Data Orchestration: Automating Complex Data Workflows for Enhanced Business Intelligence
- Platform Category: Data Orchestration Platform
- Core Technology/Architecture: Workflow Automation, Distributed Processing, Event-Driven Architecture, Microservices
- Key Data Governance Feature: Lineage Tracking, Access Control, Metadata Management
- Primary AI/ML Integration: Integration with MLOps platforms, Automated model retraining workflows, Data preparation for ML models, Feature store integration
- Main Competitors/Alternatives: Apache Airflow, Prefect, Dagster, Apache Nifi, Azure Data Factory, AWS Step Functions, Google Cloud Composer
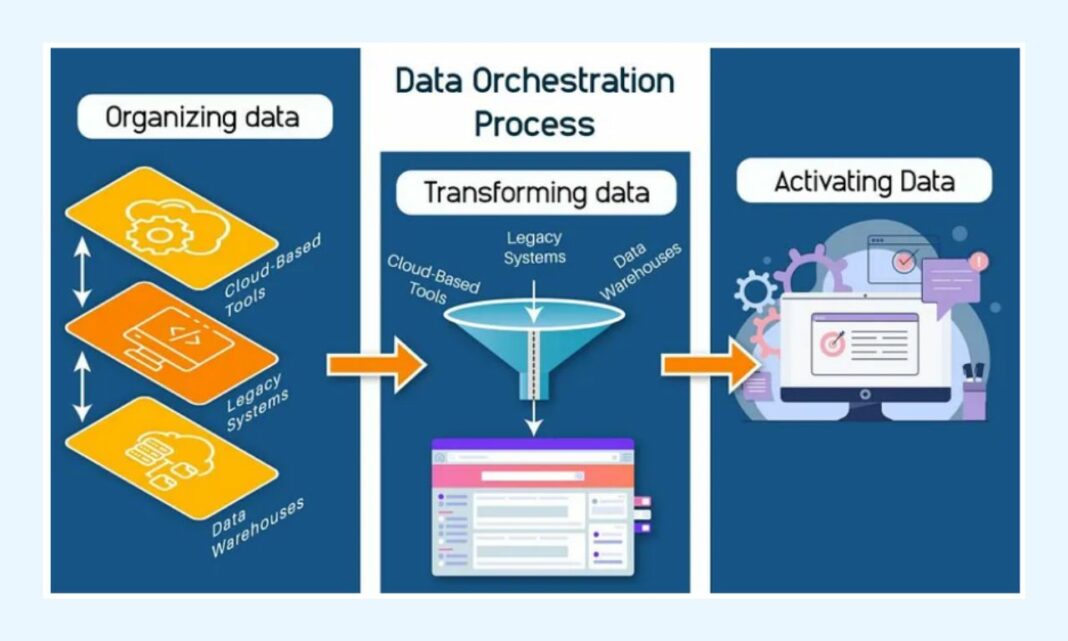
In today’s hyper-connected, data-driven enterprise, Data Orchestration has transitioned from a mere technical capability to an indispensable strategic imperative. It underpins the seamless flow of information across disparate systems, transforming raw data into refined, actionable insights at speed. By centralizing the management of intricate data workflows, organizations can ensure data integrity, drive operational efficiency, and accelerate informed decision-making across all departments.
Introduction: Unifying the Data Landscape with Data Orchestration
The modern data landscape is characterized by its sheer volume, velocity, and variety. Enterprises grapple with data residing in diverse sources – from transactional databases and IoT devices to cloud applications and social media feeds. Making sense of this deluge, transforming it, and delivering it to the right stakeholders at the right time is a monumental task. This is precisely where Data Orchestration emerges as a critical enabler. It provides the architectural framework and operational tools necessary to automate, manage, and monitor the entire lifecycle of data workflows, from initial ingestion and cleansing to transformation, enrichment, and delivery for analytics and machine learning. This article will delve deep into the technical intricacies, business value, and strategic importance of robust Data Orchestration platforms, outlining how they empower organizations to unlock the full potential of their data assets.
Data Orchestration serves as the backbone for efficient data operations across the enterprise. It unifies disparate data sources, transforming raw data into actionable intelligence. This centralized approach simplifies managing complex data flows from ingestion to analysis, providing a clear pathway for valuable information. Automating data workflows significantly reduces manual effort and human error in processing. Consistent execution of tasks ensures data quality and compliance throughout its lifecycle. Enterprises achieve greater reliability and faster time-to-insight through robust Data Orchestration implementation. Effective Data Orchestration platforms integrate pipeline management, scheduling, and monitoring capabilities. These components work in harmony to control data movement and transformation processes efficiently. Comprehensive dashboards provide real-time visibility into the health and performance of all data tasks.
Core Breakdown: The Technical Backbone and Strategic Imperatives of Data Orchestration
At its heart, Data Orchestration is the control plane for an organization’s data pipelines, defining, executing, and monitoring the sequence of tasks required to process data. It moves beyond simple batch scheduling to manage complex dependencies, conditional logic, and error handling across distributed systems. The core technologies and architectural patterns that enable sophisticated Data Orchestration include:
- Workflow Automation: This involves defining Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) that map out data dependencies, task ordering, and execution logic. Orchestration platforms handle scheduling tasks, retries, and managing state across potentially hundreds or thousands of individual operations.
- Distributed Processing: Modern data environments leverage distributed computing frameworks like Apache Spark, Flink, or Dask for processing massive datasets. Data Orchestration seamlessly integrates with these technologies, allowing the orchestration layer to trigger and manage jobs executed across clusters, optimizing resource allocation and performance.
- Event-Driven Architecture: Moving beyond scheduled jobs, many advanced Data Orchestration systems adopt an event-driven paradigm. This means workflows can be triggered automatically in response to specific events, such as a new file landing in a storage bucket, a database update, or a message appearing in a Kafka topic, enabling real-time or near real-time data processing.
- Microservices: The orchestration platform itself often comprises a suite of microservices, each responsible for a specific function (e.g., scheduler, worker, metadata service). This architectural choice enhances scalability, resilience, and modularity, allowing individual components to be updated or scaled independently.
Beyond these architectural foundations, Data Orchestration plays a crucial role in supporting specialized data operations. For AI and ML initiatives, orchestration manages workflows that prepare and transform raw data into features, often integrating with dedicated Feature Stores. It automates the data ingestion and transformation pipelines necessary to feed data to Data Labeling services, ensuring the quality and availability of training data. Furthermore, robust Data Orchestration platforms are indispensable for MLOps, automating model retraining workflows, managing data versioning for models, and ensuring data consistency across development, staging, and production environments. This continuous integration and deployment for data is a cornerstone of operationalizing AI effectively.
Challenges and Barriers to Adoption in Data Orchestration
While the benefits of Data Orchestration are profound, its implementation is not without hurdles. Organizations frequently encounter challenges that can impede adoption and effectiveness:
- Complexity of Distributed Systems: Managing dependencies, failures, and recovery across a myriad of data sources, processing engines, and downstream applications can be overwhelmingly complex. Debugging distributed workflows requires specialized skills and sophisticated tooling.
- Data Silos and Integration Debt: Despite the promise of unification, initial integration with legacy systems or deeply entrenched data silos can be a significant undertaking, often requiring custom connectors and extensive engineering effort.
- Observability and Debugging: Gaining real-time visibility into the health and performance of complex, automated workflows, identifying bottlenecks, and pinpointing the root cause of failures can be challenging. Comprehensive monitoring, logging, and alerting are critical but difficult to implement end-to-end.
- Skill Gap: Implementing and maintaining sophisticated Data Orchestration platforms requires a team proficient in distributed computing, cloud technologies, specific platform DSLs (Domain Specific Languages), and data engineering best practices. The scarcity of such talent can be a barrier.
- Data Drift and Schema Evolution: Changes in source data schemas or semantics (data drift) can silently break downstream pipelines, leading to corrupted data and erroneous insights. Orchestration systems need robust mechanisms for schema validation and handling schema evolution.
Business Value and ROI Derived from Effective Data Orchestration
Despite the challenges, the return on investment (ROI) from a well-implemented Data Orchestration strategy is substantial, yielding significant business value across the enterprise:
- Enhanced Data Quality and Reliability: By automating data pipelines and enforcing consistent transformation rules, orchestration minimizes manual errors and ensures data integrity. This leads to more trustworthy data, critical for accurate reporting and analytics.
- Accelerated Time-to-Insight: Automating repetitive data movement and transformation tasks dramatically reduces the time it takes to prepare and deliver data for analysis. This speed enables faster decision-making and quicker response to market changes.
- Operational Efficiency and Cost Reduction: Eliminating manual data processing tasks frees up valuable engineering resources, allowing them to focus on higher-value activities. Optimized resource utilization for compute and storage across distributed systems also leads to direct cost savings.
- Agility and Scalability: Robust Data Orchestration platforms provide the flexibility to rapidly integrate new data sources, adapt to evolving business requirements, and scale data processing capabilities up or down as needed, supporting business growth and innovation.
- Improved Regulatory Compliance: With features like lineage tracking and access control, orchestration platforms help organizations meet stringent regulatory requirements (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) by providing auditable trails of data movement and transformation. Metadata management ensures data definitions are consistent and understood.
- Seamless AI/ML Integration: As highlighted, orchestration is key for successful MLOps, ensuring data readiness for model training, deployment, and continuous monitoring, thus maximizing the impact of AI initiatives.

Comparative Insight: Data Orchestration vs. Traditional Data Lakes/Warehouses
It’s crucial to understand that Data Orchestration does not replace traditional data storage solutions like Data Lakes or Data Warehouses; rather, it complements and elevates their utility. A Data Warehouse is a structured repository optimized for reporting and analysis, housing curated, transformed data. A Data Lake, on the other hand, is a vast, often unstructured or semi-structured storage repository for raw data, designed for diverse analytical workloads, including big data processing and machine learning.
The distinction lies in their primary function: Data Lakes and Data Warehouses are fundamentally about storage and organization of data at rest. They are destinations. Data Orchestration, conversely, is about the movement, transformation, and management of data in motion. It’s the active engine that ensures data flows efficiently and effectively into, within, and out of these storage systems.
Consider the journey of data: raw data might first land in a Data Lake. Data Orchestration then takes over, scheduling and managing the processes that cleanse, transform, and enrich this raw data. It might then move a subset of this processed data into a Data Warehouse for business intelligence reporting. Simultaneously, other orchestrated workflows could extract specific features from the Data Lake, prepare them, and push them into a Feature Store for AI model training. Without robust Data Orchestration, managing these intricate, multi-stage processes would be a manual, error-prone, and incredibly time-consuming endeavor.
Moreover, Data Orchestration acts as the connective tissue between these storage paradigms and various operational systems. It can pull data from CRM, ERP, and IoT devices, push data back into operational databases after analytics, or trigger alerts based on real-time data streams. It bridges the gap between where data originates, where it is stored, and where it is consumed, ensuring that the entire data supply chain operates seamlessly. In essence, while Data Lakes and Warehouses provide the landscape, Data Orchestration provides the roads, bridges, and traffic management systems that make the journey of data possible and efficient.
.webp)
World2Data Verdict: Empowering the Intelligent Enterprise with Data Orchestration
In the relentlessly evolving digital economy, the ability to effectively manage, process, and derive insights from vast amounts of data is not merely an advantage; it is a fundamental prerequisite for survival and growth. Data Orchestration platforms are no longer just tools for data engineers; they are strategic assets that dictate an organization’s agility, data quality, and capacity for innovation. For World2Data, the verdict is clear: organizations must move beyond piecemeal solutions and invest strategically in comprehensive Data Orchestration capabilities. This investment should not only target workflow automation but also prioritize integration with advanced governance features, robust observability tools, and seamless connectivity to AI/ML ecosystems.
Looking ahead, the evolution towards data-as-a-product, real-time analytics, and hyper-personalized AI will make sophisticated Data Orchestration even more critical. Future platforms will likely push towards greater intelligence, incorporating AI-driven recommendations for pipeline optimization, self-healing capabilities, and more seamless integration with emerging data mesh architectures. The focus will shift from merely managing pipelines to enabling true data democratization and empowering domain teams to build and manage their data products with orchestrated ease. Embracing a mature Data Orchestration strategy today is essential for building an intelligent, adaptive, and resilient data ecosystem ready for tomorrow’s complex demands.