Revolutionizing Information Retrieval: The Power of AI Applied in Enterprise Data Search
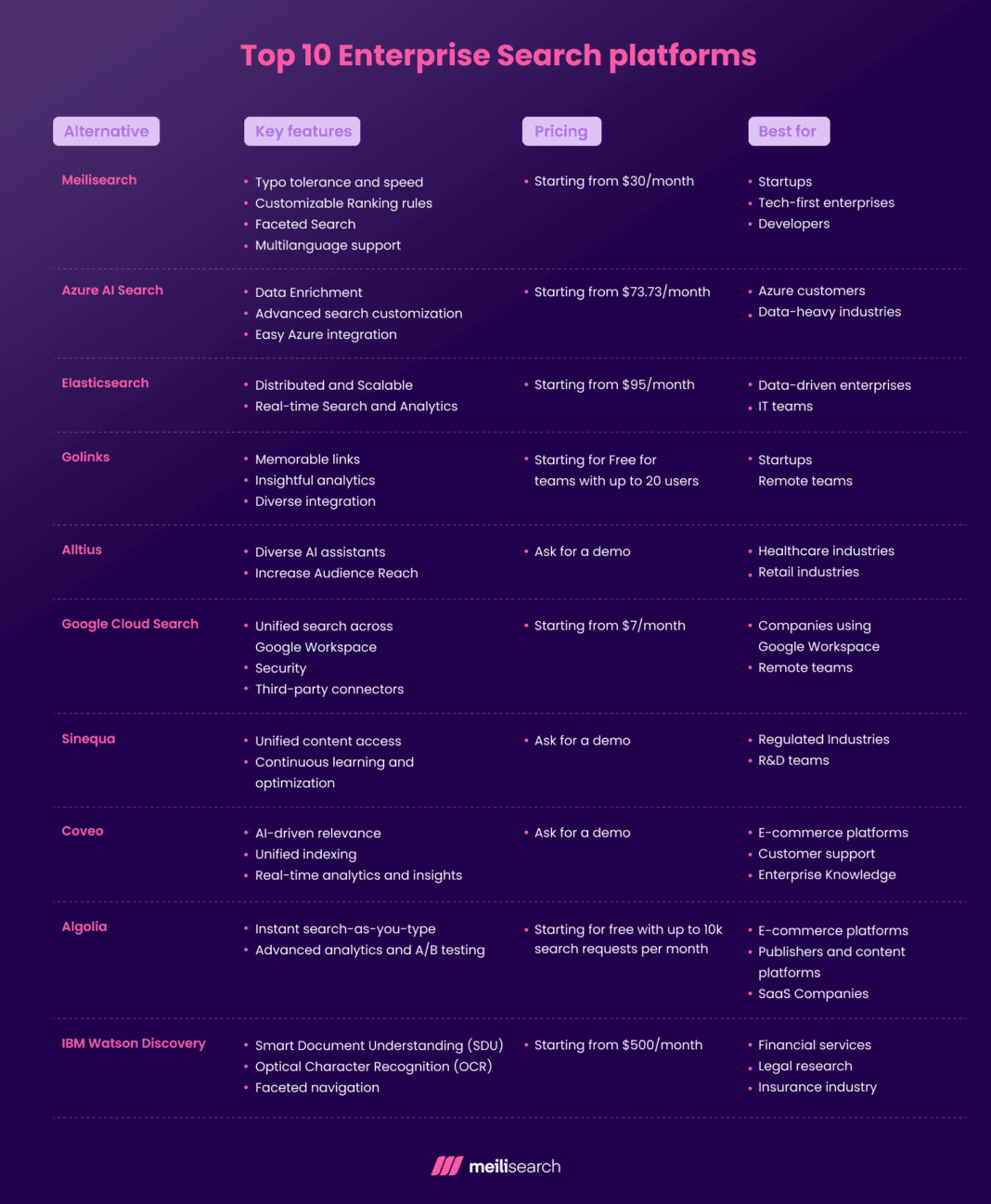
**Platform Category:** Enterprise Search Platform
**Core Technology/Architecture:** Natural Language Processing (NLP), Vector Search, Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
**Key Data Governance Feature:** Permissions and Access Control Syncing
**Primary AI/ML Integration:** Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Generative AI for Summarization
**Main Competitors/Alternatives:** Glean, Coveo, Elastic, Microsoft 365 Copilot, Google Cloud Search
The vast oceans of enterprise data, spanning documents, emails, databases, and more, have long presented a formidable challenge for businesses aiming to harness their collective knowledge. Traditional search methods, often keyword-reliant and siloed, frequently fall short, leading to lost productivity and missed opportunities. Enter AI Enterprise Data Search – a transformative paradigm that promises to unlock unprecedented levels of insight, efficiency, and agility by understanding intent and context, not just keywords.
This deep dive by World2Data explores how Artificial Intelligence is fundamentally reshaping the landscape of corporate information retrieval. We will dissect the architectural components, enumerate the immense business value, scrutinize the inherent challenges, and provide a comparative analysis against legacy systems, ultimately offering a strategic verdict for enterprises navigating this pivotal technological shift.
Introduction: Navigating the Information Deluge with AI Enterprise Data Search
The landscape of corporate information retrieval is undergoing a profound transformation with AI Applied in Enterprise Data Search. Businesses today grapple with an ever-increasing volume of data, making efficient AI Enterprise Data Search not just a convenience, but a critical imperative for competitive advantage and operational excellence. The sheer scale and diversity of modern enterprise data sources—from structured databases and CRM systems to unstructured documents, emails, chat logs, and multimedia files—create a labyrinth that traditional keyword-based search engines are ill-equipped to navigate. Employees spend countless hours sifting through irrelevant documents, a significant drain on resources and a barrier to agile decision-making. This manual, often frustrating approach, frequently leads to missed opportunities and delayed responses in dynamic market conditions, directly impacting innovation and competitive standing.
AI Enterprise Data Search revolutionizes this by introducing sophisticated Artificial Intelligence capabilities, primarily driven by Natural Language Processing (NLP), to allow systems to understand the intent behind a query, not just exact keywords. This enables contextual relevance, delivering precise results even for complex or ambiguously phrased questions through advanced semantic search and intelligent data indexing. Predictive algorithms further enhance accuracy by learning from past user interactions and data patterns. Our objective in this article is to provide a comprehensive analysis of the core technologies, practical applications, and strategic implications of integrating AI into enterprise data search, equipping businesses with the knowledge to make informed decisions about their information infrastructure.
Core Breakdown: Architecture and Capabilities of AI Enterprise Data Search
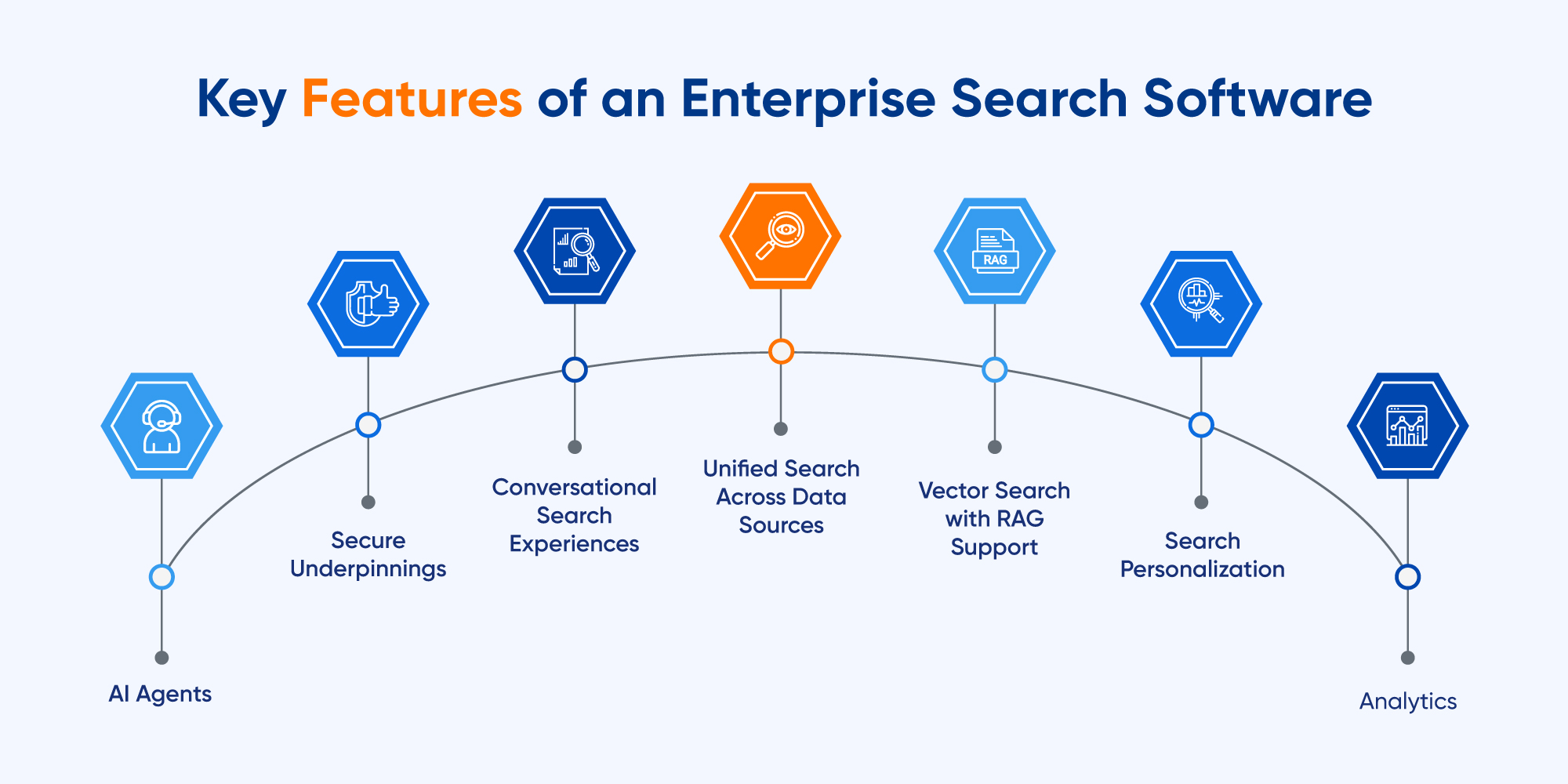
At its heart, AI Enterprise Data Search is a complex interplay of advanced AI and machine learning techniques designed to make corporate data universally discoverable and intelligently retrievable. Unlike traditional search, which acts as a mere indexer of keywords, AI-powered systems function as intelligent assistants, capable of understanding meaning, context, and relationships across disparate data types.
The core architecture typically involves several interconnected layers:
- Data Ingestion and Indexing: This foundational layer is responsible for connecting to various enterprise data sources—CRM, ERP, SharePoint, Slack, Confluence, file shares, databases, etc.—and ingesting their content. Beyond simple data extraction, AI systems employ advanced parsers and transformers to clean, normalize, and enrich the data. This includes identifying entities, categorizing content, and creating metadata that goes far beyond standard tags.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP is the backbone of intelligent search. It enables the system to understand human language, rather than just matching keywords. Key NLP techniques include:
- Tokenization and Lemmatization: Breaking down text into meaningful units and reducing words to their base forms.
- Named Entity Recognition (NER): Identifying and classifying named entities (people, organizations, locations, dates, etc.).
- Sentiment Analysis: Gauging the emotional tone of text.
- Topic Modeling: Discovering abstract topics within a collection of documents.
- Semantic Search: Moving beyond lexical matching to understand the conceptual meaning of queries and documents. This allows users to find information even if they use different terminology than the source document.
- Vector Search (Embeddings): A critical advancement, vector search transforms text (and other data types) into high-dimensional numerical representations called embeddings. These embeddings capture the semantic meaning of the content. When a user enters a query, it’s also converted into an embedding, and the search engine finds documents whose embeddings are “closest” in the vector space, indicating semantic similarity. This is far more powerful than keyword matching, enabling highly relevant results for complex queries.
- Knowledge Graphs: Many advanced AI Enterprise Data Search platforms build or leverage knowledge graphs. These graphs represent entities (people, projects, concepts) and their relationships within the enterprise data. By traversing these relationships, the search engine can provide more comprehensive and contextually rich answers, linking disparate pieces of information that would otherwise remain isolated.
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): This cutting-edge technique combines the power of retrieval with generative AI. When a user asks a question, the system first retrieves relevant documents or snippets from the enterprise knowledge base (using NLP, vector search, and knowledge graphs). Then, a large language model (LLM) is used to generate a coherent, concise, and contextualized answer based *only* on the retrieved information. This significantly reduces hallucinations common in pure generative AI models and ensures answers are grounded in verifiable enterprise data, with citations back to the source documents. This is a primary AI/ML integration, especially for generative AI for summarization.
- Machine Learning for Ranking and Personalization: Beyond just finding relevant documents, ML algorithms learn from user interactions (clicks, dwell time, feedback) to continuously improve search result ranking. Personalization engines tailor results based on an individual user’s role, past search history, department, and access permissions.
- Data Governance and Access Control: A non-negotiable component, especially in enterprises, is robust data governance. AI Enterprise Data Search systems must seamlessly integrate with existing identity and access management (IAM) systems. Key is **Permissions and Access Control Syncing**, ensuring that search results adhere strictly to the user’s existing permissions. If a user doesn’t have access to a document in its original location, it should not appear in their search results, regardless of its relevance. This is crucial for security, compliance, and preventing unauthorized information disclosure.
Challenges and Barriers to Adoption in AI Enterprise Data Search
Despite the immense potential, implementing and operating an effective AI Enterprise Data Search solution is not without its hurdles:
- Data Quality and Volume: AI models are only as good as the data they train on. Enterprises often struggle with vast quantities of low-quality, inconsistent, or duplicate data. “Garbage in, garbage out” applies here, as poor data quality will lead to inaccurate or irrelevant search results. The sheer volume also presents computational and storage challenges.
- Integration Complexity: Modern enterprises use a diverse ecosystem of applications and data silos. Integrating an AI search platform seamlessly across all these disparate sources—often with legacy systems—can be a complex and time-consuming engineering effort. APIs, connectors, and data transformation pipelines need to be robust and continuously maintained.
- Model Maintenance and Data Drift: AI models require continuous monitoring and retraining. Data within an enterprise is constantly changing; new terminology emerges, document structures evolve, and user behavior shifts. This “data drift” can degrade model performance over time if not addressed, requiring ongoing MLOps (Machine Learning Operations) practices to ensure models remain accurate and relevant.
- Bias and Fairness: AI models can inadvertently learn and perpetuate biases present in the training data, leading to unfair or discriminatory search results. Ensuring fairness, transparency, and explainability in search outcomes is an ethical and technical challenge.
- Security and Compliance: While Permissions and Access Control Syncing is critical, ensuring it’s flawless across all data sources, especially with sensitive information, is a major concern. Compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and industry-specific mandates adds layers of complexity to data handling and access auditing.
- User Adoption and Training: The shift from traditional keyword search to a more intelligent, conversational interface requires user education. Employees need to understand how to formulate effective queries for AI systems and trust the results provided.
- Cost and Resource Intensity: Developing, deploying, and maintaining AI-powered search platforms can be resource-intensive, requiring significant investment in infrastructure, specialized AI/ML talent, and ongoing operational costs.
Business Value and ROI of AI Enterprise Data Search
The successful implementation of AI Enterprise Data Search yields substantial business value and a compelling return on investment:
- Enhanced Productivity and Efficiency: Employees spend significantly less time searching for information (often cited as 20-30% of their workday). Rapid access to relevant data translates directly into higher productivity, allowing teams to focus on value-generating tasks rather than information retrieval.
- Faster, Data-Driven Decision-Making: With immediate access to comprehensive and accurate information, decision-makers can act more swiftly and with greater confidence. This agility is crucial in fast-paced markets, enabling quicker responses to competitive pressures or new opportunities.
- Improved Innovation: By breaking down information silos, AI search fosters a culture of knowledge sharing and collaboration. Researchers, developers, and product teams can easily discover existing insights, patents, and best practices across the organization, accelerating innovation cycles.
- Superior Customer Service: Customer support agents can quickly find answers to complex queries, product specifications, or troubleshooting guides, leading to faster resolution times and improved customer satisfaction.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Automating information retrieval reduces the need for manual data collation and improves efficiency across various departments, from legal and HR to R&D and sales, leading to tangible cost savings.
- Enhanced Compliance and Risk Management: A unified, searchable knowledge base with robust access controls makes it easier to track, audit, and manage sensitive information, aiding in regulatory compliance and mitigating risks associated with data breaches or information silos.
- Onboarding and Training Acceleration: New hires can quickly get up to speed by easily accessing company policies, procedures, and knowledge, reducing the time and resources required for onboarding.
Comparative Insight: AI Enterprise Data Search vs. Traditional Data Lakes/Warehouses
Understanding the distinct advantages of AI Enterprise Data Search requires a clear comparison with traditional data management paradigms like data lakes and data warehouses. While all aim to centralize and manage data, their primary objectives and retrieval mechanisms differ fundamentally.
Traditional Data Lakes and Data Warehouses:
- Data Warehouses: These are optimized for structured, pre-processed data, typically used for business intelligence (BI), reporting, and analytical queries. Data is transformed and loaded into a schema-on-write structure, making it highly organized but less flexible for diverse data types. Retrieval relies heavily on SQL queries and predefined reports.
- Data Lakes: Designed to store vast amounts of raw, unstructured, semi-structured, and structured data in its native format (“schema-on-read”). They offer greater flexibility for various analytical workloads, including big data processing and machine learning model training. However, retrieving specific information from a data lake without proper indexing and metadata management can be like finding a needle in a haystack. While they store the data, they don’t inherently provide sophisticated search capabilities for end-users beyond technical queries by data scientists or analysts.
Key Differences in Retrieval and Purpose:
- Retrieval Mechanism:
- Data Lakes/Warehouses: Primarily query-driven by technical users (analysts, data scientists) using structured languages (SQL) or specialized tools. They are designed for aggregation, reporting, and statistical analysis. Direct, intuitive search for natural language queries is not their strong suit.
- AI Enterprise Data Search: Designed for intuitive, natural language queries by *all* employees, regardless of technical expertise. It focuses on understanding intent and context to retrieve relevant documents, answers, or data snippets, often across heterogeneous data sources without requiring users to know database schemas or file structures.
- Data Scope and Unification:
- Data Lakes/Warehouses: While comprehensive for structured and semi-structured data, integrating deeply with unstructured content (e.g., PDFs, emails, chat logs) for seamless, cross-platform search remains a challenge. The focus is often on distinct datasets rather than a unified “knowledge graph” of the entire enterprise.
- AI Enterprise Data Search: Excels at unifying diverse data types—structured, semi-structured, and unstructured—from across the entire enterprise ecosystem. It creates a holistic, searchable index that transcends individual application boundaries, providing a single pane of glass for all corporate information.
- Intelligence and Contextual Understanding:
- Data Lakes/Warehouses: Offer minimal inherent intelligence in terms of understanding natural language intent. Users must phrase queries precisely to match data schemas or keywords.
- AI Enterprise Data Search: Leverages NLP, semantic search, vector embeddings, and RAG to understand the nuances of human language, infer user intent, and deliver highly contextual and semantically relevant results, even for vague or complex queries. It learns and improves over time.
- User Experience:
- Data Lakes/Warehouses: Often require specialized tools and technical skills to extract information, leading to bottlenecks and reliance on data teams.
- AI Enterprise Data Search: Provides a user-friendly, Google-like experience for employees, empowering them to self-serve their information needs quickly and efficiently.
- Active vs. Passive Information:
- Data Lakes/Warehouses: Primarily store passive data, waiting for explicit queries.
- AI Enterprise Data Search: Can proactively surface information, offer predictive insights, and even summarize complex documents, turning passive data into active knowledge.
In essence, while data lakes and data warehouses are excellent for storing and analyzing data, they are not designed for direct, intelligent, natural language-driven information retrieval by the broader enterprise workforce. AI Enterprise Data Search complements these data platforms by layering an intelligent search and discovery mechanism over them, transforming raw data into actionable knowledge accessible to everyone, all while strictly adhering to access controls and permissions.

World2Data Verdict: Embracing the Future of Knowledge Discovery
The journey towards a truly intelligent enterprise hinges on the ability to efficiently access and leverage its collective knowledge. World2Data believes that AI Enterprise Data Search is not merely an optional upgrade but a fundamental component of the modern digital workplace. Its ability to unify disparate data sources, understand natural language intent, and deliver contextualized answers represents a quantum leap beyond traditional retrieval methods. The move towards vector search and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), combined with robust data governance features like Permissions and Access Control Syncing, ensures not only powerful discovery but also secure and compliant information access. Enterprises that fail to adopt advanced AI search risk falling behind, hampered by information silos, declining productivity, and delayed decision-making.
Our recommendation for businesses of all sizes is to strategically invest in developing or integrating an AI Enterprise Data Search platform. Prioritize solutions that offer extensive data source connectors, advanced NLP capabilities, robust security models, and a clear roadmap for leveraging generative AI for summarization and contextual answering. Begin with a pilot project in a specific department to demonstrate tangible ROI, focusing on quick wins like customer support or internal knowledge management. Emphasizing continuous learning and MLOps practices will ensure the search system remains accurate and valuable as your data landscape evolves. The future of enterprise agility and innovation lies in democratizing information, making it instantly accessible and intelligently actionable for every employee, and AI Enterprise Data Search is the key to unlocking this potential.