AI Chatbot Rollout Case Study: Reducing Support Tickets by 40% and Revolutionizing Customer Service
The strategic AI Chatbot Rollout highlighted in this case study showcases a remarkable achievement in modern customer service, delivering a 40% reduction in support tickets. This transformative initiative underscores the power of conversational AI platforms in streamlining operations and significantly enhancing user experience. By automating routine inquiries and providing instant, accurate responses, businesses can address the common challenge of escalating support volumes, thereby mitigating delayed responses and customer frustration.
- Platform Category: Conversational AI Platform
- Core Technology/Architecture: Natural Language Processing (NLP), Cloud-Native
- Key Data Governance Feature: PII Redaction in Chat Logs
- Primary AI/ML Integration: Built-in NLP/NLU Models
- Main Competitors/Alternatives: Intercom, Drift, Zendesk, Ada, Google Dialogflow
Introduction: The Imperative for an Intelligent AI Chatbot Rollout
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, customer expectations for immediate and effective support are higher than ever. Organizations frequently grapple with the dual challenges of managing an ever-increasing volume of customer inquiries and optimizing their support resources. Traditional support models, heavily reliant on human agents, often struggle to scale efficiently, leading to longer wait times, inconsistent service quality, and increased operational costs. This scenario creates a compelling case for a strategic AI Chatbot Rollout, not merely as a cost-saving measure, but as a critical component of a modern customer engagement strategy.
The objective of this article is to delve into a successful AI Chatbot Rollout case study, examining the technical underpinnings, strategic planning, and measurable impact that led to a substantial 40% reduction in support tickets. We will explore how leveraging advanced Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning (ML) capabilities, integrated within a cloud-native conversational AI platform, can fundamentally reshape customer interactions and empower support teams. Furthermore, we will analyze the key architectural components, the challenges encountered, the significant business value generated, and how this modern approach contrasts with older paradigms.
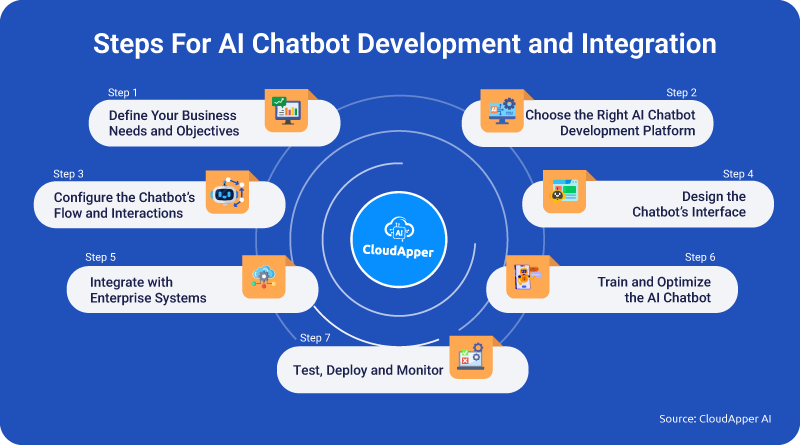
Core Breakdown: The Architecture and Enablers of a Successful AI Chatbot Rollout
The success of any intelligent automation initiative, particularly an AI Chatbot Rollout, hinges on a robust technical foundation and meticulous planning. This section dissects the core components and strategic considerations that made the ticket reduction possible.
The Conversational AI Platform: Underpinning Intelligent Interactions
At the heart of a successful AI chatbot lies a sophisticated conversational AI platform. This platform is not just a simple script-follower but an intelligent system designed to understand, process, and respond to human language naturally. Its architecture typically comprises:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) & Natural Language Understanding (NLU) Engines: These are the brains of the chatbot, responsible for interpreting user input, identifying intentions (intent recognition), and extracting key information (entity extraction). Advanced NLU models can handle nuances, slang, and misspellings, converting unstructured text into structured data that the system can process.
- Dialogue Management System: This component maintains context throughout a conversation, ensuring that the chatbot’s responses are relevant to the ongoing interaction. It manages conversational flows, understands follow-up questions, and can hand off to human agents when necessary.
- Knowledge Base Integration: For the chatbot to provide accurate answers, it must have access to a comprehensive and up-to-date knowledge base. This includes FAQs, product documentation, service policies, and troubleshooting guides. The platform intelligently queries this knowledge base to formulate responses.
- Response Generation: Based on the identified intent and extracted entities, the system generates appropriate, natural-sounding responses. This can range from pre-defined answers to dynamically generated text.
- Cloud-Native Architecture: Leveraging cloud infrastructure provides scalability, reliability, and global accessibility. It allows the chatbot to handle fluctuating query volumes, integrate seamlessly with other cloud services, and deploy updates rapidly.
Data Foundation: The Role of ‘Chatbot Feature Stores’ and ‘Data Labeling’
While the term “Feature Store” is often associated with traditional machine learning models in data platforms, its principles are equally vital for AI chatbots. In this context, a ‘Chatbot Feature Store’ can be conceptualized as an organized repository of conversational data assets that are readily available for model training and inference. This includes:
- Intent & Entity Definitions: A standardized collection of all possible user intentions the chatbot should recognize (e.g., “check order status,” “reset password,” “technical support”) and the key entities within those intents (e.g., “order number,” “email address,” “product name”).
- Utterance Examples: Thousands, if not millions, of diverse ways users might express a particular intent or entity. These form the core training data for NLU models.
- Conversation Flows & Patterns: Pre-defined or learned conversational paths that the chatbot can follow, representing successful or common user journeys.
- Historical Interaction Data: Anonymized chat logs and transcripts of past interactions (both human and bot) that provide valuable insights for continuous model improvement.
Crucially, the success of this ‘feature store’ relies heavily on meticulous ‘Data Labeling.’ This process involves human annotators reviewing raw conversational data (e.g., customer chat logs) and:
- Intent Categorization: Assigning the correct intent to each user query.
- Entity Annotation: Highlighting and labeling specific pieces of information (entities) within the user’s text.
- Sentiment Analysis: Marking the sentiment (positive, negative, neutral) of user inputs, which helps the chatbot tailor its tone or escalate to a human.
This human-in-the-loop data labeling process is paramount for creating high-quality, unbiased training datasets, directly impacting the chatbot’s accuracy and ability to understand complex queries. A critical data governance feature here is PII Redaction in Chat Logs, ensuring sensitive customer information is automatically removed before data is used for training or analysis, upholding privacy and compliance.
Challenges and Barriers to AI Chatbot Adoption
Despite the immense potential, deploying and optimizing an AI chatbot is not without its hurdles:
- Data Quality and Bias: Poorly labeled, insufficient, or biased training data can lead to a chatbot that misinterprets user intent, provides inaccurate responses, or even perpetuates societal biases. Ensuring representative and high-quality data is an ongoing challenge.
- Intent Ambiguity and Contextual Understanding: Human language is inherently ambiguous. Chatbots struggle with highly nuanced queries, sarcasm, idiomatic expressions, and maintaining complex context over long conversations.
- Integration Complexity: A truly useful chatbot needs to integrate with various backend systems (CRM, ERP, ticketing systems, knowledge bases). This integration often requires significant development effort and robust APIs.
- MLOps for Conversational AI: Managing the lifecycle of chatbot models (versioning, deployment, monitoring, retraining) is complex. Monitoring for ‘data drift’ (when user language patterns change over time) or ‘model decay’ (when performance degrades) is crucial for continuous effectiveness.
- User Acceptance and Trust: Customers may initially be wary of interacting with a bot. Designing intuitive interfaces, clearly setting expectations, and ensuring seamless human handoff are vital for building trust.
- Scalability of Human Oversight: While the bot reduces tickets, human agents are still needed for complex cases and for training the bot. Scaling the human team’s ability to label data and manage escalations can become a bottleneck.
Business Value and Measurable ROI of a Strategic AI Chatbot Rollout
The 40% reduction in support tickets achieved through this AI Chatbot Rollout is a tangible demonstration of significant business value and return on investment. This translates into several key benefits:
- Financial Savings and Resource Optimization: By automating routine inquiries, the need for human agents to handle repetitive tasks diminishes, leading to substantial cost savings in operational expenses and allowing human agents to focus on higher-value, more complex problem-solving.
- Faster Resolution Times and 24/7 Availability: Chatbots provide instant responses around the clock, eliminating wait times and resolving common queries immediately, significantly improving customer satisfaction.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Customers appreciate the convenience of getting quick answers at any time, leading to a more positive overall brand experience. The consistency of information provided by the bot also enhances reliability.
- Enhanced Agent Productivity and Morale: By offloading repetitive tasks, human agents can dedicate their skills to more challenging and engaging work, leading to higher job satisfaction and better utilization of their expertise.
- Scalability: Chatbots can handle an unlimited number of concurrent conversations, allowing businesses to scale their support operations effortlessly during peak times or periods of rapid growth without proportional increases in staffing.
- Actionable Insights from Conversational Data: The aggregated and analyzed data from chatbot interactions provides invaluable insights into customer pain points, common queries, product issues, and areas for service improvement.
Comparative Insight: AI Chatbot Rollout vs. Traditional Support Models
The advent of sophisticated AI chatbots, facilitated by modern conversational AI platforms, represents a paradigm shift from traditional customer support mechanisms. Understanding this evolution helps to appreciate the profound impact of a well-executed AI Chatbot Rollout.
Traditional Human-Centric Support
Historically, customer support has been predominantly human-centric, relying on phone calls, emails, and live chat with human agents. While offering a personalized touch for complex issues, this model faces inherent limitations:
- Scalability Issues: Human teams struggle to scale rapidly with fluctuating demand. Increasing agent numbers is costly and time-consuming.
- Limited Availability: Human support is typically restricted by business hours and agent shifts, leading to frustration for customers seeking after-hours assistance.
- Inconsistency: Responses can vary between agents, leading to inconsistent information and customer experience.
- High Operational Costs: Labor is a significant expense, especially for 24/7 operations.
- Agent Burnout: Repetitive queries can lead to monotony and burnout for support staff.
Rule-Based Chatbots (Early Generation)
The first wave of chatbots was primarily rule-based. These bots followed predefined scripts and decision trees, operating on keyword matching rather than understanding context:
- Limited Intelligence: They could only answer questions for which they were explicitly programmed. Any deviation from the script would lead to failure.
- Poor User Experience: Often frustrating for users due to their inability to understand natural language or context.
- Maintenance Overhead: Expanding their capabilities required manual updating of rules, which quickly became unmanageable.
Modern AI Chatbot Rollout Powered by Conversational AI Platforms
Today’s AI Chatbot Rollout leverages advancements in machine learning, particularly NLP and NLU, to offer a vastly superior experience:
- Contextual Understanding: Unlike rule-based bots, modern AI chatbots can understand the intent behind a user’s query, even if the phrasing is novel. They can maintain context across multiple turns in a conversation.
- Learning and Adaptation: Through continuous training on vast datasets (and the data labeling processes mentioned earlier), these bots learn and improve over time, becoming more accurate and intelligent with every interaction.
- Seamless Integration: Modern conversational AI platforms are designed to integrate deeply with enterprise systems (CRMs, knowledge bases, analytics platforms), enabling the chatbot to perform actions, retrieve personalized data, and offer comprehensive solutions.
- Proactive Engagement: Some advanced chatbots can proactively reach out to customers based on their browsing behavior or past interactions, offering assistance before a problem arises.
- Hybrid Approach: The true power lies in their ability to seamlessly hand off complex queries to human agents, providing the agent with the full chat history, ensuring a smooth transition and reducing customer effort. This intelligent routing ensures customers always receive the best possible support, whether from a bot or a human.
In essence, while traditional models provided basic answers and rule-based bots offered limited automation, a sophisticated AI Chatbot Rollout transforms the entire support ecosystem, moving towards intelligent, scalable, and highly personalized customer engagement that benefits both the business and its customers.
.png)
World2Data Verdict: The Unstoppable Ascent of Intelligent Automation in Customer Service
The demonstrated success of reducing support tickets by 40% through a strategic AI Chatbot Rollout is not an isolated incident but a clear indicator of a transformative trend. World2Data believes that conversational AI platforms are rapidly evolving from mere efficiency tools into indispensable strategic assets for businesses across all sectors. The future of customer service is undeniably hybrid, where AI chatbots serve as the first line of defense, handling routine inquiries with speed and precision, while intelligently escalating complex or sensitive issues to highly skilled human agents. Organizations that invest in robust, data-driven conversational AI platforms, prioritize ethical data governance (like PII redaction), and implement continuous MLOps practices for their chatbot models will gain a significant competitive advantage. Expect to see further refinement in NLU capabilities, deeper integration with emotional intelligence, and the proliferation of AI chatbots handling not just support, but also sales, marketing, and internal operations, driving unprecedented levels of automation and customer satisfaction. The imperative for businesses is no longer “if” but “when” and “how effectively” they will execute their next-generation AI Chatbot Rollout.