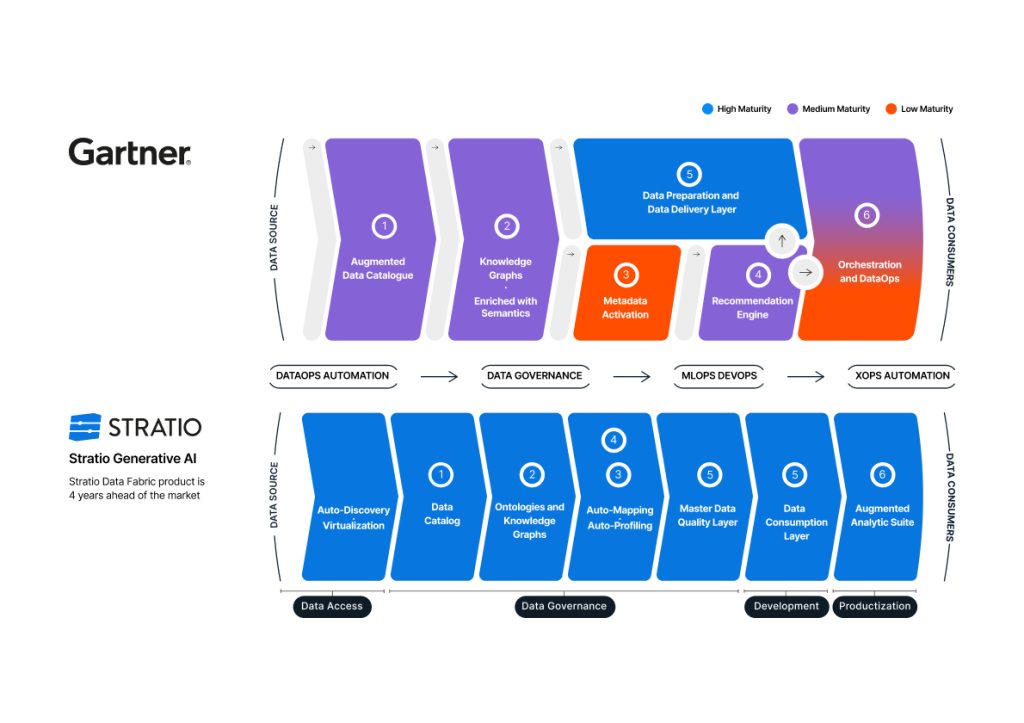
AI Data Fabric: Unlocking Next-Gen Data Architecture Trends for AI Success
- Platform Category: Data Management Architecture
- Core Technology/Architecture: Distributed Data Architecture with Active Metadata and Knowledge Graph
- Key Data Governance Feature: Unified Data Catalog with Active Metadata
- Primary AI/ML Integration: AI-powered automation for metadata discovery, data integration, and recommendations
- Main Competitors/Alternatives: Data Mesh, Data Warehouse, Data Lake
The AI Data Fabric represents a pivotal shift in how organizations perceive, manage, and harness their vast data estates. As a modern data architecture, it is rapidly redefining how organizations manage and leverage their most valuable asset – data. The emerging AI Data Fabric Trends point towards a future where data access is democratized, secure, and intelligent, moving beyond traditional, siloed approaches and empowering smarter, data-driven business decisions with unprecedented agility.
Introduction: Navigating the Complexities of Modern Data with AI Data Fabric
In today’s hyper-connected, data-rich business environment, the ability to rapidly access, integrate, and derive insights from diverse data sources is paramount. Traditional data architectures, often characterized by fragmented data silos, manual integration processes, and reactive governance, struggle to keep pace with the demands of real-time analytics and advanced Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) initiatives. This growing complexity highlights a critical need for a more intelligent, adaptable, and unified approach to data management. This is precisely where the AI Data Fabric emerges as a transformative solution, designed to create a seamless, interconnected data ecosystem capable of fueling innovation and operational efficiency. This article delves into the core tenets of the AI Data Fabric, exploring its architectural components, the challenges it addresses, its profound business value, and the significant AI Data Fabric Trends shaping its adoption and evolution.
Core Breakdown: Architecture, Components, Challenges, and Business Value
What is AI Data Fabric and Its Core Purpose
At its heart, an AI Data Fabric integrates diverse data sources across an enterprise, creating a unified, intelligent layer that abstracts away underlying complexity. This sophisticated architecture leverages AI and machine learning to automate data discovery, integration, transformation, and governance. Its core purpose is to provide seamless, on-demand access to the right data, at the right time, for the right users and applications, irrespective of where that data resides or its original format. By doing so, it greatly enhances the utility of data for advanced analytics, predictive modeling, and sophisticated artificial intelligence initiatives, empowering organizations to unlock insights that were previously unattainable due to data fragmentation and inaccessibility. It functions as a single pane of glass over a distributed data landscape, providing logical rather than physical unification.
Driving Business Agility with Unified Data Access
One of the most significant AI Data Fabric Trends is its role in boosting business agility. By offering a unified, consistent view of disparate data sources, the fabric eliminates the need for complex, costly, and time-consuming point-to-point integrations. This empowers businesses to accelerate innovation and respond to market changes faster and more effectively. The ability to quickly assemble comprehensive data streams from various operational systems, historical archives, and external sources translates directly into faster insights and more informed, timely decision-making across all operational levels. This agility is crucial in competitive markets, allowing enterprises to develop new products, optimize customer experiences, and identify emerging opportunities with unparalleled speed.
Key Components and Underlying Technologies
The effectiveness of an AI Data Fabric hinges on several critical, interconnected components and underlying technologies, each contributing to its intelligent and adaptive nature:
- Intelligent Metadata Management: This forms the backbone, providing a semantic layer that not only stores descriptive metadata (data about data) but also active metadata. Active metadata continuously observes, analyzes, and learns from data usage patterns, lineage, and semantic relationships. It fuels AI engines to suggest optimizations, identify anomalies, and enrich data context, transforming passive information into an actionable asset.
- Knowledge Graph: Often integrated with metadata management, a knowledge graph provides a powerful way to model complex relationships between data, metadata, and business concepts. It helps in understanding the context of data, enabling more sophisticated data discovery, linking disparate datasets, and facilitating natural language querying for business users.
- AI-powered Automation: Machine learning algorithms are embedded throughout the fabric to automate various data management tasks. This includes automated data discovery and classification, intelligent data integration recommendations, real-time data quality monitoring and remediation, and dynamic policy enforcement for data governance and security.
- Data Virtualization: This technology creates a virtual data layer that abstracts the physical location and structure of data, allowing users and applications to access and query data from multiple sources as if it were a single, unified database, without moving or replicating the data.
- Unified Data Catalog: A comprehensive and intelligent data catalog serves as the central hub for discovering, understanding, and accessing all enterprise data assets. Powered by active metadata and AI, it provides a rich, searchable inventory of data, complete with lineage, quality scores, ownership, and usage recommendations.
- Data Integration and Orchestration: The fabric employs a variety of integration techniques, including APIs, streaming, and batch processes, orchestrated intelligently by AI to ensure data flows seamlessly and efficiently across the enterprise.
- Data Governance and Security: Automated data governance, driven by AI, ensures compliance with regulatory requirements (like GDPR, CCPA) and internal security policies are consistently applied across all data assets without extensive manual overhead. Role-based access controls, data masking, and encryption are dynamically managed.
Addressing Modern Data Challenges Effectively
In today’s complex data landscape, organizations grapple with massive data volumes, diverse formats (structured, semi-structured, unstructured), varying velocities (batch to real-time streams), and persistent data silos that impede a holistic view. An AI Data Fabric specifically addresses these challenges by breaking down barriers between systems, making data truly accessible and usable. It ensures high data quality and integrity across the entire data estate through continuous monitoring, profiling, and automated remediation, significantly reducing the ‘garbage in, garbage out’ problem that plagues many AI initiatives. Robust, adaptable security features are inherently built-in, protecting sensitive information throughout its lifecycle, from ingestion to consumption, across hybrid and multi-cloud environments. This proactive approach to data quality and security is vital for building trust in data-driven decisions.
Challenges and Barriers to Adoption
Despite its undeniable benefits, the adoption of an AI Data Fabric is not without its hurdles. One of the primary challenges lies in the inherent complexity of integrating disparate systems and legacy architectures, which can be a significant undertaking requiring substantial upfront planning and investment. Organizations may face difficulties in aligning diverse stakeholders, including data engineers, data scientists, business analysts, and IT operations, who often have varying priorities and understandings of data management. Furthermore, the successful implementation demands a high level of expertise in areas like AI/ML, distributed systems, and advanced data governance, leading to potential skill gaps within existing teams. The initial investment in technology, infrastructure, and talent can also be a significant barrier for some enterprises. Ensuring the fabric truly provides real-time capabilities across all data sources, and managing data drift in a highly dynamic environment, adds further layers of technical complexity. Overcoming these challenges requires a clear strategic vision, strong executive sponsorship, and a phased, iterative approach to implementation.
Business Value and ROI of AI Data Fabric
The return on investment (ROI) derived from implementing an AI Data Fabric is multifaceted and profound, impacting various aspects of an organization. Firstly, it dramatically accelerates the time-to-insight, allowing businesses to make faster, more informed decisions. This leads to improved operational efficiency, reduced manual effort in data integration, and lower costs associated with data management. The fabric enhances data quality and consistency, which is critical for the reliability and performance of AI/ML models, directly improving their accuracy and business impact. For data scientists, it reduces the time spent on data preparation—often cited as 80% of their work—allowing them to focus more on model development and analysis. Moreover, by providing a unified and governed view of data, it significantly strengthens regulatory compliance and data privacy efforts, mitigating risks and potential penalties. Ultimately, an AI Data Fabric fosters innovation by democratizing data access, empowering a wider range of users to experiment with data and build new data products, thereby creating new revenue streams and competitive advantages. Faster model deployment for AI applications, driven by readily available, high-quality data, translates directly into quicker realization of value from AI investments.

Comparative Insight: AI Data Fabric vs. Traditional Architectures
To truly appreciate the transformative potential of the AI Data Fabric, it’s essential to compare it with the data architectures that preceded it: the Data Warehouse, Data Lake, and the more recent Data Mesh.
- AI Data Fabric vs. Traditional Data Warehouse: Data Warehouses are highly structured, relational databases optimized for historical data analysis and reporting. They excel at serving known queries and structured data, but struggle with varied data formats, real-time processing, and the agility required for modern AI/ML workloads. The AI Data Fabric, in contrast, handles all data types and velocities, providing a dynamic, real-time view across distributed sources, making it far more versatile for AI applications. It shifts from a centralized, pre-defined schema approach to a flexible, schema-on-demand model.
- AI Data Fabric vs. Data Lake: Data Lakes emerged to address the limitations of Data Warehouses by storing raw, unstructured, and semi-structured data at scale, offering flexibility for data scientists. However, Data Lakes often become “data swamps” due to a lack of governance, metadata management, and clear semantic understanding, making data discovery and quality problematic. The AI Data Fabric builds upon the Data Lake’s flexibility but overlays it with intelligent metadata, AI-powered automation, and robust governance, transforming raw data into highly discoverable, trustworthy, and actionable assets for AI.
- AI Data Fabric vs. Data Mesh: Data Mesh is a decentralized architectural paradigm that treats data as a product, owned and served by domain-oriented teams. It emphasizes decentralization and domain ownership. While sharing the goal of democratizing data, the AI Data Fabric takes a more unified, technological approach. A Data Fabric can actually complement a Data Mesh by providing the underlying technical capabilities (like automated metadata management, data virtualization, and intelligent integration) that enable and accelerate the “data as a product” philosophy across decentralized domains, without mandating a complete organizational restructuring as often implied by Data Mesh. The Fabric provides the technical “glue” that allows data products to be easily discoverable, governed, and consumed across domains.
In essence, while traditional architectures focus on storage and processing within defined boundaries, the AI Data Fabric focuses on intelligent, dynamic connectivity and accessibility across the entire enterprise, making it uniquely suited to power diverse and evolving AI and analytics initiatives by overcoming the inherent limitations of fragmented and siloed systems.
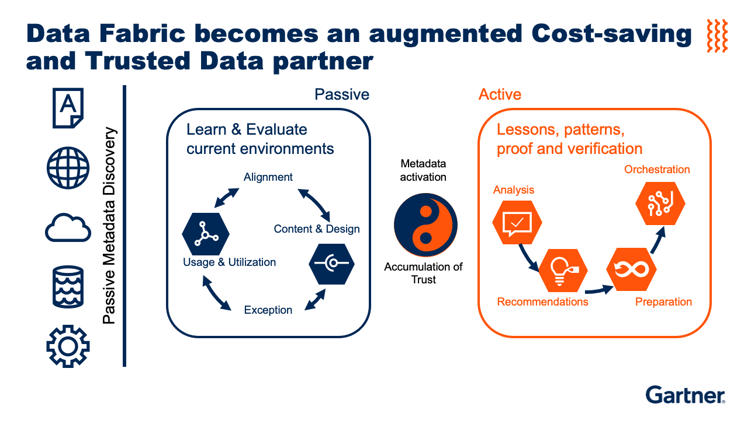
World2Data Verdict: The Strategic Imperative of AI Data Fabric
The trajectory of AI Data Fabric Trends suggests it will not merely be an option but an indispensable component of modern enterprise data strategies. As data ecosystems grow exponentially more intricate, distributed, and diverse, the adaptive and intelligent nature of the fabric offers a sustainable and future-proof solution for navigating future data demands. Organizations that embrace an AI Data Fabric proactively will be better positioned to harness the full potential of their data assets, especially for advanced AI applications and real-time operational intelligence. World2Data.com recommends that enterprises critically evaluate their current data architecture against the demands of their AI roadmap. A phased adoption of an AI Data Fabric, focusing initially on critical data domains or high-value use cases, can yield rapid ROI and build internal capabilities. This integrated, intelligent data management approach is more than a technological upgrade; it’s a strategic evolutionary step in how businesses perceive and interact with their data, continually shaping competitive landscapes and enabling truly data-driven innovation.