Data Consistency: Why It Matters and How to Achieve It for Robust Data Management
Data forms the bedrock of modern enterprises, fueling everything from daily operations to strategic decision-making and advanced analytical initiatives. At the heart of reliable data utilization lies a fundamental concept: Data Consistency. It ensures that information remains accurate, valid, and uniform across all systems and applications, regardless of how or where it’s accessed. For any organization striving for trustworthiness and efficiency, achieving and maintaining high Data Consistency is not merely an IT concern but a critical business imperative.
Introduction: The Unwavering Demand for Data Consistency
In today’s data-driven world, the proliferation of data sources and the increasing complexity of information ecosystems have amplified the challenges associated with data management. Businesses rely on diverse platforms—Database Management Systems, Data Warehouses, Data Lakes, ETL/ELT Platforms, and Master Data Management (MDM) Solutions—each contributing to the intricate web of enterprise data. Yet, the true value of this data can only be unlocked if it exhibits unwavering Data Consistency. Without it, insights derived are flawed, decisions become risky, and operational processes falter. This article delves into the critical importance of Data Consistency, dissecting the technical underpinnings, exploring the common obstacles, and outlining actionable strategies and technologies to ensure data integrity across your organization.
Core Breakdown: Understanding the Pillars of Data Consistency
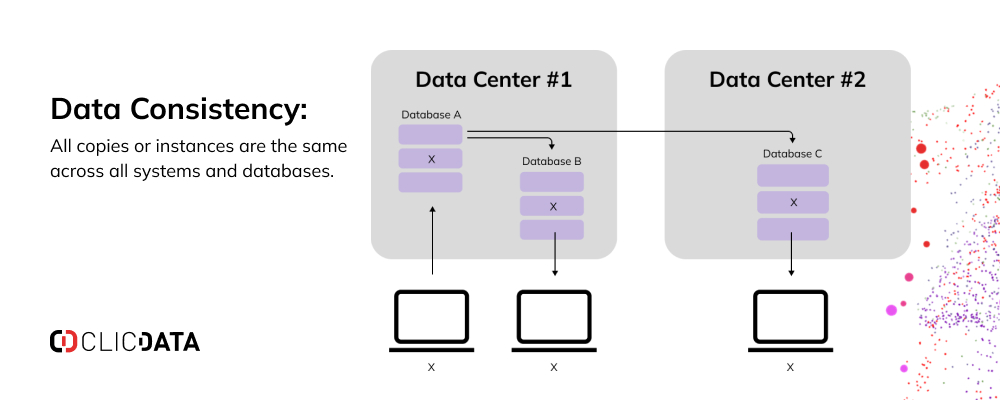
At its essence, Data Consistency refers to the state where a specific piece of information maintains the same value and format throughout its lifecycle and across all databases and applications where it resides. This uniformity is paramount for data’s trustworthiness and utility.
Defining Data Consistency and Its Foundational Technologies
The pursuit of Data Consistency is often rooted in core technological principles and architectural designs:
- ACID Properties (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability): Particularly in transactional systems, ACID properties are the gold standard for ensuring data integrity.
- Atomicity: Guarantees that all operations within a transaction are completed successfully; otherwise, the transaction is entirely aborted, leaving the database unchanged.
- Consistency: Ensures that a transaction brings the database from one valid state to another, maintaining all defined rules, triggers, and constraints. This is the direct application of Data Consistency at a transactional level.
- Isolation: Dictates that concurrent transactions execute independently without interfering with each other, ensuring that intermediate states of one transaction are not visible to others.
- Durability: Guarantees that once a transaction has been committed, it will remain permanent, even in the event of system failures.
- Transactional Systems: RDBMS (Relational Database Management Systems) leverage transactions heavily to maintain strong Data Consistency through mechanisms like two-phase commit protocols for distributed transactions.
- Data Validation Frameworks: These include rules engines and schema validation to enforce predefined quality standards and formats at the point of entry or during data movement.
- Referential Integrity Mechanisms: Using foreign keys, primary keys, and cascade rules, databases enforce relationships between tables, preventing orphaned records and ensuring related data remains consistent.
- Master Data Management (MDM) Solutions: MDM systems establish a “single source of truth” for critical business entities (customers, products, locations), consolidating and synchronizing this master data across the enterprise to prevent duplication and discrepancies.
- Data Quality Tools: Solutions like Collibra DQ or Ataccama ONE are designed to profile, cleanse, standardize, and enrich data, actively identifying and resolving inconsistencies.
- Eventual Consistency: While strong consistency (ACID) is ideal, distributed systems and certain NoSQL databases often adopt eventual consistency. This model guarantees that if no new updates are made to a given data item, eventually all accesses to that item will return the last updated value. This trades immediate consistency for higher availability and partition tolerance, crucial in highly scalable environments.
Challenges/Barriers to Achieving Robust Data Consistency
Despite its critical importance, organizations face numerous hurdles in maintaining high Data Consistency:
- Data Silos and Integration Issues: As organizations grow, data often becomes fragmented across disparate operational systems (ERPs, CRMs, legacy systems, cloud applications). Each silo might have its own data definitions, formats, and update cycles, leading to duplicated, conflicting, or outdated information when attempts are made to integrate them. Complex ETL/ELT pipelines are often required but can introduce their own consistency challenges if not meticulously designed.
- Manual Entry Errors and Human Factors: Human error remains a significant cause of inconsistencies. Typos, incorrect formatting, missing fields, or inconsistent abbreviations during manual data input can propagate rapidly throughout a system, leading to downstream data quality issues. Lack of standardized input procedures or insufficient training exacerbates this problem.
- Data Volume, Velocity, and Variety (Big Data Context): The sheer scale, speed, and diversity of big data streams (e.g., IoT sensor data, social media feeds) make real-time consistency enforcement incredibly challenging. Balancing consistency with performance and availability in such environments often leads to trade-offs, like embracing eventual consistency.
- Schema Evolution and Data Drift: Business requirements and underlying systems evolve, leading to changes in data schemas. If these changes are not carefully managed and propagated across all dependent systems, they can introduce data drift, where the meaning, structure, or quality of data changes subtly over time, leading to inconsistencies.
- Lack of Clear Data Governance: Without established policies, procedures, roles, and responsibilities for managing data assets, organizations struggle to enforce data quality standards. Ambiguity in data ownership, definitions, and update protocols often results in inconsistencies going undetected or unresolved.
Business Value and ROI of High Data Consistency
The investment in achieving and maintaining Data Consistency yields substantial returns across the enterprise:
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Consistent data provides a single, reliable source of truth, empowering leaders to make data-driven decisions with confidence. Accurate and timely data translates into better strategic planning, more effective operational adjustments, and improved predictive analytics, reducing business risk.
- Building Trust and Credibility: High Data Consistency fosters trust both internally and externally. Customers expect accurate information, and internal teams rely on data integrity for effective collaboration and compliance with regulatory bodies (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, financial reporting standards). It strengthens stakeholder confidence in the organization’s data assets.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Consistent data reduces the time and effort spent on reconciling discrepancies, correcting errors, and chasing down the “right” information. This streamlines workflows, automates processes more reliably, and reduces operational inefficiencies and rework across departments, from sales to supply chain management.
- Better Customer Experiences: With consistent customer data (contact information, purchase history, preferences) across all touchpoints, businesses can provide personalized, accurate, and seamless customer service, leading to higher satisfaction and loyalty.
- Foundation for AI/ML Initiatives: AI and Machine Learning models are notoriously sensitive to data quality. High-quality, consistent data is absolutely essential for training robust, unbiased, and performant models. Inconsistent data leads to “garbage in, garbage out,” resulting in unreliable predictions and failed AI projects.
.webp)
Comparative Insight: Data Consistency Across Paradigms – Traditional vs. Modern Approaches
The approach to Data Consistency has evolved significantly with technological advancements. Understanding these shifts is crucial for designing robust data architectures.
Traditional Relational Databases (Strong Consistency)
In the era dominated by relational databases, strong Data Consistency was paramount and achievable primarily through ACID properties. These systems were typically centralized or scaled vertically, making it easier to enforce strict transactional integrity. Data models were rigid, schemas were well-defined, and any deviation or inconsistent state was prevented at the database level. This approach is highly reliable for applications requiring immediate and absolute consistency, such as financial transactions or inventory management where data accuracy is non-negotiable at all times.
Distributed Systems and NoSQL (Eventual Consistency)
With the advent of big data and highly scalable web applications, the limitations of traditional relational databases became apparent. Distributed systems and NoSQL databases often prioritize availability and partition tolerance over immediate consistency, adhering to the CAP theorem. This led to the rise of “eventual consistency,” where data updates might not be immediately reflected across all replicas, but they are guaranteed to converge to a consistent state over time. This BASE (Basically Available, Soft state, Eventual consistency) model is suitable for use cases where high availability and horizontal scalability are more critical than immediate transactional consistency, such as social media feeds, sensor data ingestion, or content delivery networks. However, managing eventual consistency requires careful application design to handle potential temporary inconsistencies.
Data Lakes and Data Warehouses
In data lakes and data warehouses, the focus on Data Consistency shifts from real-time transactional integrity to consistency over larger analytical datasets. Data is often extracted from various source systems, transformed, and loaded (ETL/ELT) into these analytical stores. Data Consistency here means ensuring that data is cleaned, standardized, de-duplicated, and aggregated correctly to provide a unified view for reporting and analytics. Data quality checks, schema enforcement at query time (schema-on-read), and robust data governance frameworks are vital to maintaining consistency in these environments, preventing analytical errors and misleading business intelligence.
Data Consistency in the Era of Streaming and Real-time Analytics
The rise of real-time data streaming (e.g., Apache Kafka) introduces new layers of complexity for Data Consistency. Ensuring consistent processing and state across continuous data streams, especially when dealing with event ordering, deduplication, and exactly-once processing semantics, is a significant challenge. Stream processing frameworks offer features to manage this, but it requires sophisticated architectural choices and careful error handling to prevent inconsistencies in real-time dashboards or operational systems.

Strategies to Achieve Robust Data Consistency
Achieving and maintaining Data Consistency is not a one-time project but a continuous organizational commitment. It requires a blend of technological solutions, robust processes, and a culture that values data integrity.
- Implementing Strong Data Governance: This is the cornerstone of Data Consistency. Establish clear policies, procedures, and roles for managing data, including data ownership, data definitions (metadata management), data quality rules, and data lineage tracking. A data governance framework ensures accountability, adherence to standards, and proactive consistency management. Data stewards play a crucial role in enforcing these policies.
- Utilizing Data Validation and Cleansing Tools: Automated validation processes at the point of data entry (e.g., UI forms, APIs) or during data transfers (e.g., ETL pipelines) help catch and correct inconsistencies before they spread. Data profiling tools identify existing quality issues, while data cleansing and standardization tools fix inconsistencies, format data correctly, and resolve duplicates.
- Adopting Master Data Management (MDM) Solutions: For critical business entities, MDM systems are indispensable. They create a “golden record” by consolidating, reconciling, and governing master data from various sources, ensuring that a consistent, accurate, and complete view of key data is available across the enterprise.
- Leveraging Modern Data Integration Platforms (ETL/ELT): Robust ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) or ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) tools (like Talend, AWS Glue, Azure Data Factory) are crucial for moving and transforming data while preserving consistency. They allow for the application of data quality rules, schema mappings, and transformation logic to ensure data integrity as it flows between systems.
- Database Management Systems (DBMS) with ACID Guarantees: For transactional workloads, prioritizing DBMS that enforce ACID properties through referential integrity, constraints (NOT NULL, UNIQUE, CHECK), and transaction management is fundamental. These built-in features prevent inconsistent states at the database level.
- Implementing Data Observability Platforms: Proactive monitoring of data quality and consistency is becoming increasingly important. Data observability platforms (e.g., Monte Carlo, Soda) provide visibility into the health of data pipelines and datasets, automatically detecting anomalies, schema changes, and consistency issues in real-time, allowing teams to address problems before they impact downstream consumers.
- Primary AI/ML Integration for Automated Consistency: AI and Machine Learning can significantly enhance Data Consistency efforts.
- Anomaly Detection for Data Inconsistencies: ML models can be trained to identify unusual patterns or outliers in data that signify inconsistencies or errors, flagging them for human review or automated correction.
- Automated Data Quality Checks: AI can learn from historical data corrections and apply rules automatically to new data, improving efficiency and reducing manual effort.
- AI-assisted Data Cleansing and Transformation: Algorithms can suggest and even execute data standardization, deduplication, and transformation rules, especially for large, complex datasets.
- Predictive Identification of Data Errors: AI can analyze data streams to predict where inconsistencies are likely to occur, allowing for proactive intervention rather than reactive fixes.
World2Data Verdict: Data Consistency as a Strategic Imperative
In the digital economy, Data Consistency transcends a mere technical requirement; it is a strategic imperative that directly impacts an organization’s agility, trustworthiness, and competitive edge. The effort invested in ensuring high Data Consistency yields significant returns, manifesting in more reliable business operations, enhanced decision-making capabilities, stronger stakeholder trust, and a robust foundation for advanced analytics and AI initiatives. World2Data.com emphasizes that organizations must adopt a holistic approach, integrating strong data governance with modern technological solutions—from traditional ACID-compliant databases to advanced MDM and AI-powered data quality tools. The future of data management will increasingly rely on intelligent, automated systems that proactively identify and resolve inconsistencies, ensuring that data remains a true asset, not a liability. Embracing this commitment will define the leaders of the data-driven future.