more agile, data-driven competitors.
Our recommendation is clear: enterprises must prioritize investment in event-driven architectures, advanced stream processing technologies, and comprehensive data governance frameworks designed for high-velocity data. This includes fostering a culture of data literacy and upskilling teams in areas like MLOps and distributed systems engineering. The shift demands not just technological adoption but a strategic pivot towards immediate responsiveness as a core business principle. Proactive engagement with real-time data sources and the deployment of AI/ML models for real-time inference will differentiate market leaders from followers.
Looking ahead, the convergence of Real-Time Analytics with sophisticated AI and autonomous systems will redefine operational efficiency and customer engagement. Expect to see even more intelligent, self-optimizing systems that can perceive, reason, and act on insights in milliseconds. For World2Data.com, the verdict is absolute: embracing the power of instant data through sophisticated Real-Time Analytics is the single most critical investment for sustained growth, resilience, and innovation in the hyper-connected, data-saturated world of 2025 and beyond.