Master Data Management: A Complete 2025 Implementation Guide for Data Excellence
Master Data Management (MDM) stands as a critical strategic imperative for organizations aiming to achieve data excellence and drive informed decision-making in 2025. This comprehensive guide delves into the core principles, architectural blueprints, and practical implementation strategies for robust MDM systems. By establishing a single, trusted view of critical business entities, enterprises can unlock unparalleled operational efficiency, enhance regulatory compliance, and deliver superior customer experiences, transforming raw data into actionable intelligence.
Introduction: The Imperative of Master Data Management in a Data-Driven World
In an era defined by exploding data volumes, diverse data sources, and accelerated digital transformation, the ability to maintain accurate, consistent, and reliable core business data is no longer a luxury—it’s a fundamental necessity. As organizations grapple with fragmented information across disparate systems, the need for effective Master Data Management (MDM) has never been more pronounced. MDM represents the discipline of creating and maintaining a single, consistent, accurate, and authoritative record of an organization’s master data across all systems and applications. This definitive guide serves as a roadmap for business leaders and data professionals seeking to implement or optimize their MDM system in 2025, ensuring their data strategy is robust, scalable, and future-proof. We will explore the architectural considerations, key features, and practical steps required to establish an MDM framework that fuels strategic growth and operational excellence, positioning MDM not just as a technology solution, but as a cornerstone of modern Data Governance platform initiatives.
Core Breakdown: Architecting the MDM Solution for 2025 Data Excellence
Implementing a successful Master Data Management solution requires a deep understanding of its technical architecture and the strategic integration of various components. A modern MDM system is far more than a simple database; it’s a sophisticated ecosystem designed to manage the lifecycle of critical business data. In 2025, these systems are evolving rapidly, incorporating advanced technologies to meet the demands of enterprise-scale data.
MDM Architecture Deep Dive: Building the Foundation
The foundation of any robust MDM initiative lies in its architectural choice. Common architectural styles include the hub-and-spoke architecture, where a central MDM hub acts as the authoritative source, distributing master data to connected operational systems (spokes). Other styles include the registry style, which primarily links and indexes master data without necessarily storing it centrally, and the consolidation style, focused on merging and deduplicating data from multiple sources into a single view. Contemporary MDM platforms are increasingly adopting cloud-native deployments, leveraging the scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness of cloud infrastructure. These modern solutions often rely on an API-driven integration strategy, enabling seamless, real-time data exchange with other enterprise applications. Furthermore, the adoption of event-driven architecture and microservices allows for greater agility, enabling modular development, independent deployment, and enhanced resilience of the MDM platform, making it adaptable to rapidly changing business requirements and data landscapes.
Core Components and Key Data Governance Features
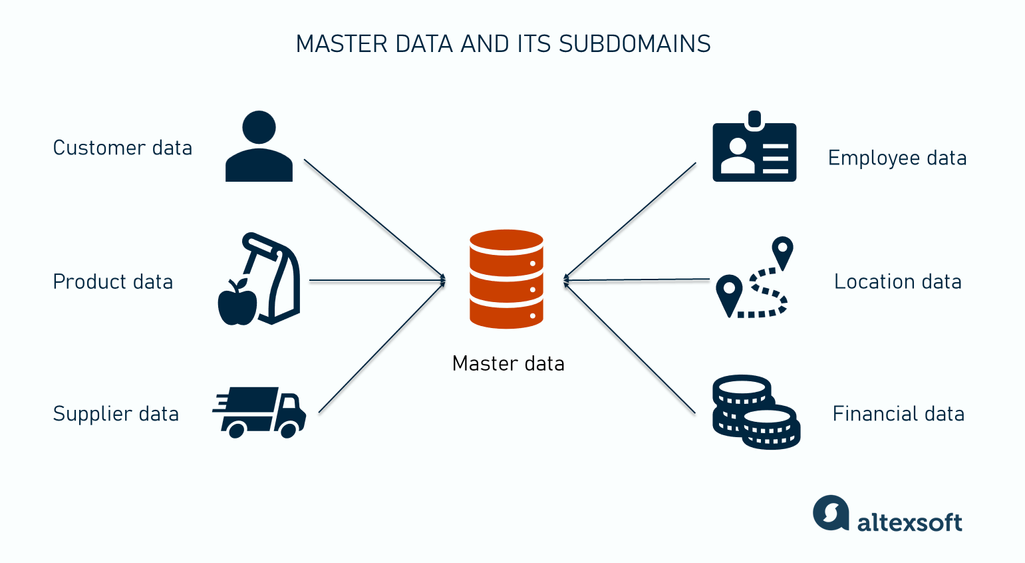
At the heart of an effective MDM system are its core functionalities, deeply intertwined with data governance principles. Key among these is comprehensive data quality management, which involves profiling, cleansing, validating, and enriching master data to ensure its accuracy, completeness, and consistency. This also includes defining and enforcing data quality rules and metrics. Integral to data quality are data stewardship workflows, which empower human data stewards to review, resolve, and approve changes to master data, ensuring that business rules and policies are consistently applied. Moreover, robust metadata management capabilities provide context for master data, detailing its definition, lineage, ownership, and usage. This is complemented by granular role-based access control, ensuring that only authorized users can view or modify sensitive master data. The ultimate goal is the creation and maintenance of a “golden record management” system—a single, definitive, and trusted version of each master data entity (e.g., customer, product, supplier). Finally, effective policy enforcement mechanisms ensure that organizational and regulatory compliance standards are consistently met across all master data operations.
Primary AI/ML Integration for Enhanced MDM
The future of Master Data Management is undeniably shaped by Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. AI/ML capabilities are revolutionizing how master data is managed, maintained, and enriched. Advanced techniques facilitate automated data matching and linking, significantly reducing the manual effort required to identify duplicate records and link related entities across disparate sources. Intelligent data classification automatically categorizes data elements, improving data organization and searchability. Furthermore, anomaly detection for data quality uses machine learning algorithms to identify unusual patterns or outliers in master data, proactively flagging potential errors or inconsistencies that might otherwise go unnoticed. Predictive data quality rules leverage historical data to anticipate and prevent future data quality issues, ensuring higher integrity from the outset. Lastly, natural language processing for data enrichment can extract valuable information from unstructured text fields, enhancing the completeness and usefulness of master data records, thereby transforming the MDM system into a truly intelligent data asset.
Challenges and Barriers to MDM Adoption
While the benefits of Master Data Management are clear, organizations often encounter significant hurdles during implementation and adoption. One primary challenge is securing strong stakeholder buy-in across various departments, as MDM initiatives require cross-functional collaboration and often involve changes to existing processes. Resistance to change, particularly concerning data ownership and stewardship, can derail even the most well-planned projects. The inherent complexity of integrating disparate legacy systems, often with inconsistent data models and quality issues, presents a substantial technical barrier. Initial data quality issues within source systems necessitate extensive data profiling, cleansing, and remediation efforts, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. Sustaining data quality over time also presents an ongoing challenge, requiring continuous monitoring and refinement. Furthermore, defining a clear and actionable data governance framework, along with assigning clear responsibilities for data stewardship, is crucial but often overlooked. Without a continuous improvement mindset and adequate resources for ongoing maintenance and adaptation, an MDM initiative can quickly lose momentum, struggling to keep pace with evolving business needs and data landscapes.
Business Value and Return on Investment (ROI)
The strategic investment in a robust Master Data Management solution yields substantial business value and a compelling return on investment. By providing a single source of truth for critical business entities, MDM significantly improves decision-making across the enterprise. Executives can rely on accurate customer insights for targeted marketing campaigns, precise product data for supply chain optimization, and consistent financial data for accurate reporting. This consistency translates directly into enhanced operational efficiency, as employees spend less time reconciling data discrepancies and more time on high-value activities. Reduced data errors and redundancy lead to lower operational costs and improved resource utilization. From a compliance perspective, MDM helps organizations meet stringent regulatory requirements (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) by ensuring consistent data definitions and robust data lineage, bolstering regulatory compliance and mitigating risks. Ultimately, a unified view of customer data enables businesses to deliver a more personalized and consistent experience, leading to enhanced customer experience and loyalty. Furthermore, MDM forms a crucial underpinning for advanced analytics and AI initiatives, providing the high-quality, trusted data required for accurate machine learning models and actionable insights, thus accelerating innovation and competitive advantage.

Comparative Insight: MDM vs. Traditional Data Lakes and Data Warehouses
While Master Data Management, data lakes, and data warehouses all play pivotal roles in an organization’s data strategy, they serve distinct yet complementary purposes. Understanding these differences is crucial for architecting a holistic data ecosystem in 2025.
A Traditional Data Warehouse is primarily designed for structured, historical data analysis. It stores transformed and integrated data from various operational systems, optimized for reporting, business intelligence, and analytical queries. Data in a data warehouse is typically clean, highly structured, and governed by a predefined schema. It provides an enterprise-wide view but focuses on aggregated, historical facts rather than the real-time, singular truth of core business entities.
Data Lakes, on the other hand, are vast repositories that store raw, untransformed data at scale, in its native format. They can accommodate structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data, making them ideal for big data analytics, machine learning, and exploratory data science. While data lakes offer immense flexibility and storage capacity, the raw nature of the data means it often lacks consistent definitions, quality, and governance, leading to potential “data swamps” if not properly managed.
Master Data Management occupies a unique and crucial position between these two. Unlike data warehouses or data lakes, an MDM system focuses specifically on creating and maintaining a single, golden record for core business entities (e.g., customer, product, employee, location). It doesn’t store all operational or analytical data, but rather the definitive, most accurate, and consistent version of the identifiers and key attributes for these master entities. MDM provides the contextual glue that connects disparate data points across the data warehouse and data lake. It ensures that when an analyst queries a customer in the data warehouse, or a data scientist trains a model on product data in the data lake, they are always referencing the same, high-quality, trusted master data definition.
In essence, a data warehouse provides the answers to “what happened” based on clean, structured analytical data, while a data lake offers the flexibility for “what could happen” using diverse, raw data for advanced analytics. MDM answers “who or what is it?” by providing the authoritative source for core business entities. Without a robust Master Data Management layer, both data warehouses and data lakes risk ingesting and perpetuating inconsistent or duplicate data, thereby undermining the reliability and trustworthiness of their analytical outputs. In 2025, integrating a strong MDM strategy with both data warehousing and data lake initiatives is paramount for achieving true data synergy and unlocking maximum business value.
A Phased Approach to 2025 MDM Implementation
Successfully implementing a Master Data Management solution is a complex journey that benefits from a structured, phased approach. This methodology minimizes risks, ensures alignment with business objectives, and facilitates continuous value delivery.
Phase 1: Discovery and Planning
- Current State Assessment: Thoroughly analyze existing data landscapes, identifying master data domains, data sources, current data quality issues, and the impact of poor data.
- Define Objectives and Scope: Clearly articulate business goals for MDM (e.g., improve customer experience, enhance regulatory compliance, streamline supply chain). Prioritize master data domains for initial implementation (e.g., customer, product).
- Stakeholder Identification and Engagement: Identify key business users, IT personnel, and data owners. Secure executive sponsorship and establish a cross-functional MDM governance committee.
- Vendor Selection: Based on requirements, evaluate and select an MDM system platform, considering factors like architecture (e.g., cloud-native deployments), integration capabilities (e.g., API-driven integration), and features (e.g., data quality management, data stewardship workflows).
Phase 2: Data Modeling and Integration Design
- Master Data Model Design: Develop a unified, canonical data model for the chosen master data domains. This involves defining attributes, relationships, hierarchies, and unique identifiers (surrogate keys).
- Source System Analysis: Map data elements from source systems to the new master data model, identifying data transformation rules and potential data quality issues at the source.
- Integration Strategy: Design the integration patterns (e.g., batch, real-time, event-driven) between the MDM hub and consuming/contributing systems, leveraging capabilities like API-driven integration.
- Data Governance Framework: Formalize roles and responsibilities, data ownership, data quality rules, and policy enforcement mechanisms.
Phase 3: Solution Configuration and Development
- Platform Setup: Install and configure the chosen MDM system, including setting up environments (development, test, production).
- Rule Configuration: Implement data quality rules, matching and merging rules for golden record management, validation rules, and transformation logic within the MDM platform.
- Workflow Development: Configure data stewardship workflows for data creation, updates, and issue resolution.
- Integration Development: Build the necessary interfaces and connectors to integrate the MDM hub with source and consuming systems.
Phase 4: Data Remediation and Initial Load
- Data Profiling and Cleansing: Use MDM tools to profile source data, identify quality issues, and execute initial data cleansing efforts.
- Data Migration Strategy: Develop and execute a strategy for migrating existing master data into the MDM hub, involving an iterative process of matching, merging, and reconciliation to establish initial golden records.
- Data Validation: Rigorously validate the newly created golden records against business rules and data quality standards.
Phase 5: Deployment, Rollout, and Optimization
- Pilot Program: Roll out the MDM solution to a limited group or department to gather feedback and refine processes.
- Phased Rollout: Gradually extend the MDM solution to more departments and data domains, ensuring smooth adoption and minimal disruption.
- Monitoring and Optimization: Continuously monitor data quality metrics, system performance, and user adoption. Refine rules, workflows, and integrations based on ongoing feedback and evolving business needs.
- Training and Support: Provide comprehensive training for data stewards, business users, and IT support staff to ensure effective use and maintenance of the MDM system.
- Embrace AI/ML: Continuously explore and integrate advanced capabilities such as automated data matching and linking, intelligent data classification, and anomaly detection for data quality to enhance and automate MDM processes over time.
World2Data Verdict: Charting the Future of Master Data Management
In the dynamic landscape of 2025, World2Data.com asserts that Master Data Management is no longer merely an IT project but a strategic business capability that underpins virtually every digital initiative. The most successful organizations will be those that view MDM as a continuous journey, not a one-time implementation. Our recommendation for enterprises is to prioritize an agile, incremental approach to MDM, focusing on immediate business value while building a scalable and adaptable foundation. Embrace cloud-native platforms, leverage AI/ML for automation and intelligence, and foster a strong culture of data stewardship across the enterprise. The future of data-driven success hinges on the integrity and trustworthiness of your master data. Organizations that master Master Data Management will not just survive but thrive, transforming data fragmentation into a unified, strategic asset that drives innovation, enhances customer trust, and ensures sustainable competitive advantage.