Data Monetization Strategies: Turning Information Into Revenue
In today’s hyper-connected business landscape, organizations are accumulating vast amounts of data at an unprecedented rate. This data, often seen merely as a byproduct of operations, holds immense untapped potential. Effective Data Monetization is no longer just a buzzword but a strategic imperative, transforming raw information into tangible financial gains and sustained competitive advantages. By strategically leveraging their data assets, companies can unlock new revenue streams, optimize existing operations, and foster deeper customer relationships, making every byte count towards the bottom line.
Introduction: Unlocking the Value Within Your Data
The digital economy has heralded an era where data is considered the new oil, a critical asset that, when refined, can fuel innovation, efficiency, and significant revenue growth. For enterprises across all sectors, understanding and implementing robust Data Monetization strategies is paramount. This deep dive explores the multifaceted approaches, underlying technologies, critical governance considerations, and the inherent challenges in transforming data into a valuable revenue source. We will dissect how businesses can move beyond mere data collection to proactive data valorization, leveraging advanced analytics and strategic data exchange to create measurable economic impact.
The journey towards successful data monetization involves a paradigm shift from viewing data as a cost center to recognizing it as a profit generator. It requires a comprehensive framework encompassing cutting-edge technology platforms like Cloud Data Platforms and Data Lakehouses, coupled with robust data governance frameworks. Furthermore, the integration of AI and machine learning techniques plays a crucial role in enriching data and extracting predictive insights, paving the way for innovative service offerings and personalized customer experiences.
The Anatomy of Data Monetization Strategies: Core Breakdown
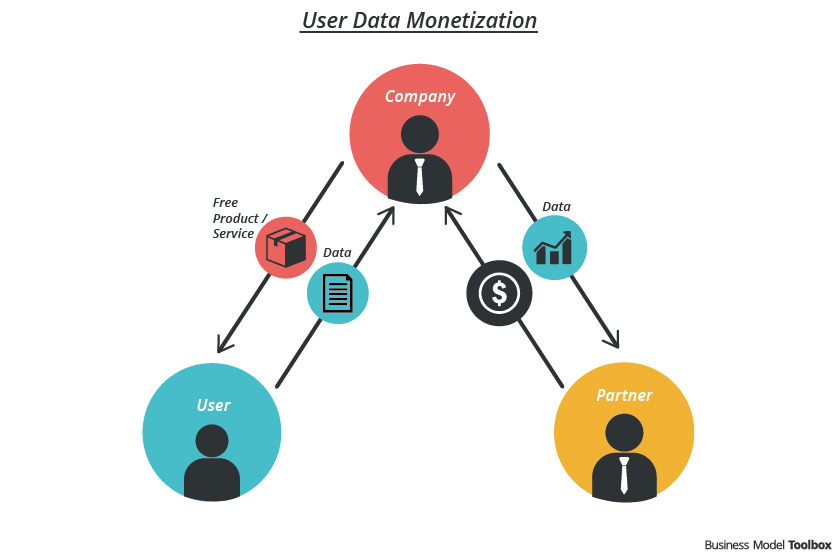
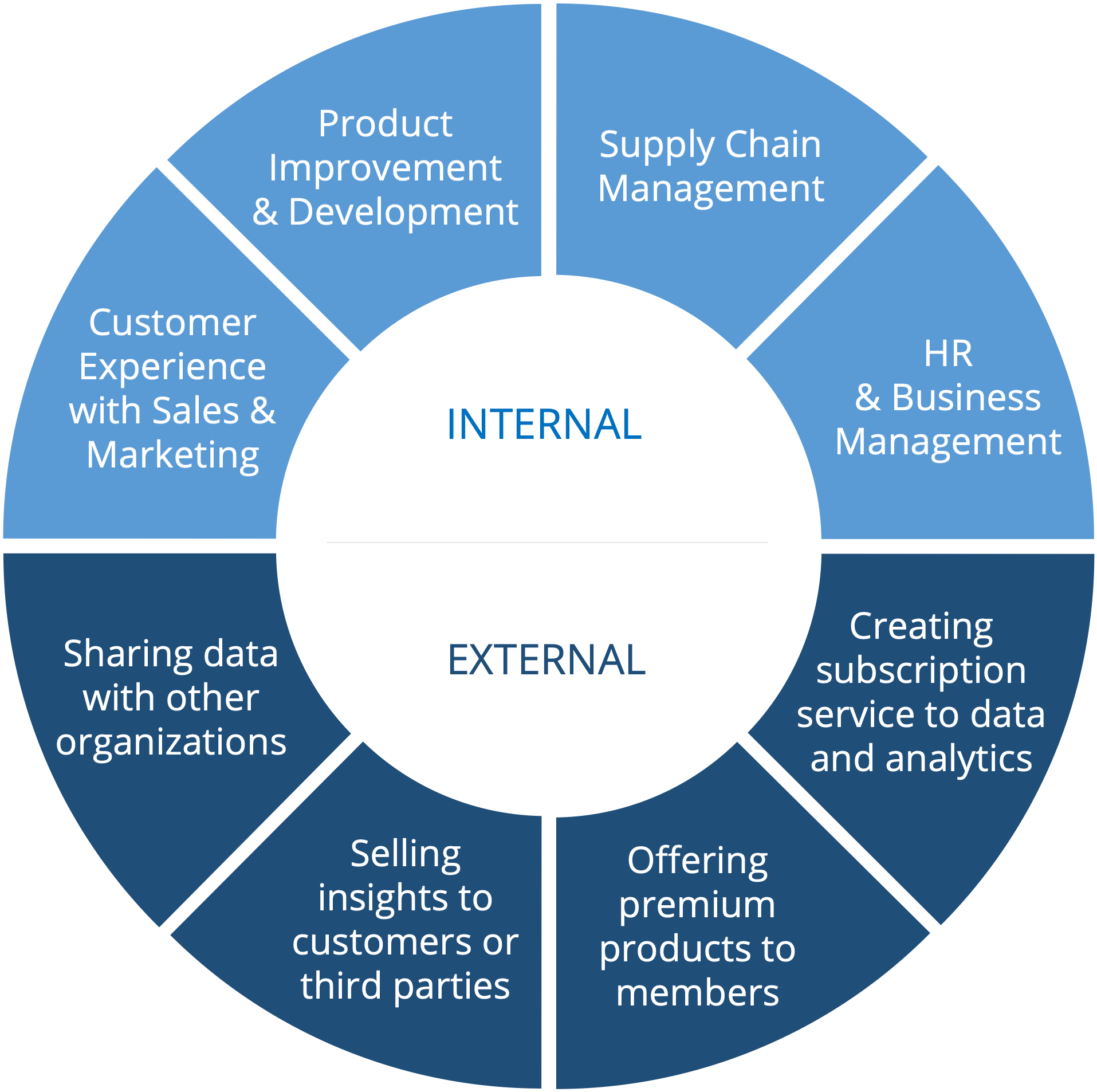
Understanding Core Data Monetization Concepts: Direct vs. Indirect Approaches
Businesses seeking effective Data Monetization must first grasp the foundational principles, primarily distinguishing between direct and indirect strategies. Direct data monetization involves explicit exchanges of data or data products for financial compensation. This can take several forms:
- Data-as-a-Service (DaaS): Offering curated, real-time access to datasets via APIs or subscription models. This is common in sectors requiring market intelligence, financial data, or consumer trends.
- Data Licensing and Strategic Partnerships: Allowing controlled access to proprietary datasets for specific use cases, often through licensing agreements with other businesses, researchers, or startups.
- Premium Data Analytics Reports and Insights: Generating and selling specialized reports, dashboards, or predictive models tailored to specific industry needs or customer segments. These “Insights-as-a-Service” offerings distill complex data into actionable intelligence.
- Data Marketplaces and Exchanges: Participating in or hosting platforms where businesses can buy and sell anonymized or aggregated datasets. These Data Exchange Platforms provide a structured environment for direct data sales.
Indirect data monetization, on the other hand, focuses on leveraging data to improve core business operations, thereby leading to increased revenue or reduced costs without directly selling the data itself. Examples include:
- Enhanced Product Offerings and Services: Using data-driven insights to refine existing products, develop new features, or create entirely new services that meet customer needs more effectively, making them more competitive and attractive. AI-driven personalization and recommendations fall squarely into this category.
- Optimizing Operational Efficiency: Analyzing operational data to identify bottlenecks, reduce waste, improve supply chain logistics, and streamline internal processes, leading to significant cost savings and improved profitability.
- Personalized Customer Experiences: Leveraging customer data to offer highly personalized marketing, product recommendations, and customer service. This fosters loyalty, increases customer lifetime value, and drives repeat business.
- Risk Management and Fraud Detection: Utilizing data and predictive analytics to identify and mitigate risks, detect fraudulent activities, and improve security, thereby protecting assets and reputation.
Technological Pillars for Effective Data Monetization
Successful Data Monetization is heavily reliant on a robust and scalable technology infrastructure. Modern data architectures provide the backbone for collecting, processing, securing, and distributing data assets. Key components include:
- Cloud Data Platforms: Public or private cloud environments offer scalable storage and compute resources, essential for handling vast datasets and complex analytical workloads. They facilitate flexibility and reduce infrastructure overhead.
- Data Lakehouses: This hybrid architecture combines the flexibility and low-cost storage of data lakes with the data management features and performance of data warehouses. Data Lakehouses are ideal for supporting both raw data ingestion and structured analytics, crucial for preparing data for monetization.
- Secure Data Sharing APIs: Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) are fundamental for enabling controlled and secure data exchange between systems and organizations. They allow partners or customers to access specific datasets or insights without compromising data integrity or security.
- Data Mesh Principles: An organizational and architectural approach that decentralizes data ownership and management, treating data as a product. Data Mesh principles advocate for domain-oriented data products, self-serve data infrastructure, federated computational governance, and an emphasis on data product discoverability, crucial for internal and external data monetization.
- Feature Stores: Centralized repositories for managing and serving machine learning features. They ensure consistency and reusability of features across different ML models, accelerating the development and deployment of AI/ML-driven data products for monetization.
The Role of Data Governance and Ethics
A solid foundation of data governance and ethical guidelines is paramount for successful and sustainable Data Monetization. Without trust and compliance, any monetization effort is doomed to fail. Key governance features include:
- Data Catalog: A comprehensive inventory of an organization’s data assets, including metadata, lineage, and usage policies. A robust Data Catalog improves data discoverability and understanding, essential for identifying monetizable assets.
- Consent Management Systems: Tools and processes for obtaining, recording, and managing user consent for data collection and usage, ensuring compliance with privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
- Anonymization/Pseudonymization: Techniques used to protect individual privacy by removing or encrypting personally identifiable information (PII) from datasets, making them suitable for sharing or selling without exposing sensitive data.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): A security mechanism that restricts system access based on the roles of individual users. RBAC ensures that only authorized personnel or systems can access specific data assets, crucial for maintaining data security and confidentiality.
- Ethical AI Guidelines: Establishing clear principles for the responsible use of AI in data enrichment and personalization, addressing bias, fairness, and transparency.
AI/ML Integrations for Enhanced Data Value
The integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning significantly amplifies the potential for Data Monetization by extracting deeper insights and automating value creation. Primary AI/ML integrations include:
- Predictive Analytics: Utilizing ML models to forecast future trends, customer behavior, or market shifts. These predictions can be monetized as subscription services or used to inform strategic business decisions.
- Machine Learning for Data Enrichment: AI algorithms can enhance raw data by identifying patterns, classifying unstructured information, or linking disparate datasets, increasing its value for monetization.
- AI-driven Personalization and Recommendations: ML models power highly personalized experiences, recommending products, content, or services based on individual user behavior. This indirectly drives revenue through increased engagement and sales.
- Automated Data Labeling: For complex datasets, particularly in computer vision or natural language processing, AI can automate portions of the data labeling process, reducing costs and accelerating the preparation of high-quality data for sale or internal use.
Challenges and Barriers to Data Monetization Adoption
Despite its immense potential, embarking on a Data Monetization journey is not without its hurdles. Organizations often face significant challenges that can impede success:
- Data Quality and Integration Issues: Poor data quality, inconsistencies, and fragmented data across disparate systems can severely limit the value that can be extracted and monetized. Integrating diverse data sources into a unified, usable format is a complex undertaking.
- Data Privacy Concerns and Regulatory Compliance: Navigating the complex landscape of global data privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA, LGPD) is a major challenge. Ensuring compliance, managing user consent, and protecting sensitive information requires sophisticated systems and legal expertise.
- Data Security Risks: Monetizing data inherently involves sharing it, increasing the attack surface for cyber threats. Robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and anomaly detection, are crucial to prevent breaches and maintain trust.
- Lack of Skilled Personnel: A significant barrier is the scarcity of talent with expertise in data science, advanced analytics, data engineering, and data ethics. Building and managing monetization initiatives requires a multidisciplinary team.
- Building a Business Case and Proving ROI: Quantifying the direct and indirect financial returns of data monetization can be challenging. Organizations need clear metrics and a strategic vision to demonstrate value and secure executive buy-in.
- Data Ownership and Valuation Complexities: Determining who owns specific datasets (especially in collaborations) and accurately valuing data assets for sale or internal use can be difficult and contentious.
- Cultural Resistance: Shifting an organization’s mindset from data as a cost center to data as a revenue generator often faces internal resistance and requires significant change management.
Business Value and ROI of Data Monetization
Despite the challenges, the return on investment (ROI) from effective Data Monetization can be transformative. The business value extends beyond direct financial gains, fostering a more agile, customer-centric, and competitive enterprise:
- New Revenue Streams: Direct sales of data, insights, or Data-as-a-Service offerings create entirely new income channels, diversifying the company’s financial base.
- Cost Reduction and Operational Efficiency: Indirect monetization through data-driven optimization leads to significant savings in operational costs, resource allocation, and waste reduction.
- Enhanced Customer Experience and Loyalty: Personalized interactions and superior product offerings, driven by data insights, lead to higher customer satisfaction, increased retention, and greater customer lifetime value.
- Competitive Advantage: Companies that effectively monetize their data gain a deeper understanding of market trends, customer needs, and operational efficiencies, enabling them to outmaneuver competitors.
- Improved Product/Service Development: Data provides direct feedback loops for product innovation, allowing for rapid iteration and the development of offerings that precisely match market demand.
- Better Decision-Making: A culture of data-driven decision-making, fostered by monetization efforts, leads to more informed strategic choices and more resilient business models.
Comparative Insight: Data Monetization vs. Traditional Data Management
The evolution from traditional data management paradigms to robust Data Monetization strategies represents a fundamental shift in how businesses perceive and leverage their information assets. Historically, data management revolved around internal reporting, operational support, and compliance. Data warehouses were built primarily to support business intelligence, providing historical insights into past performance. Data lakes emerged to store raw, unstructured data for internal analytics, often serving data scientists for one-off projects.
In this traditional model, data was largely seen as an operational necessity or even a cost center. The focus was on storage, integration, and internal consumption to improve existing processes. While valuable, this approach rarely translated directly into new revenue streams or external value creation. Data was managed to reduce risk, ensure efficiency, and provide internal decision support.
Data Monetization, in contrast, elevates data to a strategic asset with explicit financial potential. It requires a more outward-looking perspective, transforming data into a product or a service that can be sold, licensed, or used to enhance external offerings. This shift necessitates advancements in data architecture:
- From Silos to Shared Data Products: Traditional data often resided in departmental silos. Data monetization, especially with Data Mesh principles, encourages treating data as domain-owned products ready for consumption by internal and external stakeholders.
- From Internal Reporting to External Value Creation: The primary goal shifts from merely reporting on past events to predicting future trends, personalizing customer experiences, and creating new data-driven services for external markets.
- Emphasis on Security and Governance for External Sharing: While traditional data management focused on internal security, data monetization adds a critical layer of secure data sharing, consent management, anonymization, and robust access controls to protect data when it leaves organizational boundaries.
- Leveraging Advanced Analytics and AI: While traditional BI used descriptive analytics, data monetization heavily relies on predictive and prescriptive analytics, often powered by AI/ML, to extract higher-value insights that can be sold or embedded in new services.
The rise of Cloud Data Platforms and Data Lakehouses directly supports this evolution by providing scalable, flexible, and secure environments conducive to both internal analytics and external Data Monetization initiatives. They bridge the gap between raw data storage and highly curated, performant data products ready for market.
World2Data Verdict: The Imperative of Strategic Data Monetization
The journey to effective Data Monetization is a strategic imperative for any enterprise aiming for sustained growth and competitive differentiation in the digital age. World2Data.com asserts that organizations must transcend a reactive approach to data management and instead proactively cultivate data as a primary asset for revenue generation. Success hinges on a holistic strategy that combines robust technological enablement, stringent data governance, and a culture of data-driven innovation. We recommend that businesses prioritize investing in Cloud Data Platforms and Data Lakehouses, coupled with comprehensive Data Catalog and Consent Management Systems, to build a trusted and scalable foundation. Furthermore, integrating AI and ML for data enrichment and personalization is no longer optional but essential for extracting maximum value. The future belongs to those who not only collect data but master the art of transforming information into tangible economic outcomes, ensuring that every data point contributes to a thriving, data-powered enterprise.