Data Cleansing: The Cornerstone of Informed Decision-Making and Business Agility
In today’s hyper-competitive and data-driven landscape, the quality of data directly correlates with the quality of business decisions. Data Cleansing is not merely a technical task; it is a strategic imperative that ensures accuracy, consistency, and reliability across all organizational data assets. This meticulous process of identifying and correcting or removing erroneous, incomplete, inconsistent, or irrelevant data points empowers enterprises to gain trustworthy insights, optimize operations, and foster a culture of data-driven excellence.
The Indispensable Role of Data Cleansing in the Modern Enterprise
At its heart, Data Cleansing, often interchangeably referred to as data scrubbing, is the process of detecting and correcting (or removing) corrupt or inaccurate records from a record set, table, or database and refers to identifying incomplete, incorrect, inaccurate, irrelevant, etc. parts of the data and then replacing, modifying, or deleting the dirty or coarse data. Without this crucial step, even the most sophisticated analytics tools struggle to provide valuable insights, leaving businesses making decisions based on faulty information. Modern Data Cleansing is facilitated by a range of advanced solutions, falling under categories such as Data Quality Platforms, ETL Tools, Data Preparation Tools, and Master Data Management (MDM) systems.
The objective of this deep dive is to dissect the fundamental mechanisms of Data Cleansing, explore its profound impact on business intelligence and operational efficiency, and provide a comparative insight into modern approaches versus traditional pitfalls. By embracing robust Data Cleansing strategies, organizations can unlock the true potential of their data, transforming raw information into a powerful engine for growth and innovation.
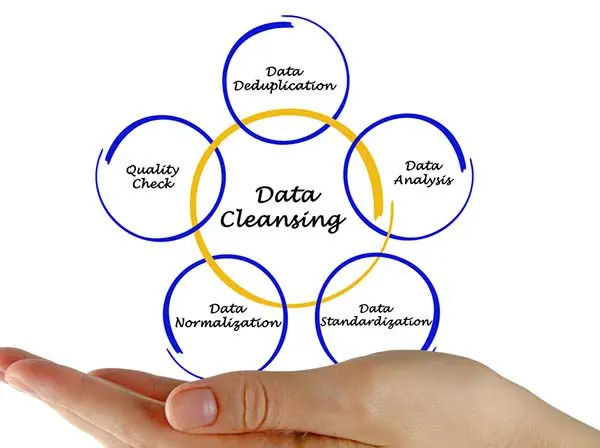
Deconstructing Data Cleansing: Processes, Technologies, and Benefits
Effective Data Cleansing is a multi-faceted process built upon several core components, each playing a vital role in elevating data quality.
Understanding the Anatomy of Unclean Data
Before diving into cleansing, it’s crucial to understand what constitutes “unclean” data. Data quality issues manifest in various forms, including:
- Incompleteness: Missing values in critical fields, leading to gaps in analysis.
- Inaccuracies: Incorrect or outdated information (e.g., wrong addresses, outdated customer details).
- Inconsistencies: Discrepant representations of the same data across different systems (e.g., “USA,” “U.S.A.,” and “United States” for the same country).
- Duplicates: Identical records for the same entity, skewing metrics and analyses.
- Invalidity: Data that does not conform to defined rules or standards (e.g., a phone number in an email field).
- Irrelevance: Data that is no longer pertinent to current business objectives.
These issues, if left unaddressed, can cascade throughout an organization, impacting everything from customer service to financial reporting.
The Pillars of Effective Data Cleansing
Modern Data Cleansing platforms leverage sophisticated technologies to systematically address these challenges:
- Data Profiling: This initial step involves scanning data to understand its structure, content, relationships, and quality. Tools use rule-based engines and pattern recognition to identify anomalies, distributions, and potential errors, providing a comprehensive overview of data health.
- Parsing and Standardization: Data from disparate sources often arrives in varying formats. Cleansing processes standardize data elements (e.g., date formats, address formats, unit measures) to ensure uniformity. Automated data transformation plays a key role here.
- Validation: Data is checked against predefined business rules, constraints, or external reference data. Data validation frameworks ensure that entries conform to expected patterns and values, catching errors like incorrect email formats or out-of-range numerical values.
- Deduplication and Matching: Identifying and merging duplicate records is critical. Fuzzy matching algorithms are employed to detect near-duplicates, even when there are slight variations (e.g., misspellings or different abbreviations), ensuring a single, accurate view of entities. AI-driven deduplication and entity resolution are advancing this area significantly.
- Correction and Enrichment: Once identified, errors are corrected, either manually or through automated rules. Data enrichment involves adding missing information from reliable external sources, enhancing the completeness and value of the dataset.
These processes are often orchestrated by ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tools and often feature robust audit trails of data changes, critical for transparency and compliance.
Challenges in Data Cleansing Implementation
Despite its undeniable benefits, implementing and maintaining a robust Data Cleansing strategy presents several challenges:
- Data Volume and Velocity: The sheer volume and continuous influx of data can overwhelm manual cleansing efforts, requiring scalable, automated solutions.
- Data Diversity and Complexity: Integrating and cleansing data from disparate sources with varying structures (structured, semi-structured, unstructured) and schemas is inherently complex. NLP for unstructured data cleansing is an emerging solution here.
- Defining “Clean”: Establishing consistent data quality rules and definitions across different departments and business units can be a significant hurdle.
- Cost and Resource Constraints: Initial investment in data quality tools and the allocation of skilled personnel for setup and oversight can be substantial.
- Data Drift: Data quality is not a static state. Data continuously changes, degrades, or drifts over time, requiring ongoing monitoring and re-cleansing processes.
- Organizational Buy-in: Securing commitment from stakeholders and fostering a data quality culture is crucial but often challenging.
Improved Business Outcomes and ROI from Clean Data
The return on investment (ROI) from a sound Data Cleansing strategy is multifaceted and profound:
- Enhanced Decision-Making Accuracy: With clean, reliable data, business leaders can trust the insights generated by analytics, leading to more accurate forecasts, better strategic planning, and confident market responses. This is the direct impact of clean data improving decision-making.
- Optimized Operational Efficiency: Eliminating redundant, error-prone data reduces manual rework, streamlines workflows, and frees up valuable resources. This translates to lower operational costs and faster process execution.
- Superior Customer Experience: Accurate customer data (e.g., contact information, purchase history) enables personalized marketing, efficient customer service, and targeted product development, fostering loyalty and driving sales.
- Regulatory Compliance and Risk Mitigation: Many regulations (GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA) mandate high data quality standards. Clean data helps organizations meet these requirements, avoiding hefty fines and reputational damage. Key Data Governance Features like data quality rule definition and enforcement, and metadata management for quality dimensions, become indispensable here.
- Foundation for Advanced Analytics and AI: Machine Learning models are notoriously sensitive to data quality. Clean data is the bedrock for effective AI/ML integration, enabling accurate predictive models, intelligent automation, and successful AI initiatives. Primary AI/ML Integration features like automated anomaly detection, intelligent data profiling, and predictive data quality scores are transformative.

Comparative Insight: Data Cleansing Platforms vs. Traditional & Manual Approaches
Historically, organizations attempted Data Cleansing through manual processes, custom scripts, or by simply ignoring data quality issues, hoping statistical methods would account for inaccuracies. These approaches, however, are fraught with limitations when compared to modern, dedicated Data Cleansing platforms and tools.
The Pitfalls of Manual and Ad-Hoc Cleansing
Manual Data Cleansing, often relying on spreadsheets and human review, is:
- Error-Prone: Human error is inevitable, especially with large datasets, leading to inconsistencies and missed issues.
- Time-Consuming and Resource-Intensive: It diverts skilled personnel from more strategic tasks and significantly delays data readiness.
- Non-Scalable: As data volumes grow, manual methods quickly become unsustainable and impractical.
- Lacking in Auditability: Without clear audit trails, it’s difficult to track changes, understand why decisions were made, or ensure compliance.
- Inconsistent: Different individuals or teams may apply varying rules, leading to inconsistent data quality across the organization.
Custom scripts, while offering some automation, often lack user-friendly interfaces, require specialized programming knowledge for maintenance, and struggle with complex, evolving data structures and fuzzy matching scenarios.
The Advantages of Modern Data Cleansing Platforms
Dedicated Data Cleansing platforms and data quality tools, like Informatica Data Quality, Talend Data Fabric, IBM InfoSphere QualityStage, Alteryx, Microsoft SQL Server Data Quality Services, and OpenRefine, offer a comprehensive and scalable solution:
- Automation and Efficiency: These platforms automate repetitive cleansing tasks, significantly reducing manual effort and accelerating data preparation time. Automated suggestion of cleansing rules, often leveraging AI, further enhances efficiency.
- Advanced Capabilities: They provide sophisticated features such as intelligent data profiling, fuzzy matching algorithms, advanced pattern recognition, and robust data validation frameworks that are difficult to replicate with manual efforts.
- Scalability: Designed to handle massive datasets from diverse sources, these tools can scale with an organization’s data growth.
- Centralized Governance: They offer centralized management of data quality rules, standards, and metrics, ensuring consistency and adherence to data governance policies. Data quality dashboards and reporting provide real-time visibility.
- Data Lineage and Auditability: Most platforms provide detailed audit trails and data lineage capabilities, showing exactly how data was transformed and corrected, which is vital for compliance and troubleshooting.
- Integration: They seamlessly integrate with other data management components like ETL tools, data warehouses, data lakes, and MDM systems, creating an end-to-end data pipeline.
- AI/ML Integration: Modern platforms are increasingly incorporating AI for tasks like automated anomaly detection, intelligent data profiling, and predictive data quality scores, making the cleansing process more proactive and adaptive.
Choosing a dedicated platform over traditional methods is a strategic move that fundamentally shifts an organization from reactive data firefighting to proactive data stewardship, laying a solid foundation for all data-driven initiatives.
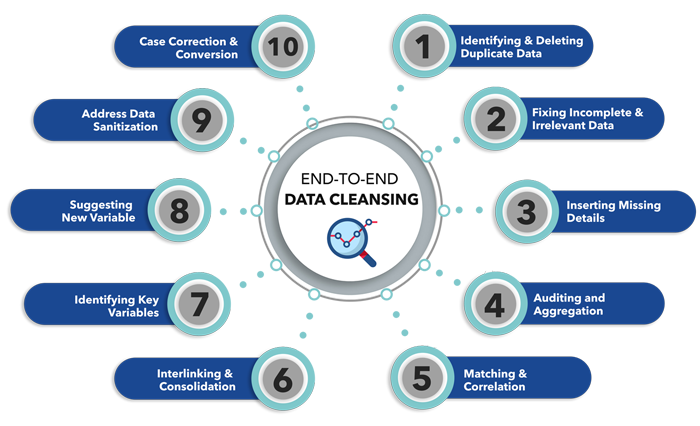
World2Data Verdict: Investing in Data Cleansing: A Non-Negotiable Imperative for Future-Proofing
The journey to becoming a truly data-driven organization begins and is sustained by a unwavering commitment to Data Cleansing. It is no longer an optional step but a foundational element of any successful data strategy. Organizations that delay or neglect thorough Data Cleansing will inevitably face diminished returns on their data investments, make flawed decisions, and struggle to keep pace with agile competitors. World2Data.com emphasizes that prioritizing investment in advanced Data Cleansing platforms and cultivating a culture of data quality is not merely about fixing errors; it is about building trust, enhancing operational efficiency, mitigating risks, and most importantly, empowering superior decision-making at every level of the enterprise.
Looking ahead, the role of AI and Machine Learning in Data Cleansing will continue to grow, leading to more intelligent, autonomous, and proactive data quality management. Features like AI-driven deduplication, automated suggestion of cleansing rules, and predictive data quality scores will become standard, making data quality an inherent part of every data pipeline. Embrace this evolution, and your data will cease to be a liability and transform into your most powerful strategic asset.



