Third-Party Data: How Companies Harness External Insights for Growth in 2025
- Platform Category: Customer Data Platforms (CDPs), Data Clean Rooms, Data Warehouses/Lakehouses
- Core Technology/Architecture: Data Clean Rooms, Cloud-Native Data Lakes/Lakehouses, Privacy-Enhancing Technologies
- Key Data Governance Feature: Consent Management Platforms, Data Catalogs, Role-Based Access Control, Data Lineage
- Primary AI/ML Integration: Built-in ML for predictive analytics and customer segmentation, Integration with major ML Clouds
- Main Competitors/Alternatives: Customer Data Platform vendors (e.g., Salesforce, Adobe), Data Clean Room providers (e.g., LiveRamp, InfoSum), Cloud Data Platforms (e.g., AWS, Azure, Google Cloud)
The business world in 2025 is increasingly reliant on external intelligence for strategic decisions, with Third-Party Data emerging as a cornerstone of modern analytics. Its strategic utilization has moved from a mere advantage to a fundamental necessity, profoundly shaping how companies understand markets, customers, and opportunities in a rapidly evolving digital ecosystem. Businesses that master the art of integrating and interpreting these vast external datasets are poised to gain unparalleled insights, driving innovation and maintaining a crucial competitive edge.
This deep dive explores the multifaceted landscape of Third-Party Data in 2025, detailing its architectural underpinnings, the challenges inherent in its deployment, and the undeniable business value it delivers. We will also compare its modern applications against traditional data management paradigms and offer a forward-looking perspective on its continued evolution.
Third-Party Data: A Strategic Imperative in 2025
In the contemporary data-driven economy, companies now widely acknowledge the immense value of aggregated external information. This data enables a critical shift from reactive problem-solving to proactive strategy formulation, empowering businesses to anticipate market shifts and customer needs rather than merely responding to them. The sheer volume and diversity of Third-Party Data available today, ranging from demographic trends to intricate behavioral patterns, offer a panoramic view of the external environment that no single organization could hope to gather on its own.
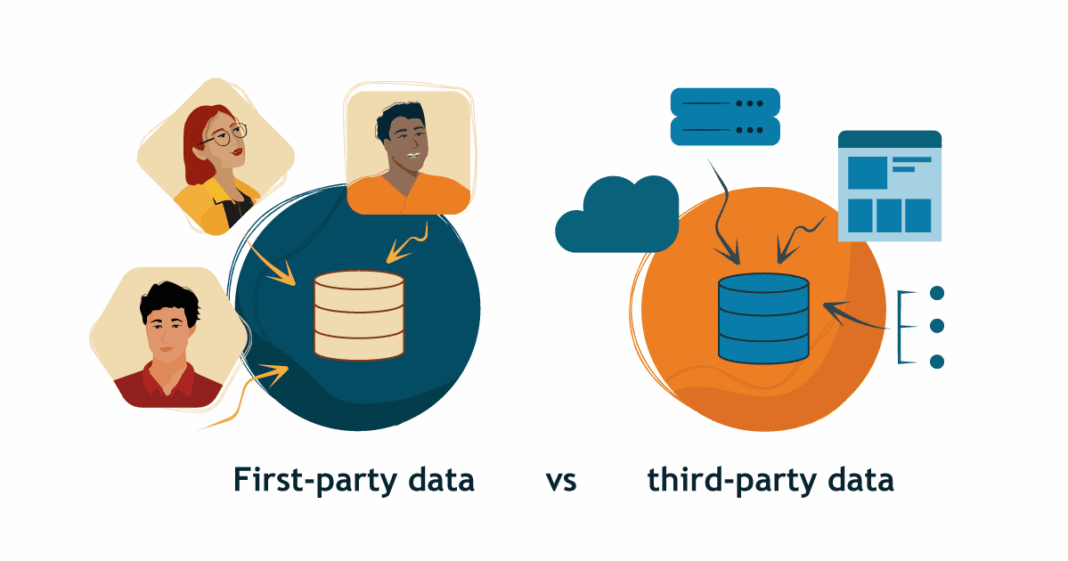
The strategic imperative for Third-Party Data stems from its ability to enrich an organization’s internal datasets. While first-party data offers depth into existing customer relationships, third-party data provides unparalleled breadth, revealing market opportunities, competitive landscapes, and nascent consumer trends outside an organization’s direct sphere of influence. This holistic perspective is crucial for informed decision-making across all facets of a business, from marketing and sales to product development and operational optimization.
Core Breakdown: Architecture and Application of Third-Party Data
The effective utilization of Third-Party Data in 2025 hinges on sophisticated technological infrastructure and well-defined processes. This involves not only the acquisition of data but also its secure storage, meticulous processing, and intelligent integration with internal systems.
Sources and Types of Third-Party Data
- Demographic Data: Age, gender, income, education, marital status – often aggregated from public records, surveys, and commercial data providers.
- Behavioral Data: Website browsing history, app usage, purchase behavior (non-first-party), social media activity, location data. This is typically collected and aggregated by data brokers, ad networks, and specialized behavioral analytics firms.
- Psychographic Data: Interests, opinions, values, attitudes, and lifestyle choices, often inferred from behavioral patterns and survey data.
- Transactional Data: Purchase histories from various retailers (non-competitors), financial data, often anonymized and aggregated by credit bureaus or financial data providers.
- Firmographic Data: For B2B contexts, this includes company size, industry, revenue, location, and other organizational attributes, critical for market segmentation and account-based marketing.
- Geospatial Data: Location intelligence, foot traffic patterns, urban development trends.
Acquisition and Integration Methodologies
Modern companies leverage various platforms and technologies to acquire and integrate Third-Party Data:
- Customer Data Platforms (CDPs): These platforms unify first, second, and third-party customer data from various sources to create a persistent, unified customer profile. CDPs are becoming central to enriching customer understanding by appending external demographic and behavioral attributes to internal records, enabling hyper-personalized marketing and service.
- Data Clean Rooms: Representing a significant advancement in privacy-preserving data collaboration, Data Clean Rooms allow multiple parties to securely combine and analyze their anonymized datasets without exposing raw, personally identifiable information. This is particularly crucial for advertisers and publishers seeking to understand cross-platform customer journeys using third-party data in a compliant manner.
- Data Warehouses and Lakehouses: Cloud-native Data Lakehouses, such as those built on AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud, serve as the backbone for storing vast quantities of raw and processed Third-Party Data. Their flexible architecture supports diverse data formats and enables scalable analytical processing, often integrating directly with advanced analytics and machine learning tools.
- Data Brokers and Exchanges: Companies continue to acquire data directly from specialized data brokers or through data marketplaces, which aggregate and sell data segments based on various attributes. The emphasis here is increasingly on vetting data sources for quality and compliance.
- APIs and Direct Integrations: Many service providers offer APIs that allow direct integration of their data feeds into a company’s systems, enabling real-time or near real-time ingestion of external insights.
Technological Underpinnings: Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs)
The increased scrutiny on data privacy has spurred the adoption of PETs, which are foundational for responsible Third-Party Data usage. These include:
- Homomorphic Encryption: Allows computations on encrypted data without decrypting it, maintaining privacy during analysis.
- Differential Privacy: Adds statistical noise to data queries to prevent re-identification of individuals while still allowing for aggregate insights.
- Secure Multi-Party Computation (SMC): Enables multiple parties to jointly compute a function over their private inputs, without revealing their inputs to each other, a core technology behind Data Clean Rooms.
- Tokenization and Hashing: Replaces sensitive data with non-sensitive substitutes or creates irreversible representations to protect privacy.
Challenges and Barriers to Adoption
Despite its immense potential, the utilization of Third-Party Data comes with significant challenges:
- Data Quality and Reliability: External data can suffer from inconsistencies, inaccuracies, and outdated information. Ensuring the quality, veracity, and relevance of purchased or acquired data is a perpetual challenge.
- Data Privacy and Regulatory Compliance: Navigating the complex and evolving landscape of global data regulations (GDPR, CCPA, LGPD, etc.) is paramount. Missteps can lead to severe penalties and reputational damage. Ethical considerations in data acquisition are increasingly prioritized to maintain consumer trust. Consent management platforms (CMPs) and robust data catalogs are critical here.
- Integration Complexity: Merging disparate datasets from various external sources with internal data requires sophisticated data engineering, robust ETL/ELT pipelines, and careful schema management.
- Data Drift: External data sources can change their collection methods, schemas, or even cease to exist, leading to data drift that can invalidate models and analyses relying on this data.
- Cost of Acquisition: High-quality Third-Party Data often comes with a significant price tag, requiring a clear ROI justification.
- Vendor Lock-in and Dependency: Over-reliance on a single third-party data provider can create dependencies and limit flexibility.
Business Value and ROI of Third-Party Data
When navigated successfully, the benefits of strategic Third-Party Data integration are substantial:
- Enhanced Personalization and Customer Experience: Tailoring marketing messages with Third-Party Data allows for hyper-personalized outreach, resonating deeply with target audiences. Predicting customer needs and behaviors becomes more accurate, leading to improved service delivery and increased customer lifetime value.
- Market Intelligence and Competitive Advantage: Comprehensive Third-Party Data provides a clearer picture of market positioning, competitor strategies, and emerging trends, enabling proactive adjustments and innovative responses.
- Optimized Product Development: External signals regarding market demands, unmet needs, and user preferences directly inform product development cycles, leading to offerings that are more aligned with customer desires.
- New Market Identification and Expansion: Third-Party Data is instrumental in identifying untapped market opportunities, allowing businesses to expand into promising sectors with greater confidence.
- Operational Efficiencies: Streamlining supply chains benefits from external intelligence on logistics, demand forecasting, and inventory optimization, reducing costs and improving resilience.
- Risk Management: External data can provide early warnings for potential risks, such as economic downturns, supply chain disruptions, or shifts in consumer sentiment, enabling proactive mitigation strategies.
Comparative Insight: Third-Party Data in Modern vs. Traditional Paradigms
The role and utility of Third-Party Data have evolved dramatically from traditional data management approaches. Historically, companies might have purchased static data lists from brokers or relied heavily on aggregated, often opaque, data from advertising networks. This traditional model was characterized by:
- Limited Transparency: Little insight into data origins, collection methods, or consent status.
- Static Data: Data often arrived in batches, quickly becoming outdated and lacking real-time relevance.
- Privacy Risks: Higher potential for privacy breaches due to less stringent data handling and fewer privacy-enhancing technologies.
- Siloed Use: Primarily used for broad targeting in advertising, with limited integration into core business intelligence or product development.
- Poor Integration: Manual or custom integrations, leading to high maintenance overhead and data integrity issues.
In contrast, the modern paradigm for Third-Party Data, especially in 2025, is built around greater transparency, real-time insights, stringent privacy controls, and deep integration:
- Privacy by Design: Modern platforms like Data Clean Rooms and CDPs, combined with Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs), ensure that data is handled with privacy in mind from ingestion to analysis. Consent Management Platforms (CMPs) are integrated to track and manage user preferences, aligning with regulatory requirements.
- Dynamic and Integrated: Data is often streamed or updated frequently, integrated seamlessly into cloud-native data lakes/lakehouses, and made accessible to AI/ML models for real-time predictions and segmentation. This facilitates immediate action based on fresh insights.
- Ethical Sourcing and Governance: There is a heightened emphasis on ethical data sourcing, supplier vetting, and robust data governance frameworks (e.g., Data Catalogs, Data Lineage tools) to ensure compliance and build trust.
- Strategic Application: Beyond advertising, Third-Party Data now informs a wide array of strategic decisions – from identifying new market segments and optimizing product features to enhancing supply chain resilience and refining customer service protocols.
- AI and Machine Learning Augmentation: AI and machine learning are augmenting data analysis capabilities, extracting deeper, more subtle insights from vast datasets of Third-Party Data, moving beyond simple segmentation to predictive and prescriptive analytics.
The key differentiator lies in the shift from simply *having* external data to *intelligently and compliantly leveraging* it as a strategic asset. The modern approach treats Third-Party Data not as a disposable resource but as a valuable component of a comprehensive data ecosystem, continuously refined and governed to yield sustainable competitive advantages.

World2Data Verdict: The Future of External Insights Integration
The strategic utilization of Third-Party Data will continue to be a defining factor for market leaders in the coming years. World2Data predicts that success will hinge not merely on the volume of external data acquired, but on the sophistication of its integration, the robustness of its governance, and the ethical rigor of its deployment. Companies must move beyond siloed data acquisition to establish comprehensive hybrid data strategies, combining proprietary first-party data with rich, privacy-compliant external sources. This necessitates significant investment in advanced data platforms—like next-generation CDPs, federated data lakes, and secure data clean rooms—that can facilitate seamless, ethical data sharing and analysis. The ongoing importance of data quality, coupled with the increasing adoption of AI and machine learning for predictive analytics and customer segmentation, will ensure that these insights remain reliable, actionable, and contribute directly to demonstrable business value. Ultimately, the ability to effectively harness and interpret Third-Party Data, grounded in transparency and consumer trust, will distinguish the innovative from the obsolete in the rapidly evolving digital landscape.