Data Auditing: Ensuring Transparency and Accountability in Modern Enterprises
Platform Category: Data Governance Platform, Data Security Solution, Compliance Management Software
Core Technology/Architecture: Immutable transaction logs, Centralized logging, Cryptographic data integrity, Event streaming
Key Data Governance Feature: Detailed logging of data access and modifications, Immutable audit trails, Data lineage tracking, Role-based access control logging, Compliance reporting
Primary AI/ML Integration: Anomaly detection for unusual data access or modification patterns, Automated policy compliance validation, Predictive risk assessment for potential breaches
Main Competitors/Alternatives: Data Governance Suites (e.g., Collibra, Informatica Axon), Data Security Platforms (e.g., Varonis, Imperva), GRC Software (e.g., ServiceNow GRC), SIEM Tools (e.g., Splunk, Microsoft Sentinel)
Data Auditing: Ensuring Transparency and Accountability is no longer a luxury but a fundamental necessity for any organization navigating today’s complex digital landscape. A thorough data audit provides the critical insight needed to maintain integrity and build stakeholder trust. This essential practice rigorously examines an organization’s data management processes, from collection to storage, processing, and usage, confirming adherence to regulations and internal policies.
Understanding the core value of a data audit forms a foundation for trust within any enterprise. The critical role of a data audit extends beyond mere compliance; it forms the bedrock of reliable decision-making and operational excellence. Every organization needs robust data auditing to mitigate potential risks like data breaches, regulatory fines, and reputational damage that can stem from poorly managed information. A systematic data audit pinpoints vulnerabilities effectively.
Introduction to Data Auditing and Its Paramount Importance
In an era defined by ubiquitous data and stringent regulatory frameworks, the practice of data auditing has transcended its traditional role as a periodic compliance check to become a continuous, strategic imperative. Organizations worldwide are grappling with escalating data volumes, increasing data complexity, and an ever-evolving landscape of privacy regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and many others. These factors collectively underscore the paramount importance of robust data auditing mechanisms.
The objective of this deep dive is to explore the multifaceted nature of a comprehensive data audit, examining its core technical components, the challenges organizations face in its adoption, and the significant business value it delivers. We will also draw a comparative insight between modern and traditional approaches to data auditing, ultimately culminating in World2Data’s verdict on its future trajectory. A well-executed data audit is not merely about identifying problems; it’s about fostering an environment of trust, transparency, and accountability that underpins every data-driven decision.
Core Breakdown: The Architecture and Mechanism of a Modern Data Audit
The core principles of an effective data audit demand objectivity and independence in all processes to yield credible results. This ensures that findings are unbiased and accurately reflect the true data environment. A comprehensive scope, examining data from collection to deletion, means a data audit scrutinizes the entire data lifecycle, leaving no stone unturned in its quest for accuracy and security. Modern data auditing relies on sophisticated technical and architectural components to achieve this.
Technical and Architectural Analysis
- Immutable Transaction Logs: At the heart of a secure data audit system are immutable transaction logs. These logs record every data interaction—access, modification, deletion, creation—in a way that cannot be altered or deleted. This immutability provides non-repudiation, meaning an action cannot be denied by the entity that performed it, which is critical for forensic analysis, compliance, and legal defensibility.
- Centralized Logging: To manage the vast amount of audit data generated across disparate systems, centralized logging is essential. A unified platform aggregates logs from databases, applications, cloud services, and network devices, offering a single pane of glass for monitoring and analysis. This central repository simplifies incident response, streamlines compliance reporting, and provides a holistic view of data activity.
- Cryptographic Data Integrity: Ensuring that audit logs themselves have not been tampered with is paramount. Cryptographic techniques such as hashing and digital signatures are employed to guarantee the integrity of audit trails. Each log entry can be cryptographically linked to the previous one, forming a tamper-proof chain. Any unauthorized alteration would break this chain, immediately alerting administrators to potential tampering.
- Event Streaming: Modern data auditing moves beyond batch processing to real-time event streaming. Data events (e.g., a user accessing a sensitive record, a system modifying a dataset) are captured and processed as they occur. This enables immediate detection of suspicious activities, facilitating proactive security measures and reducing the window of vulnerability.
Key Data Governance Features for Robust Auditing
- Detailed Logging of Data Access and Modifications: A robust data audit capability must capture granular details: who accessed what data, when, from where, using which application, and what actions were performed (read, write, delete, export). This level of detail is indispensable for tracing data lineage and investigating incidents.
- Immutable Audit Trails: As mentioned, the ability to generate and maintain audit trails that cannot be altered is fundamental. These trails serve as the definitive record of all data-related activities, providing irrefutable evidence for regulatory compliance and internal accountability.
- Data Lineage Tracking: Understanding the journey of data from its origin to its current state, including all transformations and movements, is vital for a comprehensive data audit. Data lineage tools visualize this flow, helping identify data quality issues, compliance gaps, and the impact of changes.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) Logging: Effective data auditing includes logging not just data access, but also changes to access permissions. RBAC logging monitors who has privileges to access certain data, who granted those privileges, and when changes occurred, ensuring that access rights are consistent with policy.
- Compliance Reporting: Automated generation of compliance reports for various regulatory mandates (e.g., GDPR, SOX, HIPAA) significantly reduces the burden on compliance teams. These reports aggregate relevant audit data, demonstrating adherence to specific regulations and simplifying external audit processes.
Challenges and Barriers to Adoption in Data Auditing
While the benefits of robust data auditing are clear, organizations often encounter significant hurdles in its implementation and ongoing management:
- Data Volume and Velocity: The sheer volume and high velocity of data generated daily can overwhelm traditional auditing systems. Capturing, storing, and analyzing petabytes of audit logs in real-time requires substantial infrastructure and advanced processing capabilities, leading to scalability challenges.
- Complexity of Data Ecosystems: Modern enterprises operate with diverse and distributed data environments, including on-premise systems, multiple cloud providers, various databases, data lakes, and streaming platforms. Integrating data auditing across this heterogeneous landscape presents considerable technical and architectural challenges.
- Resource Constraints and Expertise Gap: Implementing and maintaining sophisticated data auditing solutions demands specialized skills in data governance, security, compliance, and analytics. Many organizations face a shortage of personnel with the necessary expertise, alongside budgetary constraints for tool acquisition and talent recruitment.
- Privacy Concerns in Auditing Itself: The act of auditing data can sometimes raise its own privacy concerns, especially when personal or sensitive data is part of the audit trail. Organizations must ensure that their data audit processes are designed to respect privacy principles, potentially using anonymization or pseudonymization techniques for audit logs themselves.
- Organizational Buy-in and Cultural Resistance: Implementing comprehensive data auditing often requires significant changes to existing workflows and processes, potentially leading to resistance from various departments. Overcoming internal silos and fostering a culture of data accountability across the organization is crucial but challenging.
- Alert Fatigue: Automated auditing systems can generate a massive number of alerts, many of which may be false positives. Analysts can quickly become overwhelmed, leading to “alert fatigue,” where critical warnings are missed amidst the noise. Effective filtering and anomaly detection using AI/ML are vital to mitigate this.

Business Value and ROI of Effective Data Auditing
Benefits extend far beyond simple compliance, truly driving business value. Enhanced data quality and reliability achieved through data audit activities empower better strategic planning and informed decision-making. Furthermore, mitigating risks and strengthening security with data audit insights protects sensitive information and intellectual property. The proactive identification of weaknesses through a regular data audit ultimately saves resources in the long run by preventing costly incidents.
- Risk Mitigation and Compliance Assurance: Perhaps the most immediate ROI of data auditing is its ability to significantly reduce regulatory fines, legal penalties, and reputational damage stemming from non-compliance or data breaches. By providing immutable evidence of adherence to policies and regulations, organizations can confidently navigate audits and legal challenges.
- Improved Data Quality and Trust: Through continuous monitoring and analysis, data auditing helps identify data quality issues, inconsistencies, and errors. This leads to cleaner, more reliable data, which is foundational for accurate analytics, machine learning models, and strategic decision-making. Trust in data fuels trust in insights.
- Enhanced Security Posture: Proactive detection of unusual data access patterns, unauthorized modifications, or suspicious data movements through data auditing significantly bolsters an organization’s cybersecurity defenses. It acts as an early warning system, allowing security teams to respond to threats before they escalate into major incidents.
- Operational Efficiency and Cost Savings: By optimizing data flows and identifying bottlenecks through audit insights, organizations can improve operational efficiency. Preventing data loss, corruption, or unauthorized usage avoids costly recovery efforts and downtime. Automation in data auditing also reduces manual effort associated with compliance checks.
- Boosted Customer Confidence and Brand Reputation: In an age where data privacy is a top concern for consumers, demonstrating a strong commitment to data stewardship through transparent and accountable practices like data auditing builds significant customer trust. This positively impacts brand reputation and competitive standing.
- Empowered Decision-Making: Leaders and analysts can make more confident, data-driven decisions when they have assurance of data integrity and reliability. A robust data audit instills this confidence, transforming data from a potential liability into a strategic asset.
Comparative Insight: Data Auditing in Modern vs. Traditional Data Architectures
The evolution of data architectures has profoundly impacted the methods and effectiveness of data auditing. Traditionally, auditing was often a reactive, manual, and periodic process, largely constrained by the limitations of relational databases and siloed systems. Modern data architectures, however, present both opportunities and new challenges for sophisticated data auditing.
Traditional Data Auditing (Data Warehouses & Legacy Systems)
In older, monolithic data warehouse environments or legacy systems, data auditing typically involved:
- Batch Processing: Audit logs were often collected and analyzed in batches, leading to significant delays between an event occurring and its detection.
- Siloed Logs: Logs were scattered across various application servers, databases, and operating systems, making a unified view challenging and requiring manual correlation.
- Limited Granularity: Audit trails might only capture high-level events, lacking the granular detail needed for in-depth forensic analysis.
- Manual Review: A heavy reliance on human analysts to sift through log files and generate reports, which was time-consuming, error-prone, and unsustainable for large datasets.
- Reactive Posture: Auditing was often a response to an incident or a regulatory mandate, rather than a continuous, proactive effort to prevent issues.
This approach made it difficult to detect real-time threats, ensure comprehensive compliance, or gain a true end-to-end understanding of data lineage.
Modern Data Auditing (Data Lakes, Data Platforms, and Cloud-Native Ecosystems)
Modern data architectures, characterized by data lakes, stream processing, distributed databases, and cloud-native services, offer a much richer canvas for data auditing, though they also introduce complexity:
- Real-time and Continuous Monitoring: Leveraging event streaming technologies (e.g., Apache Kafka, AWS Kinesis), modern platforms enable continuous, real-time capture and analysis of data events. This shifts data auditing from a periodic check to an always-on security and compliance function.
- Unified Data Catalogs and Metadata Management: Modern data platforms often incorporate data catalogs that provide a centralized repository of metadata, including audit-relevant information. This allows for easier tracking of data lineage, data ownership, and compliance attributes across diverse data sources.
- AI/ML-Powered Anomaly Detection: The sheer volume of audit data in modern systems makes manual analysis impossible. AI and ML algorithms are crucial for sifting through data, identifying unusual patterns (e.g., a user accessing data outside their normal working hours or a sudden spike in data exports), and flagging potential threats or policy violations automatically. This includes features like “Anomaly detection for unusual data access or modification patterns” and “Automated policy compliance validation.”
- Automated Policy Enforcement: With programmatic access and API-driven control planes common in cloud environments, modern data auditing can integrate with automated policy enforcement tools. This allows for immediate remediation actions, such as blocking unauthorized access or quarantining compromised data, based on audit findings.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud-native auditing tools and services offer elastic scalability, allowing organizations to manage vast amounts of audit data without upfront infrastructure investments. They also integrate seamlessly with cloud data services, offering built-in auditing capabilities.
While modern architectures provide powerful tools for data auditing, their distributed nature and dynamic environments also mean that comprehensive coverage requires careful planning and robust integration strategies. The emphasis shifts from simply logging to intelligent analysis and proactive response, ensuring that the benefits of scale and flexibility don’t compromise security or compliance.

World2Data Verdict: The Imperative for Intelligent, Continuous Data Auditing
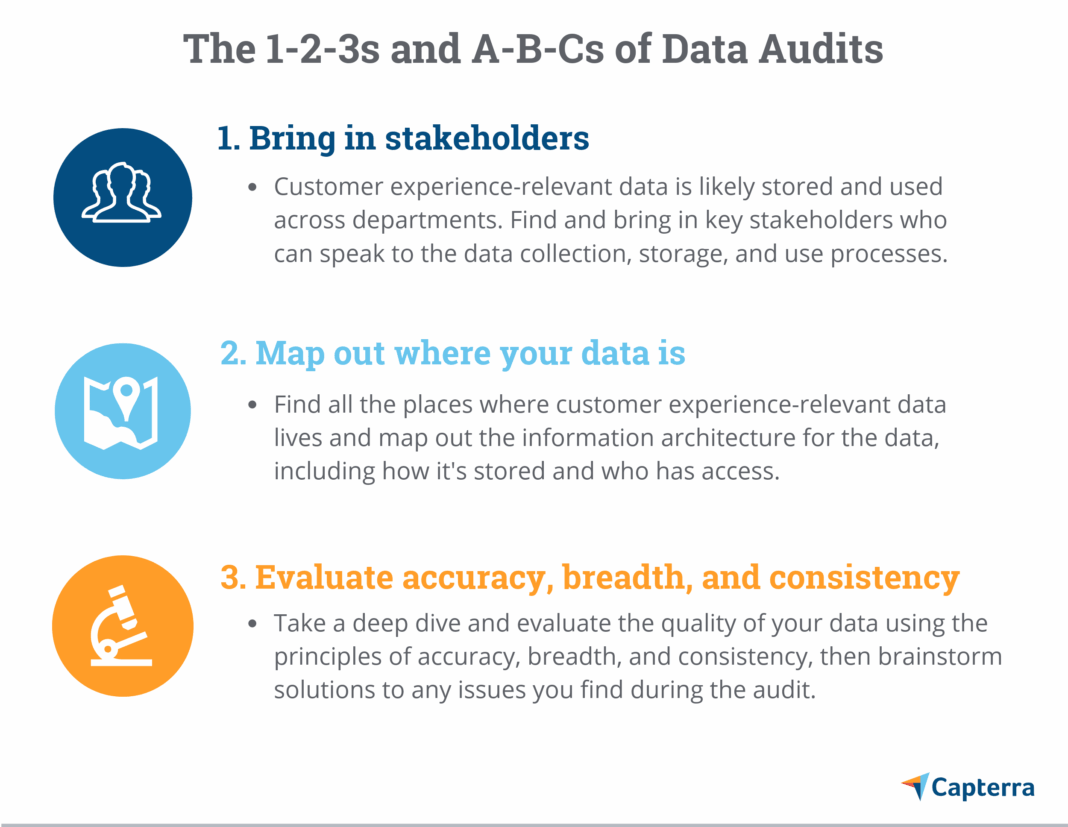
The future of data auditing centers on continuous improvement and adaptability. Adapting to evolving data landscapes is crucial as regulations, technologies, and data volumes constantly shift. Cultivating a culture of accountability ensures that data governance becomes an integral part of daily operations, not just a periodic check. Embracing continuous monitoring and regular data audit reviews will cement an organization’s commitment to responsible data stewardship, allowing businesses to confidently leverage their information assets while upholding the highest standards of integrity. Implementing successful data audit strategies involves meticulous planning, execution, and detailed reporting. Key steps for a thorough data audit implementation include defining scope, selecting tools, and engaging relevant stakeholders across departments. Leveraging technology in your data audit journey, such as specialized software, can streamline complex analyses and improve efficiency significantly. Organizations must prioritize resources for effective data audit procedures and continuous improvement.
At World2Data, we assert that data auditing is no longer a peripheral function but a foundational pillar of any resilient, data-driven enterprise. The era of manual, reactive data audits is drawing to a close, replaced by an imperative for intelligent, continuous, and AI-augmented auditing capabilities. Organizations that fail to invest in sophisticated data auditing risk not only severe regulatory penalties and crippling data breaches but also the erosion of stakeholder trust and a critical disadvantage in a competitive landscape increasingly reliant on trustworthy data. We recommend that organizations prioritize the adoption of unified, real-time data auditing platforms that leverage machine learning for anomaly detection and predictive risk assessment. Furthermore, fostering a data-aware culture where accountability is ingrained at every level will be critical for operationalizing effective data auditing. The commitment to transparent and accountable data practices, spearheaded by robust data audit mechanisms, will define the leaders of the digital economy.