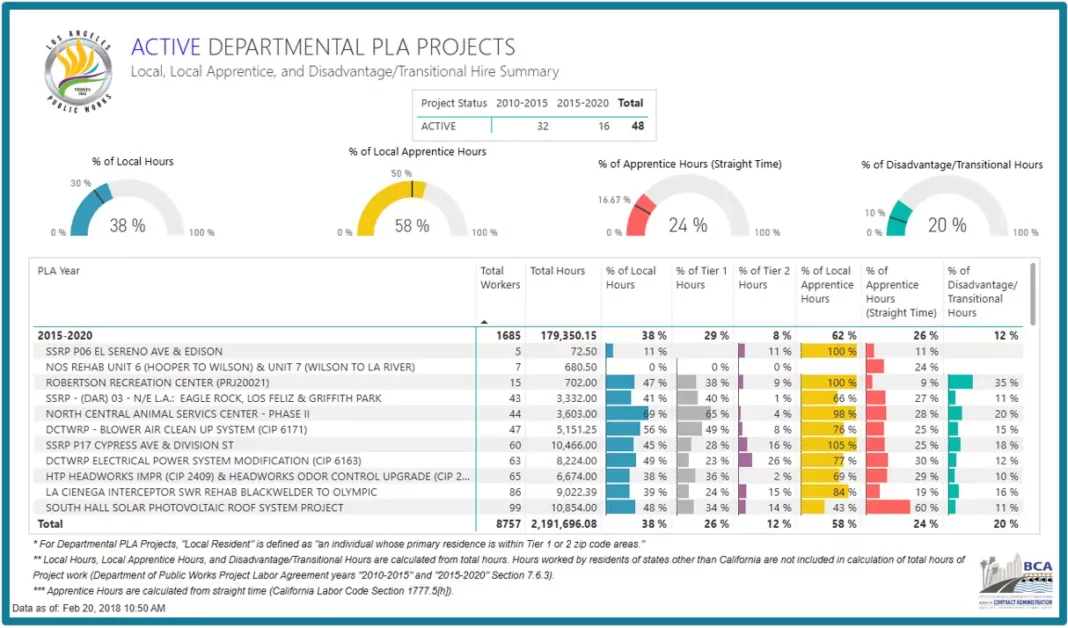
BI Dashboard Case Study: Transforming Data Chaos into Actionable Business Insights
Platform Category: BI & Data Visualization Platform
Core Technology/Architecture: Self-Service Analytics
Key Data Governance Feature: Role-Based Access Control
Primary AI/ML Integration: Natural Language Query (NLQ)
Main Competitors/Alternatives: Tableau, Microsoft Power BI, Looker, Qlik
The digital age has brought an unprecedented deluge of data, often leaving organizations struggling to extract meaningful intelligence from the noise. This in-depth BI Dashboard Case Study delves into how modern enterprises are conquering this challenge, leveraging sophisticated Business Intelligence (BI) platforms to transform sprawling datasets into coherent, actionable insights. Moving beyond mere data aggregation, this analysis showcases the strategic shift from reactive reporting to proactive, data-driven decision-making, emphasizing the profound impact of well-implemented BI solutions.
Introduction: Bridging the Gap Between Data Overload and Strategic Decision-Making
In today’s hyper-competitive landscape, the ability to make rapid, informed decisions is paramount. Yet, many businesses find themselves drowning in data, grappling with disconnected systems, manual reporting processes, and a severe lack of real-time visibility. The consequence is often delayed strategic responses, missed opportunities, and an inability to accurately gauge performance. This is where the power of a comprehensive BI Dashboard Case Study becomes evident. It highlights how integrating diverse data sources into a centralized, interactive dashboard environment empowers stakeholders at all levels to access critical information instantly, fostering a culture of informed action rather than guesswork. Our objective is to meticulously examine the journey from data chaos to clarity, illustrating the technical underpinnings, strategic implementations, and tangible business benefits that define successful BI deployments.
Core Breakdown: The Architecture of Actionable Intelligence
A robust BI dashboard ecosystem is far more than just a collection of charts; it represents a sophisticated architectural framework designed to ingest, process, analyze, and visualize data in a meaningful way. At its heart lies the principle of Self-Service Analytics, enabling business users to explore data independently without constant reliance on IT departments.
Key Components and Technical Analysis:
- Data Sources and Integration: Modern BI platforms must seamlessly connect to a myriad of data sources, including operational databases (SQL, NoSQL), enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, marketing automation tools, cloud storage (data lakes), and external APIs. Efficient Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) or Extract, Load, Transform (ELT) processes are critical to consolidate and cleanse this disparate data.
- Data Warehousing/Data Marts: Transformed data is typically stored in optimized data warehouses or smaller, subject-oriented data marts. These structures are designed for analytical querying, ensuring high performance for complex aggregations and historical trend analysis.
- BI Platform Core: Solutions like Tableau, Microsoft Power BI, Looker, and Qlik provide the engine for data modeling, calculation, and visualization. They offer robust data connectors, in-memory processing capabilities for speed, and powerful analytical functions.
- Visualization Layer: This is the user-facing component, translating complex datasets into intuitive, interactive dashboards. Key elements include various chart types (bar, line, pie, scatter, geographical maps), filters, drill-down capabilities, and pivot tables. The goal is to make complex information digestible and discoverable.
- AI/ML Integration – Natural Language Query (NLQ): A significant advancement, NLQ allows users to ask questions in plain language (e.g., “Show me sales performance by region last quarter”) and receive visual answers. This lowers the barrier to entry for non-technical users, making data exploration more accessible and conversational.
- Data Governance – Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Essential for security and compliance, RBAC ensures that users only see the data they are authorized to access. This protects sensitive information, maintains data integrity, and supports regulatory requirements by controlling access at various levels (dashboard, report, row-level data).
Challenges and Barriers to Adoption: Navigating the Implementation Minefield
Despite the clear advantages, implementing a successful BI dashboard solution is not without its hurdles. Organizations frequently encounter several significant barriers:
- Data Silos and Integration Complexity: Often, data resides in fragmented systems across different departments, each with its own format and governance rules. Integrating these disparate sources into a unified view requires significant effort, technical expertise, and a clear data architecture strategy.
- Data Quality and Trust: “Garbage in, garbage out” remains a fundamental truth. Inconsistent, incomplete, or inaccurate data can erode user trust in the dashboards, leading to underutilization and poor decision-making. Robust data cleansing, validation, and master data management processes are critical.
- User Adoption and Training: While BI tools are increasingly user-friendly, overcoming resistance to change and ensuring widespread adoption requires comprehensive training and continuous support. Users need to understand not just how to use the tools, but also how to interpret the data and apply insights to their daily tasks.
- Cost and ROI Justification: The initial investment in BI software, infrastructure, and skilled personnel can be substantial. Demonstrating a clear return on investment (ROI) and securing sustained funding requires careful planning and measurable outcomes.
- Data Security and Privacy: As more data becomes centralized and accessible, ensuring its security and compliance with privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) becomes paramount. Mismanagement can lead to data breaches, legal penalties, and reputational damage.
Business Value and ROI: The Transformative Impact of Data-Driven Insights
When successfully implemented, BI dashboards deliver profound and measurable business value, significantly contributing to the organization’s bottom line and strategic agility.
- Enhanced Decision-Making Speed and Accuracy: Real-time dashboards provide instant access to key performance indicators (KPIs) and operational metrics, allowing leaders to make faster, more informed decisions based on current data rather than outdated reports or intuition. This agility can be a critical competitive differentiator.
- Operational Efficiency and Cost Reduction: By identifying bottlenecks, optimizing resource allocation, and streamlining workflows, BI dashboards can lead to significant operational efficiencies. For example, supply chain dashboards can reduce inventory costs, while marketing dashboards can optimize campaign spend.
- Improved Customer Experience and Retention: Analyzing customer behavior data through BI dashboards can reveal preferences, pain points, and churn risks. This enables businesses to personalize offerings, proactively address issues, and enhance overall customer satisfaction, leading to increased loyalty and retention.
- Competitive Advantage through Predictive Insights: Beyond descriptive and diagnostic analytics, advanced BI platforms, especially those integrating AI/ML, can offer predictive capabilities. Foreseeing market trends, customer demands, or potential risks allows businesses to stay ahead of the curve and innovate strategically.
- Measurable ROI via Performance Tracking: The direct impact on sales, marketing effectiveness, operational costs, and customer lifetime value can be quantified. This robust tracking not only justifies the initial investment but also provides a continuous feedback loop for strategic refinement.

Comparative Insight: BI Dashboards vs. Traditional Data Lakes & Static Reporting
Understanding the true value of a modern BI dashboard implementation requires a comparison with older paradigms of data management and reporting. Traditionally, organizations relied on basic reporting tools, spreadsheets, and often, massive data lakes or data warehouses that served primarily as repositories rather than active insight generators.
The Limitations of Traditional Approaches:
- Data Lakes/Warehouses as Raw Repositories: While crucial for storing vast amounts of structured and unstructured data, traditional data lakes and warehouses, in isolation, do not provide immediate insights. They are backend infrastructures that require specialized data engineers and analysts to query and extract information, leading to bottlenecks and delays.
- Static Reports and Spreadsheets: Prior to advanced BI, business users often received static PDF reports or complex Excel spreadsheets. These reports were typically outdated by the time they reached decision-makers, lacked interactivity, and offered limited drill-down capabilities. They answered “what happened” but rarely “why” or “what to do next.”
- Lack of Real-time Visibility: Updates to traditional reports could take hours, days, or even weeks. In fast-moving markets, this delay means decisions are made on stale data, leading to missed opportunities or misguided strategies.
- Limited Accessibility and Self-Service: Access to data insights was often restricted to a few technical users who could write complex queries. This created a significant dependency and prevented broader organizational engagement with data.
The Transformative Power of BI Dashboards:
A modern BI Dashboard Case Study demonstrates a clear departure from these limitations, offering:
- Interactive and Dynamic Visualization: Dashboards transform raw data into intuitive charts, graphs, and maps that users can interact with. They can filter, sort, drill down into specifics, and explore different dimensions of data on the fly, moving from high-level overviews to granular details effortlessly. This enhances `Data Visualization` considerably.
- Real-time or Near Real-time Reporting: With efficient data pipelines and in-memory processing, BI dashboards provide up-to-the-minute information, enabling proactive responses to changing market conditions or operational incidents. This ensures `Real-time Reporting` for critical metrics.
- Empowered Self-Service Analytics: As discussed, the core technology of `Self-Service Analytics` allows non-technical users to independently answer their own business questions. This democratizes data access, reduces reliance on IT, and speeds up the insight generation process across the enterprise.
- From Descriptive to Prescriptive: While traditional methods focused on ‘what happened’, BI dashboards, especially with integrated `AI/ML` capabilities like `Natural Language Query`, push towards ‘why it happened’ (diagnostic) and even ‘what should happen’ (prescriptive analytics). This provides genuinely `Actionable Insights` for strategic planning.
- Centralized and Unified View: By aggregating data from diverse sources, dashboards provide a single source of truth, eliminating discrepancies and fostering a consistent understanding of performance across departments.
In essence, while data lakes and warehouses provide the necessary foundation for storing and managing data, BI dashboards act as the crucial layer that unlocks the data’s potential, making it accessible, understandable, and directly applicable for driving `Business Intelligence` and `Data-Driven Decision Making` at every level of an organization. They bridge the critical gap between raw data assets and strategic business outcomes.
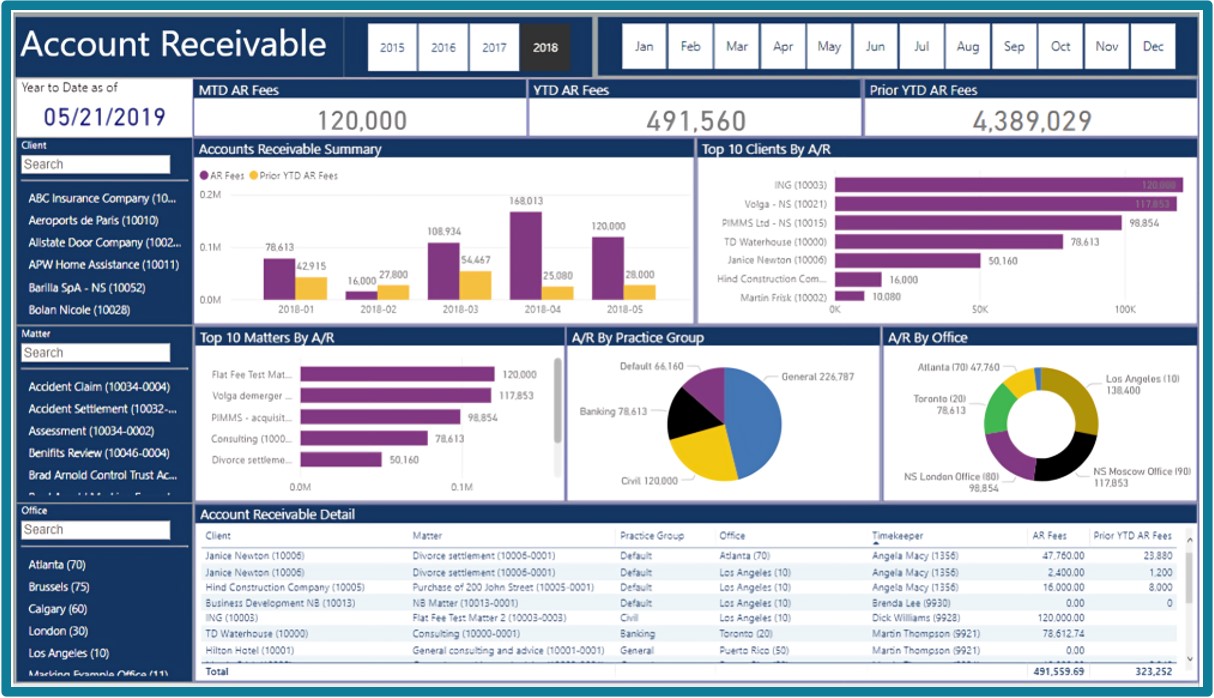
World2Data Verdict: The Future is Interactive, Intelligent, and Integrated
The findings from this comprehensive BI Dashboard Case Study unequivocally demonstrate that Business Intelligence dashboards are no longer a luxury but a fundamental necessity for competitive enterprises. World2Data.com asserts that the future of data platforms lies in increasingly intuitive, AI-augmented, and deeply integrated analytics solutions. Organizations must move beyond the passive consumption of reports towards active, dynamic engagement with their data, fostering a truly `Data-Driven Culture`. The next wave of innovation will see further advancements in predictive analytics, automated insight generation, and embedded BI directly within operational applications, making data intelligence an invisible, yet omnipresent, part of every business process. Companies that commit to continuous evolution of their BI capabilities, leveraging advanced features like `Natural Language Query` and robust `Role-Based Access Control`, will be those that not only survive but thrive, consistently turning vast data chaos into precise, `Actionable Insights` and sustainable growth. The imperative is clear: embrace the interactive intelligence of modern BI to secure a proactive and profitable future.