AI Processing Unstructured Data: Unlocking Hidden Value and Strategic Insights
1. Platform Category: AI/ML Platform, Document Intelligence Platform
2. Core Technology/Architecture: Natural Language Processing (NLP), Computer Vision, Large Language Models (LLMs), Vector Databases
3. Key Data Governance Feature: Automated PII detection and redaction, Content-based data classification
4. Primary AI/ML Integration: Pre-trained models for entity recognition/classification, Custom model training capabilities
5. Main Competitors/Alternatives: Google Cloud AI, AWS AI Services (Textract, Comprehend), Databricks, Azure AI Services
AI Processing Unstructured Data is profoundly transforming how businesses unlock value and derive critical insights from their vast information reservoirs. The landscape of information is dominated by chaotic, human-generated content, and effective AI Unstructured Data Processing is the key to navigating this complexity. This critical capability enables organizations to move beyond rigid, structured datasets and embrace the rich, nuanced understanding hidden within everyday communications and media, translating raw data into actionable intelligence. By harnessing advanced AI, enterprises can now perceive patterns and extract meaning from sources previously considered intractable, revolutionizing decision-making.
Introduction: The Imperative of AI Unstructured Data Processing
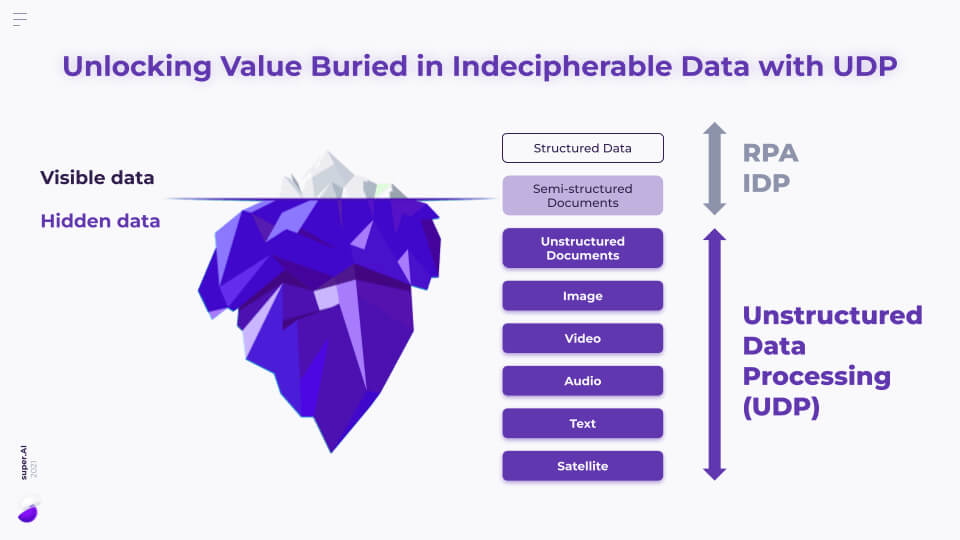
The inherent challenge of unorganized information demands advanced solutions for modern enterprises. Businesses today are awash in data, with estimates suggesting that 80-90% of all data generated is unstructured. This includes everything from customer emails, social media posts, support tickets, voice recordings, video files, PDFs, and legal documents. Enterprises face an overwhelming bottleneck in utilizing critical data locked within these disparate formats. Traditionally, extracting meaningful insights from such varied and complex data sources was a laborious, manual, and often error-prone process, severely limiting the scope of analysis and decision-making. Unlocking this hidden knowledge is paramount for competitive advantage, driving innovation, and achieving a deeper understanding of market dynamics, customer needs, and operational efficiencies.
The rise of artificial intelligence has provided the breakthrough needed to tackle this monumental challenge. AI Unstructured Data Processing capabilities empower comprehensive data transformation across all sectors. It’s no longer sufficient to merely store this data; the real value lies in the ability to process, interpret, and act upon it. This introduction sets the stage for a deep dive into the technologies, methodologies, and profound business benefits of effectively leveraging AI to turn the torrent of unstructured data into a strategic asset.
Core Breakdown: Architecture and Components of AI Unstructured Data Processing
Effective AI Unstructured Data Processing relies on a sophisticated interplay of cutting-edge technologies and robust architectural components. These systems are designed to ingest, analyze, interpret, and extract meaningful information from diverse unstructured data types, converting them into a format that can be easily queried and utilized by downstream applications and models.
Key Technologies Underpinning Unstructured Data Analysis:
-
Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP is at the heart of text-based unstructured data processing. It allows machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language. Key NLP techniques include:
- Entity Recognition: Identifying and classifying key information such as names, organizations, locations, and dates within text.
- Sentiment Analysis: Determining the emotional tone or sentiment expressed in a piece of text (positive, negative, neutral).
- Topic Modeling: Discovering abstract “topics” that occur in a collection of documents.
- Text Summarization: Condensing longer texts into shorter, coherent summaries.
- Language Translation: Converting text from one human language to another.
NLP specifically deciphers human language nuances, allowing machines to understand sentiment, context, and key entities from text, which is crucial for analyzing customer feedback, legal documents, and market research.
-
Computer Vision (CV): For visual unstructured data (images, videos), Computer Vision systems enable machines to “see” and interpret visual information. This involves:
- Object Detection and Recognition: Identifying and locating objects within images or video frames.
- Image Classification: Categorizing an entire image based on its content.
- Facial Recognition: Identifying or verifying individuals from digital images.
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR): Extracting text from images, making scanned documents searchable and editable.
Simultaneously, Computer Vision analyzes visual content, identifying patterns, objects, and relationships automatically without manual tagging, extending the reach of data analysis dramatically.
- Large Language Models (LLMs): Modern LLMs, such as those powering generative AI, have revolutionized unstructured data processing. These models are trained on vast corpora of text and can perform a wide range of tasks, including complex text generation, sophisticated summarization, question answering, and even code generation. Their ability to understand context and generate human-like responses makes them invaluable for extracting nuanced insights and automating content-related tasks.
- Vector Databases: A crucial component for managing and querying the embeddings generated by NLP, CV, and LLMs. When unstructured data is processed by these models, it’s often transformed into high-dimensional numerical representations (vectors or embeddings). Vector databases are optimized to store, index, and query these embeddings efficiently, enabling fast similarity searches, semantic retrieval, and contextual understanding. This allows applications to find similar documents, images, or concepts based on meaning rather than just keywords.
Key Enablers and Architectural Considerations:
- Machine Learning Algorithms and Deep Learning Networks: These form the foundational intelligence. Machine learning algorithms are trained on massive datasets to accurately categorize, extract key entities, and identify anomalies within complex unstructured content. Furthermore, deep learning networks enhance accuracy and provide sophisticated pattern recognition, crucial for predictive analysis and automating tasks that previously required extensive human effort. They are used for tasks like custom entity recognition, intent classification, and anomaly detection in unstructured streams.
- Data Labeling and Annotation Platforms: The efficacy of supervised machine learning models for unstructured data heavily relies on high-quality labeled data. Data labeling platforms are essential for annotating text (e.g., tagging entities, sentiments), images (e.g., bounding boxes for objects, segmentation masks), and audio (e.g., transcribing speech, identifying sounds). This human-in-the-loop process ensures that models are trained on accurate ground truth, allowing them to generalize and perform reliably on new, unseen data.
- Feature Stores: While commonly associated with structured data, Feature Stores play an increasingly vital role in AI Unstructured Data Processing. After features are extracted from unstructured data using NLP or CV (e.g., sentiment scores, entity counts, image tags, text embeddings), these processed features can be stored in a feature store. This enables reusability, consistency, and efficient serving of features to various AI models, preventing redundant processing and ensuring all models access the same, validated feature definitions.
Challenges and Barriers to Adoption:
Despite the immense potential, implementing robust AI Unstructured Data Processing solutions comes with significant hurdles:
- Data Variability and Complexity: Unstructured data is inherently messy and diverse. Variations in language, dialects, slang, image quality, document formats, and multimedia codecs pose significant challenges for model generalization and consistency. Handling sarcasm, irony, and nuanced context in text, or occlusions and differing lighting conditions in images, requires highly sophisticated models.
- Data Quality and Bias: The “garbage in, garbage out” principle applies even more critically here. Biases present in training data (e.g., historical documents reflecting societal prejudices) can be amplified by AI models, leading to discriminatory or inaccurate outcomes. Ensuring representative and unbiased training data is a continuous and complex task.
- Computational Resources: Training and deploying advanced NLP, CV, and LLM models require substantial computational power, including GPUs and TPUs, which can be costly and resource-intensive, especially for large datasets.
- Data Drift and Model Maintenance: Unstructured data environments are dynamic. Language evolves, new visual patterns emerge, and contextual meanings shift. This leads to “data drift,” where the characteristics of incoming data diverge from the data used for training, degrading model performance over time. Continuous monitoring, retraining, and MLOps strategies are crucial but complex to implement for these dynamic datasets.
- MLOps Complexity for Unstructured Data: Managing the entire lifecycle of AI models handling unstructured data is incredibly challenging. This includes versioning models, managing diverse feature pipelines (text embeddings, image features), orchestrating retraining workflows, and monitoring model performance on real-time unstructured inputs. The complexity escalates with the need to handle different data modalities and the often subjective nature of evaluation metrics.
- Data Governance and Privacy: Unstructured data often contains sensitive information (PII, confidential business data). Ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA, implementing automated PII detection and redaction, and maintaining content-based data classification are critical but complex aspects of data governance within unstructured datasets.
Business Value and ROI of AI Unstructured Data Processing:
The strategic advantages of mastering AI Unstructured Data Processing translate into tangible business value and significant ROI across various sectors:
- Improved Customer Experience: By analyzing customer feedback from social media, support tickets, emails, and call transcripts, businesses can gain deep insights into customer sentiment, pain points, and preferences. This leads to personalized experiences, proactive issue resolution, and more relevant product development. Automated chatbots powered by LLMs can provide instant, intelligent support, improving customer satisfaction and reducing operational costs.
- Enhanced Risk Assessment and Compliance: Analyzing legal documents, contracts, regulatory filings, and news articles with AI can identify potential risks, compliance breaches, and fraudulent activities much faster than manual reviews. Automated content-based data classification helps ensure sensitive information is handled according to regulations, reducing legal and financial exposure.
- Significant Operational Efficiencies: Automating tasks like document processing, data entry from scanned forms, email classification, and content moderation frees up human resources for higher-value activities. This leads to streamlined workflows, reduced manual errors, and substantial cost savings. For instance, invoice processing or claim handling can be accelerated from days to minutes.
- Faster Model Deployment and Better Data Quality for AI: By automating the extraction, transformation, and feature engineering from unstructured data, AI platforms can more rapidly generate high-quality datasets for training new models. This accelerates the entire AI development lifecycle, allowing businesses to deploy new AI capabilities much faster and respond to market changes with agility. The ability to consistently extract structured features from unstructured sources significantly improves the quality and breadth of data available for all AI/ML initiatives.
- Competitive Intelligence: Analyzing market reports, competitor websites, industry news, and social media discussions provides crucial insights into market trends, competitor strategies, and emerging opportunities, enabling businesses to make more informed strategic decisions.

Comparative Insight: AI Unstructured Data Processing vs. Traditional Methods
To fully appreciate the transformative power of AI Unstructured Data Processing, it’s essential to compare it with traditional approaches to handling chaotic data, including simple data lakes and manual processing methods. Historically, unstructured data was either ignored, manually reviewed at great expense, or stored in data lakes with minimal processing, often becoming a “data swamp.”
Traditional Data Lakes/Warehouses and Unstructured Data:
Traditional data lakes excel at storing vast quantities of raw data, including unstructured formats, at low cost. Data warehouses, on the other hand, are highly optimized for structured, transactional data. Neither, however, inherently possesses the capability to *understand* the content within unstructured files. A data lake might store millions of PDF documents, customer emails, or images, but without advanced processing, these remain inert. Retrieving information from them typically involves keyword searches (which miss context and synonyms) or labor-intensive manual reading.
The limitations of traditional approaches include:
- Lack of Semantic Understanding: Traditional systems can find keywords but cannot grasp the meaning, sentiment, or relationships between entities within text. They cannot interpret the content of an image or video beyond basic metadata.
- Scalability Bottleneck for Insights: While scalable for storage, traditional methods are not scalable for insight extraction from unstructured data. Manual review is slow and expensive; rule-based systems are brittle and require constant maintenance for evolving content.
- Limited Predictive Power: Without structured features extracted from the unstructured data, it’s difficult to feed this information into predictive models that require numerical inputs, severely limiting advanced analytics capabilities.
- High Cost of Human Labor: Relying on human analysts to sift through massive volumes of unstructured data for insights is prohibitively expensive, slow, and prone to human error and bias.
The AI Unstructured Data Processing Advantage:
In contrast, dedicated AI Unstructured Data Processing platforms and techniques fundamentally change this paradigm:
- Automated Semantic Extraction: AI, particularly NLP and LLMs, can automatically extract entities, themes, sentiments, and relationships from text with high accuracy and at scale. Computer Vision does the same for visual data, identifying objects, scenes, and actions. This transforms unstructured data into valuable, machine-readable structured features.
- Contextual Understanding: Advanced AI models move beyond keywords to understand the context and intent behind the data. This means identifying not just what words are present, but what they *mean* in a given situation, leading to far richer and more accurate insights. Vector databases play a key role here by enabling semantic search.
- Scalability and Speed: AI systems can process petabytes of unstructured data in fractions of the time it would take humans or traditional rule-based systems. This enables real-time insight generation and automation of tasks previously considered impossible to scale.
- Fueling Advanced Analytics and AI: By transforming unstructured data into structured features (e.g., sentiment scores, entity counts, topic probabilities, image embeddings), these platforms directly feed into other AI/ML models for predictive analytics, personalization, anomaly detection, and more. The feature store becomes a critical bridge.
- Enhanced Data Governance: AI can automate the identification and redaction of sensitive information (PII) within documents, emails, and images, and perform content-based classification to ensure data privacy and compliance far more effectively than manual methods.
- Iterative Improvement: Unlike static rule-based systems, AI models can continuously learn and improve from new data and feedback, adapting to evolving patterns and increasing their accuracy over time. This dynamic adaptability is crucial for handling the ever-changing nature of unstructured information.
In essence, while traditional data platforms provide the reservoir, AI Unstructured Data Processing provides the sophisticated filtration and purification system that extracts the pure, valuable essence from the raw input, making it potable for strategic consumption.

World2Data Verdict: The Future is Unstructured, Understood
The era of treating unstructured data as a secondary or intractable asset is definitively over. World2Data.com asserts that for any organization aspiring to genuine data-driven decision-making and competitive advantage, robust AI Unstructured Data Processing capabilities are no longer a luxury but a fundamental necessity. The complexity and volume of human-generated information will only continue to grow, making manual or rudimentary keyword-based approaches obsolete.
Our recommendation is clear: enterprises must prioritize investments in comprehensive AI platforms that integrate state-of-the-art NLP, Computer Vision, and Large Language Models, supported by efficient vector databases and MLOps practices tailored for multi-modal data. The focus should be on building scalable pipelines that not only extract but also contextualize and transform raw unstructured data into high-quality, reusable features within a managed feature store. Organizations that proactively embrace and master AI Unstructured Data Processing will be the ones best positioned to innovate, optimize operations, and deeply understand their customers and markets, securing a significant lead in the intelligence economy. The future of data belongs to those who can understand it all, regardless of its form.