AI Data Governance: Automating Data Policies – The Imperative for World2Data
Platform Category: Data Governance Platform
Core Technology/Architecture: AI/ML-driven Policy Engines, Policy-as-Code
Key Data Governance Feature: Automated Data Classification and Tagging
Primary AI/ML Integration: Built-in ML for sensitive data discovery and policy enforcement
Main Competitors/Alternatives: Immuta, Collibra, Privacera, Alation, AWS Lake Formation
The explosion of data, driven by digital transformation and AI adoption, has made manual data governance approaches obsolete. Organizations today grapple with unprecedented volumes of information, diverse data sources, and an ever-tightening web of regulatory compliance. This makes the implementation of AI Data Governance Automation not merely an advantage, but an urgent necessity. World2Data.com explores how automating data policies through artificial intelligence transforms data management, ensuring compliance, enhancing security, and unlocking the true value of data for advanced analytics and AI initiatives.
Introduction: Navigating the Complexities of Modern Data
In an era where data is the new oil, its governance has become a formidable challenge. Traditional, human-centric data governance models, often reliant on spreadsheets and siloed processes, simply cannot keep pace with the velocity, volume, and variety of modern data ecosystems. From global regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA to industry-specific mandates, the stakes for data misuse or non-compliance are higher than ever, carrying severe financial and reputational penalties. This escalating complexity necessitates a paradigm shift towards proactive, intelligent solutions. Enter AI Data Governance Automation, a transformative approach that leverages artificial intelligence and machine learning to define, implement, monitor, and enforce data policies across the entire data lifecycle. This article delves into the core components, benefits, challenges, and future trajectory of automating data policies, highlighting its critical role in building robust, compliant, and efficient data platforms fit for the age of AI.
Core Breakdown: Architecture and Impact of Automated Data Policies
At its heart, an effective AI Data Governance Automation framework is built upon sophisticated technological pillars that move beyond simple rule engines. These systems are designed to understand data contextually, apply policies intelligently, and adapt dynamically to changing environments.
AI-Powered Policy Engines and Automated Data Classification
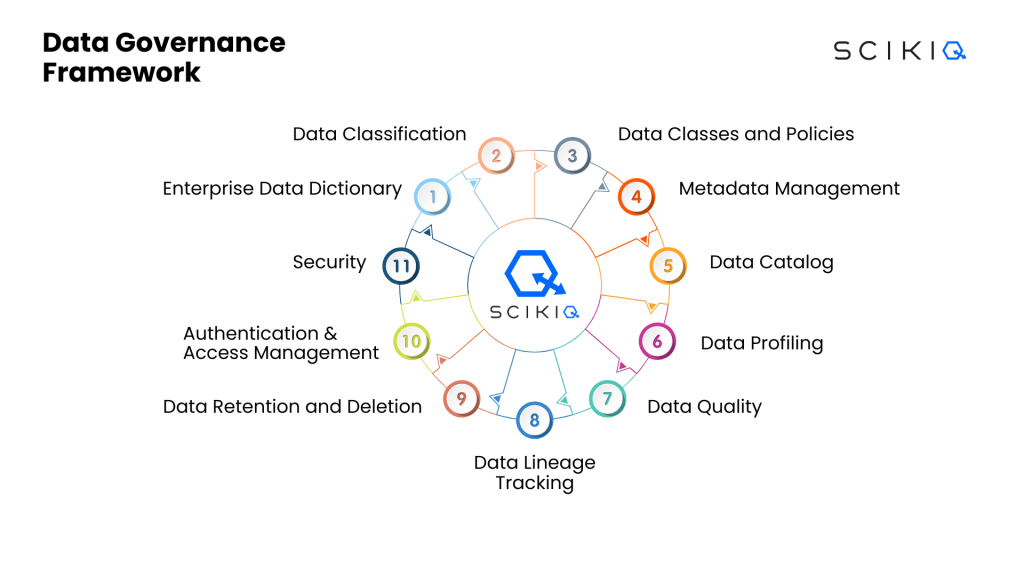
The foundation of automated data governance lies in AI-powered policy engines. These engines utilize advanced machine learning techniques, including Natural Language Processing (NLP) and deep learning, to automatically scan, classify, and tag vast datasets across structured, semi-structured, and unstructured formats. They can identify sensitive information such as Personally Identifiable Information (PII), Protected Health Information (PHI), financial data, and intellectual property with high accuracy. This automated classification drastically reduces the manual effort traditionally required for data identification, ensuring that data is consistently categorized based on its sensitivity, compliance requirements, and business value. Furthermore, these engines can learn from human feedback and historical policy enforcement, continuously improving their accuracy and adaptability. This leads to granular metadata management, where every data asset is enriched with context-rich tags that inform policy application.
Policy-as-Code and Dynamic Enforcement
Central to modern AI Data Governance Automation is the concept of Policy-as-Code. This approach treats governance policies as executable code, allowing them to be defined, managed, version-controlled, and deployed using software development best practices. Policies become declarative, written in human-readable languages, and can be integrated directly into MLOps pipelines and data workflows. This ensures that policies are consistently applied from data ingestion to consumption, across different environments and tools. Coupled with Policy-as-Code are real-time monitoring and enforcement mechanisms. These systems continuously observe data flows, access patterns, and usage behaviors. They can detect anomalies, flag potential policy violations instantly, and even trigger automated remediation actions, such as blocking unauthorized access, encrypting data, or alerting security teams. This dynamic enforcement capability is a stark contrast to traditional, often reactive, audit-based approaches.
Adaptive Governance and Continuous Optimization
One of the most powerful features of AI in data governance is its ability for dynamic policy adaptation. As regulatory landscapes evolve, new data types emerge, or business requirements shift, the AI system can learn from these changes. By analyzing audit trails, security incidents, and updates to regulatory frameworks, the AI can suggest modifications to existing policies or even automatically implement new ones. This continuous optimization ensures that the governance framework remains relevant, robust, and effective without constant manual recalibration, preventing data drift in policy effectiveness and ensuring enduring compliance.
Challenges and Barriers to Adoption
While the promise of AI Data Governance Automation is immense, organizations face several challenges during its adoption:
- Data Sprawl and Heterogeneity: Integrating AI governance tools across diverse, often siloed, legacy systems and cloud environments can be complex, requiring robust connectors and data virtualization capabilities.
- Data Drift in Classification: AI models used for sensitive data discovery and classification can experience concept drift if the underlying data patterns change significantly over time, requiring continuous monitoring and retraining.
- MLOps Complexity Integration: Embedding governance directly into complex MLOps pipelines to ensure models themselves are compliant (e.g., fairness, bias, explainability) adds another layer of technical challenge.
- Talent Gap: A shortage of professionals skilled in both data governance principles and AI/ML technologies can hinder effective implementation and management.
- Cultural Resistance: Shifting from manual, departmentalized governance to an automated, centralized system requires significant organizational change management and stakeholder buy-in.
- Regulatory Overload: The sheer volume and frequent changes in global data regulations make it difficult to codify all rules into AI systems accurately and comprehensively without specialized expertise.
Business Value and ROI of AI Data Governance Automation
Despite the challenges, the return on investment (ROI) for AI Data Governance Automation is compelling:
- Enhanced Compliance and Reduced Risk: Proactive identification and mitigation of compliance risks, minimizing the likelihood of costly fines, legal battles, and reputational damage. Automated audit trails provide irrefutable proof of compliance.
- Operational Efficiency and Cost Savings: Significant reduction in manual effort for data classification, policy enforcement, and audit preparation. This frees up data stewards and compliance officers to focus on strategic initiatives rather than repetitive tasks.
- Improved Data Quality and Trust: Consistent policy application across all data assets leads to higher data quality, reliability, and trustworthiness, which are crucial for accurate analytics and effective AI model training.
- Faster Time-to-Value for AI Initiatives: By securely democratizing access to high-quality, compliant data, AI Data Governance Automation accelerates data science projects, allowing faster model development and deployment.
- Competitive Advantage: Organizations that master automated data governance can leverage their data more strategically, fostering innovation while maintaining security and compliance, giving them a significant edge in the market.

Comparative Insight: AI Data Governance vs. Traditional Approaches
Understanding the transformative power of AI Data Governance Automation requires a look at its predecessors – the traditional data lake and data warehouse governance models. Historically, data governance in these environments has been largely reactive, manual, and often siloed. In a traditional data warehouse, governance policies were typically applied at the point of ingestion or during ETL processes, primarily focusing on structured data. Enforcement was often achieved through static access controls and periodic audits, which struggled to keep pace with dynamic data access patterns and evolving regulatory requirements.
Data lakes, while offering flexibility for diverse data types (structured, semi-structured, unstructured), compounded the governance challenge. The “dump first, ask questions later” philosophy often led to “data swamps” where identifying sensitive data, applying consistent policies, and maintaining data quality became Herculean tasks. Manual tagging, disparate toolsets, and a lack of real-time monitoring made comprehensive governance nearly impossible, leaving organizations vulnerable to security breaches and non-compliance.
AI Data Governance Automation fundamentally shifts this paradigm. Instead of reactive audits, it offers proactive, continuous enforcement. Unlike static rule sets, AI-powered engines adapt and learn. Key differentiators include:
- Automated Discovery and Classification: AI systems automatically discover and classify data at scale, regardless of its format or location, a task that is largely manual and error-prone in traditional settings.
- Real-time, Context-Aware Enforcement: Policies are enforced dynamically based on user roles, data sensitivity, access context, and regulatory requirements, not just static permissions. This enables fine-grained access control (e.g., Attribute-Based Access Control – ABAC) that far surpasses traditional Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) limitations.
- Policy-as-Code for Agility: Policies are treated as code, allowing for version control, automated testing, and rapid deployment, integrating seamlessly into CI/CD pipelines – a concept alien to traditional governance frameworks.
- Adaptive Learning: AI systems learn from usage patterns, security incidents, and regulatory updates to refine and optimize policies continuously, ensuring evergreen compliance and security posture.
- Holistic Coverage: Automated governance extends across the entire data lifecycle – from ingestion and processing to storage and consumption – providing end-to-end visibility and control, unlike piecemeal traditional solutions.
This evolution transforms data governance from a compliance burden into a strategic enabler, fostering trust and accelerating innovation across the entire data landscape.

World2Data Verdict: Embracing the Automated Future of Data Policy
The journey towards a fully data-driven enterprise is inextricably linked with robust and adaptable data governance. World2Data.com asserts that AI Data Governance Automation is no longer a futuristic concept but a present-day imperative for any organization serious about data security, regulatory compliance, and unlocking the full potential of its data assets for AI. The complexities of modern data ecosystems demand an intelligent, automated approach that traditional methods simply cannot provide. Organizations must strategically invest in AI-powered policy engines, embrace Policy-as-Code methodologies, and cultivate a culture that prioritizes automated, intelligent governance. We recommend a phased adoption strategy, starting with critical data domains and gradually expanding, while also focusing on integrating these automated capabilities seamlessly into existing data platforms and MLOps pipelines. The future of data policy management lies in continuous learning and predictive analytics, where AI systems not only enforce rules but anticipate risks and proactively adapt policies. By making AI Data Governance Automation a cornerstone of their data strategy, businesses can transform compliance from a cost center into a competitive advantage, ensuring trust, accelerating innovation, and securely navigating the ever-evolving data landscape.