How to Create an Effective Data Policy for Your Company: A Comprehensive Guide to Data Governance
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, establishing an effective Data Policy is no longer optional—it’s a strategic imperative. This comprehensive framework acts as the bedrock for robust data governance, ensuring regulatory compliance, mitigating risks, and fostering an environment of data integrity and trust. An expertly crafted Data Policy defines how an organization collects, processes, stores, and protects its most valuable asset, transforming raw information into actionable insights while safeguarding privacy and security.
Introduction: The Indispensable Role of a Robust Data Policy in Modern Business
The proliferation of data across enterprises has amplified the need for structured management and clear guidelines. An effective Data Policy serves as the cornerstone of any successful data governance strategy, outlining the principles and procedures that dictate an organization’s interaction with information. This article delves into the critical elements required to construct a resilient Data Policy for your company, ensuring it acts as a dynamic component of your data governance framework. From establishing strategic data management principles to embedding privacy-by-design mandates, a well-defined policy is essential for navigating the complex terrain of data security, compliance, and ethical usage, especially in the context of emerging AI/ML applications.
Core Breakdown: Architecting Your Company’s Data Policy Framework
Creating a truly effective Data Policy involves a detailed architectural analysis of your data ecosystem and a commitment to integrating strategic principles across all data platforms. It moves beyond a simple document, establishing a living framework that governs data through its entire lifecycle as a critical Data Governance Framework Component.
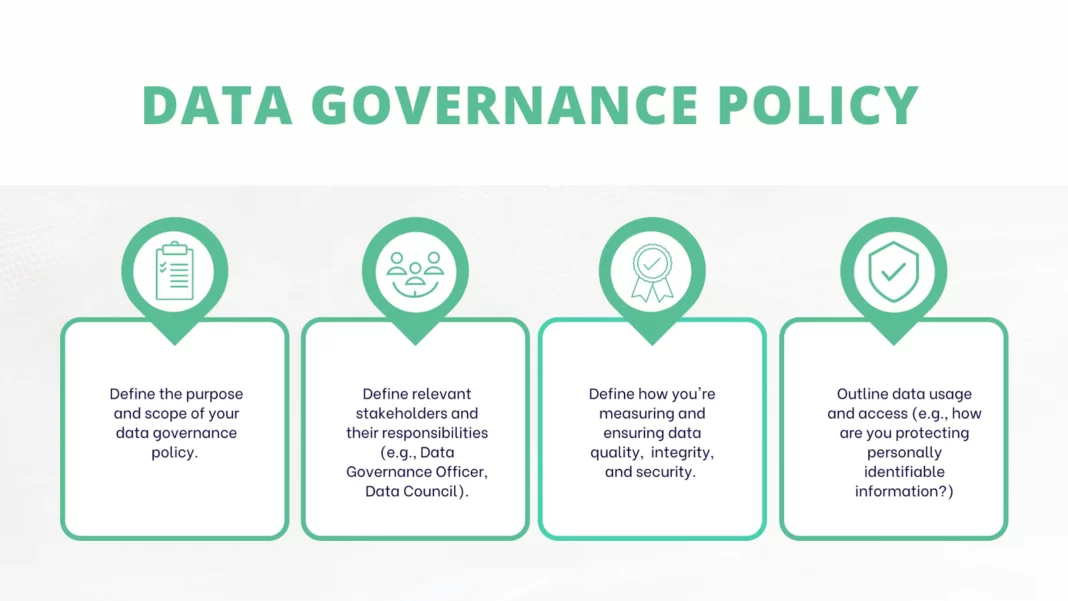
Defining the Scope and Objectives of Your Data Policy
The initial step in crafting your Data Policy is to meticulously define its scope and articulate clear objectives. This involves identifying all key data types your company handles—from sensitive Personal Identifiable Information (PII) and financial records to intellectual property and operational telemetry. Your policy should categorize data based on its sensitivity, regulatory requirements, and business value. The objectives should clearly state what the policy aims to achieve: whether it’s primarily about achieving regulatory compliance (e.g., GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA), fostering innovation through secure data usage, enhancing overall data quality, or building customer trust through transparent practices. This foundational analysis helps to tailor the policy to your specific organizational needs and legal obligations, thereby establishing strategic data management principles from the outset.
Key Components of a Comprehensive Data Policy
A robust Data Policy, serving as a critical component of your data governance framework, must address several core areas to be truly effective:
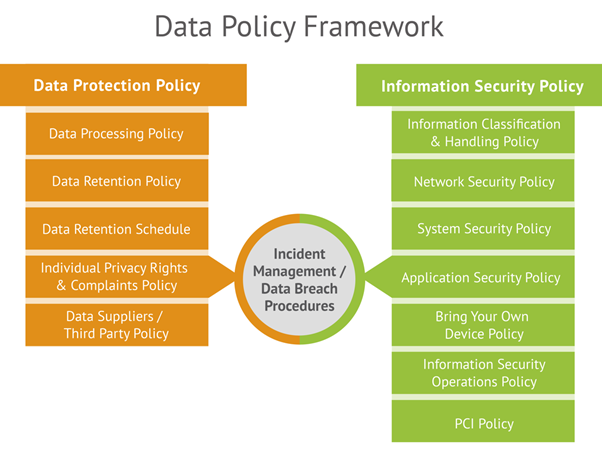
- Data Collection and Usage Guidelines: This section mandates how data is acquired, processed, and utilized. It should emphasize transparency, necessity, and legality, ensuring data is collected for specific, legitimate purposes and not subsequently used in a manner incompatible with those purposes. For AI/ML integrations, this includes providing ethical guidelines for data collection and usage in AI/ML.
- Data Classification Standards: A fundamental aspect of data management, these standards define categories of data (e.g., public, internal, confidential, restricted) based on sensitivity and business impact. Proper data classification is crucial for implementing appropriate security controls and ensuring compliance.
- Data Storage and Retention Protocols: Your policy must detail secure storage methods—whether on-premises, cloud-based, or hybrid—and specify data retention and deletion schedules. This prevents indefinite data hoarding, reduces storage costs, and minimizes the risk exposure associated with holding outdated or unnecessary information.
- Ensuring Data Security and Access Control: This is a cornerstone of any effective Data Policy. It necessitates the implementation of granular access control policies, defining who can access specific data sets, under what conditions, and for what purposes. This includes robust authentication mechanisms, encryption standards for data at rest and in transit, and guidelines for protecting against unauthorized access, data breaches, and misuse. These elements form the bedrock of your data security architecture guidelines.
- Compliance with Regulations: The policy must explicitly mandate adherence to relevant national and international data protection regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, and industry-specific standards. It should outline mechanisms for regular audits and assessments to ensure ongoing compliance, incorporating privacy-by-design mandates across all data platforms.
- Data Quality Standards: To ensure the reliability and usability of data for decision-making and AI applications, the policy must set clear data quality standards, addressing aspects like accuracy, completeness, consistency, and timeliness.
- Data Ownership and Accountability: Clearly assigning data ownership and accountability for specific data sets or domains is vital. This clarifies roles and responsibilities for data management, maintenance, and compliance throughout the organization.
Primary AI/ML Integration Considerations within the Data Policy
As organizations increasingly leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning, the Data Policy must evolve to encompass these advanced applications. For AI/ML integration, the policy should:
- Provide ethical guidelines for data collection and usage in AI/ML, particularly concerning sensitive data employed in AI/ML model training.
- Define stringent data privacy and anonymization requirements for AI training datasets to prevent re-identification and ensure individual rights are protected.
- Set clear rules for bias detection and mitigation strategies within datasets and algorithms, promoting fairness and preventing discriminatory outcomes in AI applications.
- Ensure data provenance for AI applications, meticulously tracking the origin, transformations, and usage of data throughout the AI lifecycle to ensure transparency, explainability, and reproducibility.
Challenges and Barriers to Adoption of an Effective Data Policy
Despite the undeniable benefits, implementing and enforcing an effective Data Policy faces several hurdles:
- Legacy Systems and Data Silos: Integrating a new policy across disparate, often outdated systems and breaking down long-standing data silos can be technically complex and resource-intensive, hindering the establishment of unified data standards.
- Lack of Executive Buy-in and Budget: Without strong support from leadership and adequate financial allocation, the initiative may lack the necessary authority and resources to succeed, leading to ad-hoc data management practices.
- Complexity of Regulatory Landscape: Navigating the ever-increasing and often conflicting global data protection regulations requires specialized expertise and continuous monitoring, making compliance a moving target and increasing the risk of regulatory non-compliance.
- Employee Resistance and Awareness: Employees may resist changes to established workflows or lack understanding of the policy’s importance, leading to non-compliance. Comprehensive training and ongoing communication are crucial to overcome this, fostering a culture of data responsibility.
- Data Drift and Evolving Business Needs: Data landscapes are dynamic. The policy must be flexible enough to adapt to changes in data types, sources, volumes, and new business requirements without constant overhauls, ensuring its ongoing relevance.
- Measuring ROI: Quantifying the direct return on investment for a data policy can be challenging, making it harder to justify initial expenditures to stakeholders who may perceive it as an overhead rather than a strategic asset.
Business Value and ROI of a Robust Data Policy
The investment in creating and maintaining an effective Data Policy yields significant returns, offering a clear competitive advantage:
- Enhanced Regulatory Compliance and Reduced Risk: A well-defined policy ensures adherence to legal requirements, significantly reducing the risk of hefty fines, legal battles, and reputational damage associated with data breaches or non-compliance. This proactive stance on compliance with regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) safeguards the organization.
- Improved Data Quality for AI and Analytics: By mandating data quality standards, the policy ensures that data used for business intelligence, analytics, and AI/ML models is accurate, consistent, and reliable, leading to better decision-making and more effective AI applications.
- Faster Model Deployment and Innovation: With clear guidelines on data access, usage, and privacy, data scientists and machine learning engineers can acquire and prepare data more efficiently and securely, accelerating the development and deployment of new models. This enables faster innovation while adhering to ethical guidelines for data collection and usage in AI/ML.
- Increased Operational Efficiency: Standardized data practices, clear ownership, and streamlined access controls reduce redundant efforts, minimize errors, and improve overall data management efficiency, moving away from siloed data operations.
- Strengthened Brand Trust and Reputation: Demonstrating a commitment to data privacy and security through a transparent policy builds confidence among customers, partners, and stakeholders, fostering a positive brand image and mitigating reputational risks.
- Competitive Advantage: Companies with superior data governance, underpinned by a strong data policy, can leverage their data more effectively and ethically, gaining a competitive edge in data-driven markets by ensuring data provenance for AI applications and setting rules for bias detection and mitigation.
Comparative Insight: Data Policy vs. Ad-Hoc Data Management Practices
The contrast between an organization operating with an effective Data Policy and one relying on ad-hoc data management practices or, worse, an absence of unified data standards, is stark. The latter scenario often leads to a chaotic and perilous data environment, aligning with what the “Main Competitors/Alternatives” section describes as “ad-hoc data management practices, absence of unified data standards, siloed data operations, and regulatory non-compliance.”
The Risks of Ad-Hoc Approaches
Without a formalized Data Policy, companies invariably face:
- Increased Security Vulnerabilities: Inconsistent security measures, varying access controls, and a lack of clear ownership create gaping holes for potential data breaches and cyberattacks, undermining data security architecture guidelines.
- Regulatory Non-Compliance: Operating without defined data retention, privacy, or security protocols makes organizations highly susceptible to failing compliance audits, resulting in significant fines and legal repercussions, as well as severe reputational damage.
- Poor Data Quality: Siloed data operations and the absence of unified data standards lead to inconsistent, inaccurate, and incomplete data. This compromises the reliability of analytics, business intelligence, and the effectiveness of AI/ML models, often resulting in flawed insights and poor decision-making due to a lack of data quality standards.
- Operational Inefficiencies and Redundancy: Without clear guidelines, different departments may implement their own data management solutions, leading to duplicated efforts, wasted resources, and difficulty in integrating data across the enterprise, as well as an inability to define data classification standards uniformly.
- Erosion of Trust: Customers and partners are increasingly aware of data privacy issues. An organization perceived as careless with data can quickly lose trust, impacting customer loyalty and business relationships.
- Hindered Innovation: Data scientists and analysts spend excessive time cleaning and validating data or navigating complex access barriers, slowing down innovation and the deployment of new data-driven products or services.
The Strategic Advantage of a Formal Data Policy
Conversely, a company that strategically implements an effective Data Policy transforms these risks into opportunities. It establishes a coherent framework that not only defines data classification standards, access control policies, and data retention schedules but also mandates data quality standards and ensures compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. This proactive approach:
- Centralizes Control and Enhances Security: By implementing unified data security architecture guidelines and access control policies, the policy significantly reduces vulnerabilities and provides a clear, defensible posture against threats.
- Guarantees Regulatory Adherence: A formal policy ensures that privacy-by-design mandates are embedded from the outset, leading to consistent compliance with regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) and avoiding penalties.
- Fosters a Culture of Data Responsibility: It assigns clear data ownership and accountability, promoting a company-wide understanding of data’s value and the responsibilities associated with its handling.
- Drives Data-Driven Innovation: With high-quality, securely managed data and clear ethical guidelines for AI/ML, organizations can rapidly develop and deploy advanced analytics and AI solutions, leveraging their data as a true strategic asset. It defines data privacy and anonymization requirements for AI training datasets and sets rules for bias detection and mitigation, ensuring data provenance for AI applications.
In essence, an effective Data Policy elevates data from a mere operational byproduct to a managed, valuable asset, differentiating proactive organizations from those struggling with data chaos and providing a distinct competitive edge.

World2Data Verdict: The Future is Policy-Driven Data Intelligence
At World2Data, we assert that the future of enterprise data management lies firmly in the realm of policy-driven data intelligence. An effective Data Policy is not merely a bureaucratic overhead; it is the ultimate enabler for deriving maximum value from your data assets while rigorously upholding ethical standards and regulatory mandates. Organizations that proactively invest in and rigorously enforce a comprehensive Data Policy will possess an unparalleled strategic advantage, allowing them to innovate faster, build deeper customer trust, and navigate the complex data landscape with confidence. We recommend all companies, irrespective of size or industry, treat their Data Policy as a living, evolving strategic document, continuously adapting it to technological advancements and regulatory shifts. This proactive approach ensures not just compliance, but sustained growth and competitive differentiation in the global data economy, making your data a truly intelligent and responsibly managed asset.