Optimizing Enterprise Data: A Deep Dive into Managing and Leveraging Corporate Information for the AI Era
In today’s hyper-competitive digital landscape, the strategic management and leveraging of Enterprise Data are no longer optional but foundational for sustained success. Organizations are realizing that their vast reservoirs of corporate information hold the key to unlocking unprecedented insights, fueling innovation, and driving intelligent automation. An advanced Enterprise Data platform acts as the central nervous system, transforming raw, disparate data into a cohesive, actionable asset, primed for both traditional business intelligence and sophisticated AI/ML applications.
Introduction: The Unfolding Power of Enterprise Data
The sheer volume and complexity of Enterprise Data generated by modern businesses present both immense opportunities and significant challenges. From customer interactions and operational logs to financial transactions and IoT sensor readings, every piece of corporate information contributes to a massive, intricate puzzle. Effectively managing and leveraging this diverse data stream is paramount for gaining a competitive edge, fostering informed decision-making, and adapting swiftly to market dynamics. This article delves into the critical aspects of Enterprise Data, exploring its strategic management, technological underpinnings, and its pivotal role in the burgeoning AI economy. We will examine how a modern Enterprise Data Platform, embracing principles like cloud-nativity and data fabric, serves as the ultimate engine for unlocking the full potential of your corporate information assets.
Core Breakdown: Architecture, Components, and Value of an Enterprise Data Platform
An advanced Enterprise Data Management and Analytics Platform provides a unified, comprehensive approach to handling all corporate information assets. It moves beyond siloed solutions, integrating various data sources and functionalities into a cohesive ecosystem.
Architectural Foundations: Cloud-Native, Data Fabric, and Data Mesh
The bedrock of a modern Enterprise Data Platform lies in its architectural principles.
- Cloud-Native Design: Leveraging cloud infrastructure (PaaS, IaaS) enables unparalleled scalability, elasticity, and cost-efficiency. Cloud-native platforms are built to take full advantage of distributed computing, auto-scaling, and managed services offered by major cloud providers (e.g., AWS, Azure, Google Cloud). This ensures the platform can effortlessly handle petabytes of Enterprise Data and support thousands of concurrent users and analytical workloads without manual intervention.
- Data Fabric Principles: A data fabric creates a unified, intelligent, and flexible platform that supports end-to-end integration and delivery of data across disparate environments. It provides a layer of services (data integration, governance, security, and consumption) that orchestrates access to Enterprise Data regardless of where it resides (on-premises, multi-cloud, edge). Key elements include dynamic data integration, intelligent metadata management, and knowledge graphs to understand and connect data relationships.
- Data Mesh Principles: Complementing the data fabric, a data mesh shifts ownership and responsibility for data to domain-oriented teams. Data is treated as a product, owned and served by specific business domains, improving data quality, accessibility, and relevance. This decentralized approach, while challenging to implement, enhances agility and scalability for complex organizations dealing with vast amounts of diverse Enterprise Data.
Key Components of an Integrated Enterprise Data Platform
A robust Enterprise Data Platform typically comprises several integrated components designed to manage the entire data lifecycle:
- Data Ingestion and Integration: Facilitates the collection of Enterprise Data from diverse sources, including transactional systems, CRM, ERP, IoT devices, social media, and third-party APIs. It supports various methods like batch processing (ETL/ELT), real-time streaming, change data capture (CDC), and API-driven integration.
- Data Storage and Processing: Provides scalable and cost-effective storage solutions like data lakes (for raw, unstructured data), data warehouses (for structured, analytical data), and data marts. It incorporates powerful processing engines (e.g., Apache Spark, Presto, Flink) to handle complex transformations and analytical queries on massive datasets.
-
Data Governance and Security: This is a critical feature, ensuring the trustworthiness and compliance of all Enterprise Data.
- Data Catalog: An inventory of all available data assets, their definitions, and usage.
- Metadata Management: Captures technical, business, and operational metadata, providing context and lineage.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Granular security mechanisms dictating who can access what data and under what conditions.
- Data Lineage: Tracks the origin and transformations of data, crucial for auditing and debugging.
- Compliance Features: Tools and processes to adhere to regulations like GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, ensuring data privacy and ethical use of corporate information.
- Data Quality and Enrichment: Modules for profiling, cleansing, validating, and enriching Enterprise Data to ensure accuracy, completeness, and consistency. This includes master data management (MDM) for creating a “single source of truth” for core business entities.
- Analytics and Business Intelligence (BI): Provides tools for generating reports, dashboards, and conducting ad-hoc queries, transforming raw Enterprise Data into actionable insights for operational and strategic decision-making.
-
Primary AI/ML Integration: A modern platform is inherently designed to be AI-ready.
- Built-in ML for Predictive Analytics: Incorporates machine learning algorithms to perform forecasting, anomaly detection, customer segmentation, and recommendation engines directly on the curated Enterprise Data.
- Data Quality Automation: ML models can automate the identification and remediation of data quality issues, learning patterns of errors over time.
- Integration with Major ML Platforms: Seamless connectivity with external ML platforms (e.g., TensorFlow, PyTorch, SageMaker, Azure ML) allows data scientists to easily access, prepare, and train models using the platform’s clean and governed Enterprise Data.
- Feature Store: A centralized repository for managing, serving, and monitoring machine learning features. It ensures consistency, reusability, and discoverability of features derived from Enterprise Data across different models and teams, significantly accelerating ML development and deployment.
- Data Labeling Management: While often handled by specialized services, the platform can manage the lifecycle of datasets requiring human annotation, integrating with labeling tools to prepare supervised learning datasets from corporate information.
Challenges and Barriers to Enterprise Data Platform Adoption
Despite the immense benefits, implementing and adopting an integrated Enterprise Data Platform comes with its own set of hurdles:
- Data Silos and Integration Complexity: Organizations often contend with fragmented data stored across legacy systems, departmental databases, and cloud applications. Integrating these disparate sources into a unified platform is technically challenging and time-consuming.
- Data Quality Issues: Years of inconsistent data entry, lack of standardization, and inadequate governance lead to “dirty data.” Cleansing and transforming this vast quantity of existing Enterprise Data is a monumental task.
- Data Governance and Compliance: Establishing robust data governance policies and ensuring compliance with a constantly evolving regulatory landscape (GDPR, CCPA, etc.) requires significant organizational effort, legal expertise, and technological capabilities.
- Talent Gap: A scarcity of skilled data engineers, data scientists, and MLOps specialists can impede the effective deployment and utilization of an advanced data platform.
- Cost and Scalability Management: While cloud-native offers scalability, managing costs for massive data storage, compute resources, and specialized tools requires careful optimization and FinOps practices.
- Data Drift: For AI/ML applications, data drift (changes in the input data distribution over time) can severely degrade model performance. Detecting and mitigating drift within dynamic Enterprise Data streams requires continuous monitoring and robust MLOps practices.
- MLOps Complexity: Operationalizing machine learning models built on Enterprise Data – from deployment and monitoring to retraining and versioning – is a complex discipline that requires specialized tools and processes.
Business Value and ROI of a Unified Enterprise Data Platform
The strategic investment in a comprehensive Enterprise Data Platform yields substantial returns across the organization:
- Faster Model Deployment and Time-to-Market for AI: By providing clean, governed, and readily accessible data, along with capabilities like Feature Stores, the platform dramatically accelerates the development, testing, and deployment of AI/ML models, bringing innovative solutions to market quicker.
- Improved Data Quality for AI: High-quality, consistent Enterprise Data is the lifeblood of effective AI. The platform ensures data integrity, leading to more accurate, reliable, and trustworthy AI models, reducing bias and improving prediction accuracy.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Executives and operational teams gain access to real-time, accurate insights derived from consolidated Enterprise Data, enabling proactive, data-driven decisions that impact strategy, operations, and customer experience.
- Operational Efficiency and Cost Reduction: Automation of data pipelines, reduced manual data preparation, and optimized resource utilization lead to significant operational efficiencies and cost savings.
- Innovation and New Revenue Streams: By understanding customer behaviors, market trends, and operational patterns through advanced analytics and AI on Enterprise Data, businesses can identify opportunities for new products, services, and revenue streams.
- Competitive Advantage: Organizations that master their Enterprise Data become more agile, resilient, and insightful, allowing them to outmaneuver competitors and secure a leading position in their respective industries.
Comparative Insight: Enterprise Data Platform vs. Traditional Data Architectures
Understanding the evolution from traditional data architectures to modern Enterprise Data Platforms is crucial for appreciating their value.
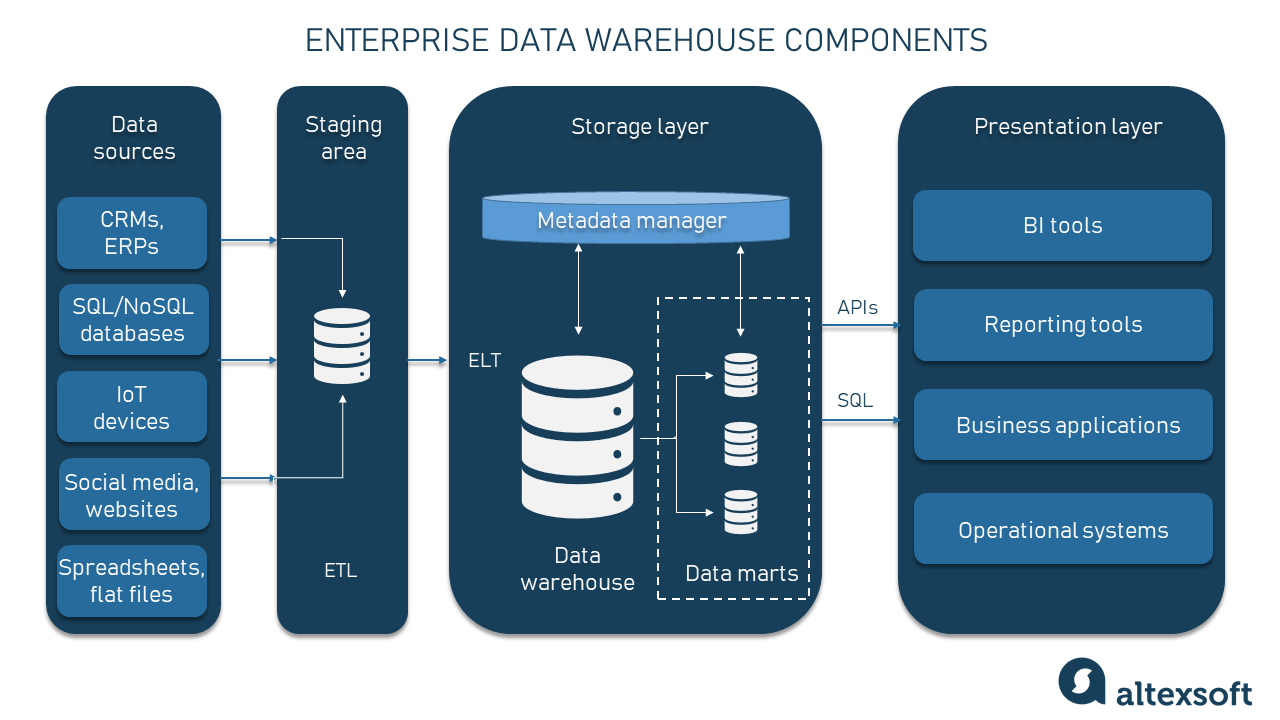
Traditional Data Warehouse: For decades, data warehouses served as the backbone for business intelligence. They are highly structured, schema-on-write systems optimized for structured, historical data used in reporting and analytics. While excellent for consistent BI, they struggle with semi-structured or unstructured Enterprise Data, lack agility for rapid schema changes, and are not inherently designed for AI/ML workloads or real-time processing. Scaling costs can also be prohibitive for growing data volumes.
Traditional Data Lake: Emerging to address the limitations of data warehouses, data lakes allow organizations to store vast quantities of raw, multi-structured Enterprise Data at low cost. They operate on a schema-on-read principle, offering flexibility. However, data lakes can quickly devolve into “data swamps” without robust governance, metadata management, and data quality controls. They also require significant expertise to extract value, often falling short on integrated AI/ML readiness and centralized governance across diverse data types.
Modern Enterprise Data Platform: The Enterprise Data Platform transcends these earlier models by integrating their strengths while addressing their weaknesses. It typically encompasses a data lake for raw storage and a data warehouse layer for structured analytics, but crucially adds:
- Unified Governance: A comprehensive data catalog and metadata management provide a single pane of glass for all Enterprise Data, irrespective of its underlying storage, ensuring trust and compliance.
- AI/ML Readiness: Built-in capabilities like Feature Stores, MLOps tooling, and seamless integration with ML platforms make it inherently designed for advanced analytics and AI model deployment.
- Data Fabric/Mesh Principles: Enables flexible, agile access and consumption of data across the enterprise, breaking down silos and empowering domain-specific data products.
- Cloud-Native Scalability: Offers elastic compute and storage, adapting to fluctuating workloads and massive data growth without requiring extensive hardware management.
- Real-time Capabilities: Supports streaming data ingestion and processing, enabling real-time analytics and immediate insights from dynamic Enterprise Data.
In essence, an Enterprise Data Platform is not just a storage or processing solution; it’s a strategic infrastructure that unifies data, governance, and analytics capabilities, making Enterprise Data a truly actionable asset for the entire organization, especially for those venturing deep into AI and machine learning. It streamlines the journey from raw data to actionable intelligence and automated insights, a crucial differentiator in today’s data-driven world.
World2Data Verdict: Embracing a Data-Centric Future
The future of business is inextricably linked to how effectively organizations manage and leverage their Enterprise Data. World2Data.com strongly recommends that enterprises prioritize the adoption of a unified, cloud-native Enterprise Data Platform built on data fabric or mesh principles. Such a platform is not merely a technological upgrade but a strategic imperative that transforms corporate information from a liability into a dynamic, intelligent asset. By investing in robust data governance, integrating AI/ML capabilities, and fostering a data-centric culture, businesses can unlock unparalleled insights, accelerate innovation, and achieve sustainable competitive advantage. The ability to seamlessly prepare, govern, and utilize Enterprise Data for advanced analytics and AI models will be the ultimate differentiator for success in the evolving digital economy. Ignore your Enterprise Data at your peril; master it, and you master your destiny.



