Data Accuracy: The Cornerstone of Reliable Information for Strategic Decision Making
In today’s fast-paced, data-driven world, the reliability of information is not just a preference, but a fundamental requirement. Data Accuracy stands as the linchpin, determining the efficacy and trustworthiness of every insight and strategic choice an organization makes. This article from World2Data.com delves into the critical importance of achieving and maintaining high Data Accuracy, exploring its technical underpinnings, the challenges involved, and the profound business value it unlocks. Without a robust commitment to Data Accuracy, even the most sophisticated analytics platforms risk delivering flawed conclusions, leading to costly missteps and eroding stakeholder trust.
- Platform Category: Data Quality Platform
- Core Technology/Architecture: Data Profiling, Data Validation Engines, Data Cleansing, Data Lineage
- Key Data Governance Feature: Data Quality Rules Management, Data Stewardship Workflows, Metadata Management
- Primary AI/ML Integration: Automated Anomaly Detection, Predictive Data Quality, Smart Data Matching
- Main Competitors/Alternatives: Informatica Data Quality, Talend Data Quality, IBM InfoSphere QualityStage, Collibra Data Quality & Governance
Introduction: Why Data Accuracy is Non-Negotiable for Modern Enterprises
The digital transformation sweeping across industries has elevated data from a mere byproduct of operations to an invaluable strategic asset. Yet, the true value of this asset is entirely contingent upon its quality, with Data Accuracy being the paramount dimension. Simply put, inaccurate data leads to inaccurate insights, which inevitably lead to poor decisions. Whether it’s optimizing supply chains, personalizing customer experiences, detecting fraud, or forecasting market trends, the integrity of the underlying data dictates the success or failure of these initiatives. Ensuring Data Accuracy is no longer a peripheral IT concern; it is a core business imperative, directly impacting an organization’s profitability, reputation, and competitive edge.
Modern enterprises are awash in oceans of data, generated from myriad sources at unprecedented velocities. This abundance presents both immense opportunity and significant challenges. Without a dedicated focus on Data Accuracy, organizations risk making decisions based on incomplete, outdated, or erroneous information. This deep dive will explore how dedicated Data Quality Platforms, equipped with advanced technologies and integrated with robust governance frameworks, empower businesses to achieve and sustain the high levels of Data Accuracy required to navigate complex markets and make reliably informed strategic decisions.
Core Breakdown: Architecting for Pristine Data Accuracy
Achieving and maintaining Data Accuracy at scale requires a sophisticated blend of technology, process, and people. A comprehensive Data Quality Platform serves as the central nervous system for this endeavor, integrating various components to ensure data trustworthiness throughout its lifecycle.
The Pillars of Data Quality Platforms
- Data Profiling: This is the foundational step, involving the systematic examination of data from various sources to collect statistics and information about its quality. Data Profiling helps organizations understand the characteristics, patterns, and anomalies within their datasets. By revealing unique values, missing percentages, data types, and potential inconsistencies, it provides a crucial baseline for establishing data quality rules and identifying areas needing immediate attention for Data Accuracy improvement. It acts like a diagnostic tool, providing a holistic view of data health.
- Data Validation Engines: These are critical for preventing inaccuracies at the point of entry and ensuring consistency across systems. Validation engines enforce predefined business rules and constraints (e.g., format checks, range checks, referential integrity, cross-field validation) on data as it is captured or transformed. By rejecting or flagging non-compliant data in real-time, they act as gatekeepers, significantly bolstering Data Accuracy and reducing the downstream effort required for cleansing.
-
Data Cleansing: Once inaccuracies are identified, Data Cleansing processes step in to correct, standardize, and enrich the data. This involves a suite of techniques such as:
- Deduplication: Identifying and merging redundant records to create a single, accurate view of entities (e.g., customers, products).
- Standardization: Bringing data into a consistent format (e.g., addresses, names, dates).
- Imputation: Filling in missing values using statistical methods or business rules.
- Transformation: Converting data from one format or structure to another to ensure consistency and usability.
Effective data cleansing is vital for rehabilitating existing datasets and making them suitable for reliable analysis and decision-making.
- Data Lineage: Understanding the origin, journey, and transformations a piece of data undergoes is crucial for building trust and ensuring auditability. Data Lineage tools map out the complete path of data from its source to its destination, including all intermediate systems, transformations, and quality checks. This transparency is indispensable for debugging issues, proving compliance, and validating the trustworthiness and Data Accuracy of derived insights.
Data Governance for Enduring Accuracy
Technology alone cannot sustain Data Accuracy. It must be underpinned by robust data governance frameworks that define policies, roles, and processes.
- Data Quality Rules Management: This involves the centralized definition, maintenance, and application of business rules that govern data quality. These rules specify what constitutes “good” data and are essential for automated validation and monitoring efforts.
- Data Stewardship Workflows: Data stewards are individuals or teams responsible for the quality of specific datasets. Data stewardship workflows provide structured processes for identifying, investigating, and resolving data quality issues, ensuring accountability and timely remediation.
- Metadata Management: Comprehensive metadata—data about data—provides context, meaning, and definitions. It describes data sources, transformations, ownership, and quality metrics, making it easier for users to understand and trust the Data Accuracy of the information they are working with.
Leveraging AI/ML for Proactive Data Accuracy
The integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning is revolutionizing how organizations approach Data Accuracy, moving from reactive fixes to proactive and predictive management.
- Automated Anomaly Detection: ML algorithms can learn normal data patterns and automatically flag outliers or anomalies that indicate potential data quality issues. This significantly reduces the manual effort required to identify errors and allows for much faster remediation.
- Predictive Data Quality: By analyzing historical data quality trends and operational patterns, AI can predict where and when data quality issues are likely to arise. This enables organizations to implement preventative measures, addressing potential inaccuracies before they impact critical business processes.
- Smart Data Matching: Advanced ML models enhance deduplication and record linking by using fuzzy matching, natural language processing, and entity resolution techniques. This goes beyond simple exact matches to identify and consolidate records that are subtly different but refer to the same entity, greatly improving Data Accuracy in customer and product master data.
Navigating the Minefield: Challenges to Sustained Data Accuracy
Despite the clear benefits, maintaining high Data Accuracy is fraught with challenges, often stemming from the very nature of modern data ecosystems.
- Data Volume, Velocity, and Variety (the 3 Vs): The sheer scale, speed of generation, and diverse formats of data make manual quality control virtually impossible. Each new data source introduces new potential points of failure and complexity in maintaining Data Accuracy.
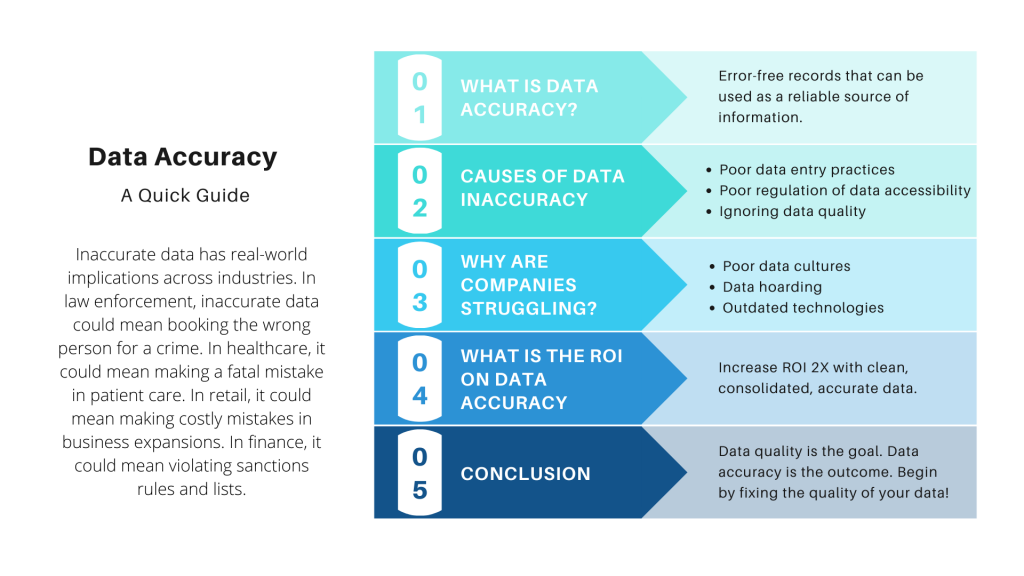
- Data Silos and Integration Complexity: Organizations often have data fragmented across numerous legacy systems, cloud applications, and external sources. Integrating these disparate systems without introducing inconsistencies or errors is a significant hurdle. Data silos prevent a unified view and make it challenging to apply consistent data quality rules.
- Human Error: Manual data entry, incorrect data transformations, or simple oversight remains a pervasive source of inaccuracies. Even with automated systems, human intervention in defining rules or overriding validations can introduce errors.
- Evolving Business Rules and Data Schemas: Business requirements, regulatory landscapes, and underlying data structures are constantly changing. Data quality rules and validation logic must continuously adapt to these changes, or they quickly become outdated, leading to a decline in Data Accuracy.
- Lack of Organizational Data Culture: Without a company-wide commitment to data integrity, where every employee understands their role in contributing to or maintaining Data Accuracy, even the best technological solutions will struggle. This often manifests as a lack of investment in data literacy and stewardship.
The Tangible Rewards: Business Value and ROI of High Data Accuracy
The investment in Data Accuracy yields substantial returns, translating directly into enhanced business performance and a stronger competitive stance.
- Improved Decision-Making Confidence: When data is accurate, leaders can trust the insights derived from it, enabling faster, more agile, and more effective strategic decisions with a higher probability of success.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: Accurate data reduces rework, eliminates errors in processes (e.g., billing, logistics), and streamlines operations, leading to significant cost savings and increased productivity.
- Superior Customer Experiences: With accurate customer data, organizations can deliver personalized marketing, relevant product recommendations, and efficient customer service, fostering loyalty and driving revenue. Inaccurate data, conversely, leads to frustrating experiences and churn.
- Reduced Compliance and Regulatory Risks: Many industries face strict data quality requirements for regulatory compliance (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, financial reporting). High Data Accuracy minimizes the risk of non-compliance fines, legal repercussions, and reputational damage.
- Better Resource Allocation: Reliable data allows for more precise forecasting and planning, ensuring that resources (human, financial, material) are allocated optimally, preventing waste and maximizing impact.
Comparative Insight: Beyond Storage – Why Dedicated Data Quality Platforms Outperform Generic Solutions
Many organizations mistakenly believe that investing in a robust data lake or data warehouse is sufficient to address their data needs, including quality. While these platforms are crucial for data storage, integration, and analytics, they are primarily designed for collection and access, not inherently for guaranteeing Data Accuracy. A data lake, for instance, is excellent for storing raw, varied data, often without a predefined schema. This “store everything” approach is powerful for flexibility but means that “garbage in” can indeed lead to “garbage out” if not followed by rigorous data quality processes.
Similarly, data warehouses, while offering structured and aggregated data, still depend heavily on the quality of the source data fed into them. If the ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes are not meticulously engineered with Data Accuracy in mind, or if source data is inherently flawed, the warehouse will simply perpetuate these inaccuracies. Neither a data lake nor a data warehouse inherently possesses the sophisticated profiling, validation, cleansing, and lineage capabilities that are the bread and butter of a dedicated Data Quality Platform.
A specialized Data Quality Platform, on the other hand, is purpose-built to tackle the complexities of data integrity head-on. It provides a proactive layer that ingests data from various sources and subjects it to a battery of checks and transformations *before* it lands in a data lake, data warehouse, or operational system. This ensures that the data available for analytics and decision-making is consistently accurate, complete, and reliable. These platforms complement generic storage solutions by feeding them high-quality data, thereby maximizing the return on investment in data infrastructure. They shift the paradigm from reactive data cleaning to proactive quality assurance, integrating deeply into the data pipeline to instill Data Accuracy at every stage.
World2Data Verdict: Your Data Accuracy Imperative
In the data-saturated economy, Data Accuracy is not merely a desirable trait; it is the bedrock of competitive advantage and sustainable growth. Organizations that view data quality as an afterthought, or solely as a technical task, do so at their peril. The future belongs to those who recognize Data Accuracy as a strategic investment, driving everything from operational efficiency and customer satisfaction to regulatory compliance and innovation. World2Data.com asserts that embracing a dedicated Data Quality Platform, integrated with a strong data governance framework and empowered by AI/ML capabilities, is no longer optional but essential. Proactively ensuring the reliability of your information flow will transform your decision-making processes, mitigate risks, and solidify your position as a trusted, data-driven leader.




