Attribution Modeling Explained: Unlocking True Marketing Impact with Data Analytics
Attribution Modeling Explained: Tracking True Marketing Impact is essential for any modern marketer aiming to truly understand where their investment yields results. Effective attribution modeling helps businesses move beyond last-click assumptions to accurately measure the contribution of every touchpoint along the customer journey. This deeper insight allows for more informed decision-making and optimized marketing strategies, driving measurable improvements in ROI.
For World2Data.com, understanding the technical underpinnings and practical applications of sophisticated analytical tools like Attribution Modeling is paramount. Here’s a quick overview of its context within the data landscape:
- Platform Category: Marketing Analytics Platform
- Core Technology/Architecture: Multi-touchpoint Data Integration
- Key Data Governance Feature: Data Lineage for Marketing Data
- Primary AI/ML Integration: Algorithmic Attribution Modeling
- Main Competitors/Alternatives: Last-click attribution, First-click attribution, Linear attribution, Time Decay attribution, Position-based attribution (these are models, not competitors in the platform sense, but represent alternative approaches to credit assignment).
Introduction: Decoding the Customer Journey with Attribution Modeling
In today’s complex digital marketing landscape, customers interact with brands across numerous channels before making a purchase. From social media ads and search engine results to email campaigns and website visits, each touchpoint plays a role in influencing the final conversion. Without a robust system to assign appropriate credit to each of these interactions, marketers are left guessing, often overvaluing the last touch and overlooking critical early-stage engagements. This is where Attribution Modeling becomes indispensable. It is the analytical framework that allows businesses to move beyond simplistic views of customer behavior, providing a granular understanding of how different marketing efforts contribute to sales and conversions.
The objective of this deep dive is to demystify attribution modeling, exploring its diverse methodologies, technical requirements, and profound business implications. We will delve into how these models are constructed, the data challenges they address, and how they empower data-driven marketers to optimize their strategies for maximum impact. By accurately tracking the true influence of each marketing touchpoint, organizations can allocate budgets more effectively, personalize customer experiences, and ultimately achieve a superior return on their marketing investment. Understanding attribution modeling is not just about measuring; it’s about predicting, optimizing, and strategically shaping the customer journey.
Core Breakdown: The Architecture and Mechanics of Attribution Modeling
At its core, Attribution Modeling is a system for assigning credit to various marketing touchpoints that contribute to a conversion. This involves collecting, cleaning, and analyzing vast amounts of user interaction data across a multitude of channels. The complexity arises from the non-linear nature of customer journeys and the varying impact each touchpoint can have.
The technical foundation of a sophisticated attribution modeling system relies heavily on robust Multi-touchpoint Data Integration. This means seamlessly pulling data from diverse sources such as CRM systems, advertising platforms (Google Ads, Facebook Ads), email marketing tools, web analytics (Google Analytics), mobile app analytics, and offline data. A centralized data platform, often a data lake or data warehouse optimized for analytical workloads, is crucial for consolidating this disparate information into a unified customer view. Furthermore, maintaining high Data Lineage for Marketing Data is essential, ensuring transparency and trustworthiness in how data flows from source to attribution model, critical for auditability and compliance.
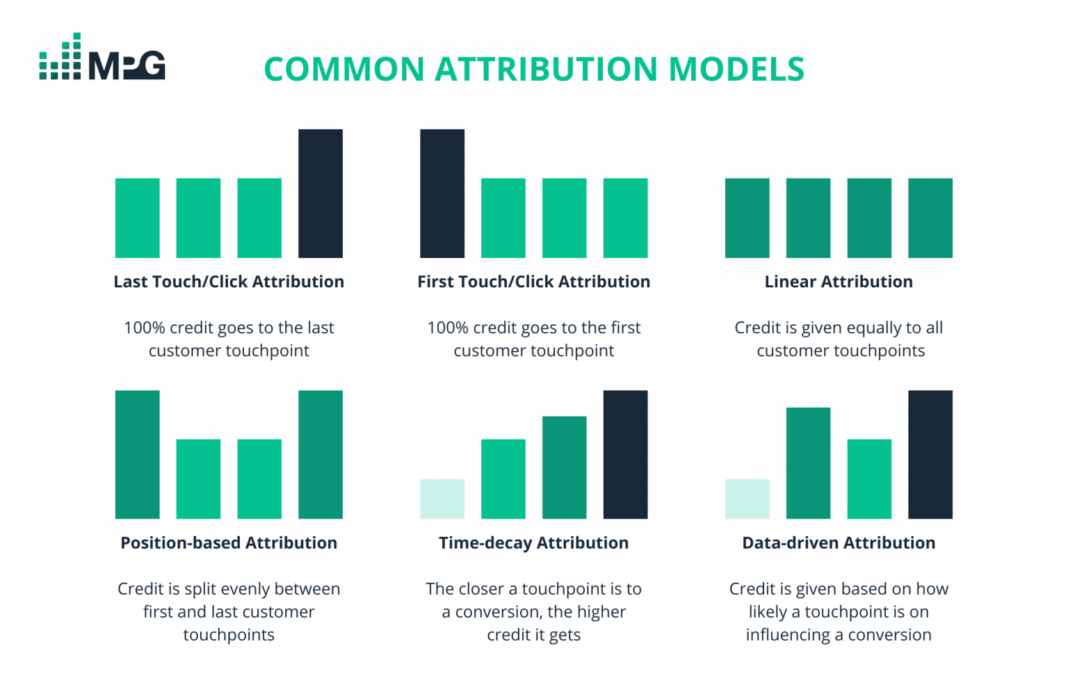
Various models exist, each with its own methodology:
- Single-Touch Models: These are the simplest.
- First-Click Attribution: Assigns 100% of the credit to the very first marketing touchpoint a customer had. Good for understanding initial awareness.
- Last-Click Attribution: Assigns 100% of the credit to the final touchpoint immediately preceding the conversion. Easy to implement but often misrepresents the full journey.
- Multi-Touch Models: These distribute credit across multiple touchpoints.
- Linear Attribution: Divides credit equally among all touchpoints in the customer journey. Provides a balanced view but might not reflect actual impact.
- Time Decay Attribution: Gives more credit to touchpoints that occurred closer in time to the conversion. Useful for shorter sales cycles.
- Position-Based (U-shaped/Bathtub) Attribution: Assigns more credit to the first and last touchpoints (e.g., 40% each), with the remaining credit (20%) distributed equally among middle touchpoints. Valuables for both awareness and conversion drivers.
- W-Shaped Attribution: Similar to position-based but also assigns significant credit to a “middle” touchpoint, often defined as the point of initial engagement or lead creation.
- Algorithmic/Data-Driven Models: These represent the cutting edge.
- Algorithmic Attribution Modeling: Leverages advanced statistical methods and machine learning algorithms (e.g., Markov Chains, Shapley Values, Logistic Regression) to dynamically assign credit based on actual historical data and the probability of conversion. These models analyze paths that lead to conversion versus those that don’t, identifying true causal relationships. This is where AI Data Platform capabilities become highly relevant, providing the computational power and analytical tools necessary for complex model development and deployment.
Challenges and Barriers to Adoption in Advanced Attribution Modeling
Despite its immense potential, implementing and maintaining sophisticated attribution modeling, especially Algorithmic Attribution Modeling, is not without its hurdles. One of the most significant challenges is Data Fragmentation. Marketing data often resides in silos across various platforms, making a unified view difficult to achieve. Integrating these disparate data sources effectively requires robust engineering efforts and a clear data strategy.
Another critical barrier is Data Quality for AI. Poor data quality – inconsistent formatting, missing values, duplicates, or inaccurate tracking – can severely compromise the reliability of any attribution model. Ensuring clean, accurate, and consistent data requires continuous monitoring, validation, and governance processes. The ephemeral nature of user identifiers, particularly with the deprecation of third-party cookies, further complicates cross-device and cross-platform tracking, making it harder to stitch together a complete customer journey.
The complexity of model selection and validation is also a major challenge. Choosing the right model depends on the business objectives, industry, and typical customer journey length. Furthermore, models need to be regularly re-evaluated and recalibrated due to Data Drift – changes in customer behavior, market conditions, or campaign strategies. Without continuous monitoring and adaptation, models can quickly become outdated and misleading.
Finally, the operationalization of advanced algorithmic models introduces MLOps Complexity. While not directly “MLOps” in the traditional sense of deploying AI models, the principles apply: managing the lifecycle of attribution models, from experimentation and deployment to monitoring and retraining, requires specialized skills and infrastructure. This includes version control for models, automated data pipelines, performance monitoring, and rapid iteration capabilities – all of which can be resource-intensive for organizations without a mature data science or AI Data Platform capability.
Business Value and ROI of Advanced Attribution Modeling
The investment in advanced Attribution Modeling yields substantial business value and a significant return on investment. Foremost, it enables truly Precise Budget Allocation. By understanding which channels and campaigns are genuinely driving conversions, marketers can shift spending from underperforming areas to high-impact ones, ensuring every dollar spent contributes optimally to revenue goals. This moves beyond traditional guesswork, leading to a demonstrable increase in marketing efficiency and effectiveness.
Moreover, sophisticated attribution provides unparalleled insights into the customer journey, facilitating Optimized Customer Journeys and enhanced personalization. Marketers can identify key touchpoints, understand customer behavior patterns, and tailor messaging and offers at each stage. This leads to more relevant and engaging experiences, reducing churn and improving conversion rates.
For data-driven organizations, Attribution Modeling improves Data Quality for AI initiatives. The meticulous collection and integration of multi-touchpoint data, necessary for accurate attribution, creates a richer, cleaner dataset that can then be leveraged for other AI and machine learning applications, such as customer lifetime value prediction or churn forecasting. Furthermore, with Algorithmic Attribution Modeling, there’s a push towards Faster Model Deployment for analytical insights, allowing businesses to react quickly to market changes and refine campaigns in real-time.
Ultimately, the main benefit is a clear, quantifiable understanding of marketing ROI. Businesses can move away from siloed reporting and embrace a holistic view of performance, justifying marketing spend with confidence and strategically planning for future growth based on data, not assumptions.

Comparative Insight: Attribution Modeling vs. Traditional Data Approaches
To truly appreciate the power of advanced Attribution Modeling, it’s beneficial to compare it against more traditional data management and analysis approaches, such as standalone data lakes or data warehouses, without a specific attribution layer. While traditional data infrastructures are excellent for storing, processing, and reporting large volumes of data, they often lack the inherent mechanisms and methodologies for sophisticated marketing attribution.
A typical data lake, for instance, serves as a vast repository for raw, unstructured, and semi-structured data. It can store all the individual touchpoint data from various marketing channels. However, merely having the data doesn’t equate to attribution. Without a dedicated framework for Multi-touchpoint Data Integration, data points remain disconnected. A traditional data warehouse, while structured for analytical queries, might aggregate data in ways that obscure individual customer journeys, especially if designed for top-level financial or operational reporting rather than granular marketing insights.
The key differentiator for Attribution Modeling is its focus on the sequence and interplay of interactions. Traditional reporting often relies on channel-specific metrics (e.g., clicks from Google Ads, opens from email campaigns) or last-touch conversions, which credit only the final interaction. This leads to fragmented insights, where the true cross-channel impact of marketing efforts is obscured. Marketing teams might see a channel performing well on a last-click basis, but fail to recognize its crucial role in an earlier stage of the funnel.
Advanced Algorithmic Attribution Modeling, on the other hand, actively builds the customer journey by stitching together touchpoints from disparate sources, often requiring significant data engineering to achieve true Data Lineage for Marketing Data. It then applies sophisticated algorithms to calculate the marginal contribution of each touchpoint. This shifts the paradigm from simple data storage and retrieval to predictive analytics and causal inference. Where a data warehouse might tell you “how many conversions came from PPC last month,” an attribution model can tell you “how much did PPC contribute to conversions when it was the first touch, compared to when it was a middle touch, or the final touch, alongside other channels.”
Furthermore, traditional systems often struggle with the dynamic nature of marketing. Customer journeys are not static; they evolve with new technologies, consumer behaviors, and market trends. An effective Attribution Modeling platform is designed to be agile, capable of incorporating new data sources, adapting to changing tracking methods (e.g., cookieless solutions), and recalibrating models to reflect current realities. This contrasts sharply with static reporting dashboards or traditional business intelligence tools that may require significant manual effort to update or reconfigure for new analytical challenges. In essence, while traditional data platforms provide the raw materials, Attribution Modeling provides the sophisticated architectural blueprint and the construction tools to build a comprehensive, intelligent understanding of marketing performance.

World2Data Verdict: The Imperative of Algorithmic Attribution
The landscape of digital marketing is irrevocably moving towards a data-first approach, and within this shift, Attribution Modeling stands as a non-negotiable component for competitive advantage. World2Data.com asserts that while foundational models (like last-click) offer a starting point, true market leaders will differentiate themselves through the adoption of advanced, Algorithmic Attribution Modeling. The future of marketing impact measurement lies in leveraging the full potential of a robust AI Data Platform capable of handling complex Multi-touchpoint Data Integration and ensuring impeccable Data Lineage for Marketing Data.
Our recommendation is clear: businesses must move beyond simplistic methodologies and embrace the complexities inherent in modern customer journeys. This necessitates not just the technology for sophisticated modeling but also the organizational commitment to data governance, continuous model validation, and iterative refinement. Organizations should prioritize building or investing in capabilities that support automated data pipelines, facilitate the integration of diverse marketing data, and empower data scientists to develop and deploy custom, data-driven attribution models. This includes focusing on addressing challenges like cross-device tracking and preparing for a cookieless future by investing in first-party data strategies.
The ultimate goal of attribution modeling is not just to measure, but to predict and optimize. By continuously refining these models, businesses can proactively steer their marketing investments, uncover hidden opportunities, and foster deeper, more profitable customer relationships. The return on investment for mastering attribution modeling will be seen not just in improved campaign performance, but in a holistic transformation towards a truly intelligent, data-driven marketing organization that can adapt and thrive in an ever-evolving digital world.