Data Fabric: Seamlessly Connecting All Data Across the Enterprise for Smarter Insights
As a foundational shift in data management, the Data Fabric represents an **Integrated Data Management Architecture** designed to unify disparate data sources across an organization. Its core technological backbone leverages **Knowledge Graph**, **Active Metadata Management**, **Data Virtualization**, a robust **Semantic Layer**, and **Automated Data Integration**. For robust **Data Governance**, it incorporates features such as **Automated Policy Enforcement**, a **Unified Data Catalog**, comprehensive **Data Lineage Tracking**, and granular **Role-Based Access Control**. Crucially, its primary **AI/ML Integration** capabilities ensure the provision of governed and contextualized data for machine learning models, simultaneously utilizing AI for advanced active metadata processing and semantic mapping. While offering unparalleled advantages, it operates within a competitive landscape that includes **Data Mesh**, various **Data Virtualization Solutions**, traditional **Data Warehouses and Data Lakes**, and established **Enterprise Data Integration Platforms**.
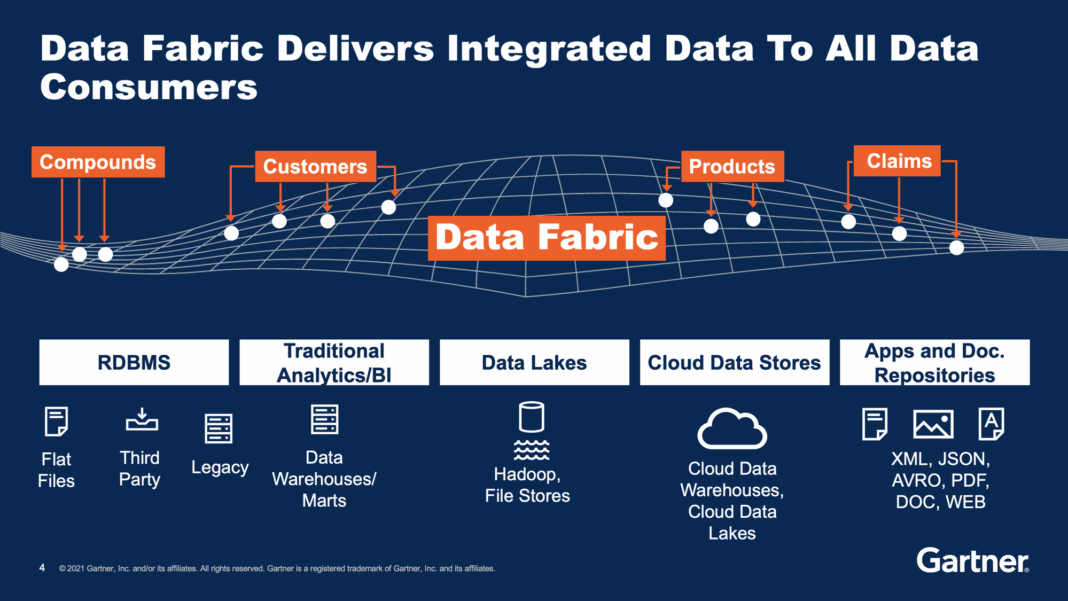
In today’s complex digital landscape, organizations grapple with an ever-increasing volume of data, scattered across diverse systems and environments. The Data Fabric emerges as a transformative solution, designed to integrate and manage this fragmented data, making it readily accessible and usable across the entire enterprise. It addresses the critical challenge of disparate data sources, unifying data silos for enhanced accessibility and a holistic view of information assets. This innovative approach is no longer a futuristic concept but an essential strategy for modern businesses striving for agility and data-driven decision-making.
The Imperative for a Unified Data Ecosystem – Embracing Data Fabric
Modern enterprises face an unprecedented challenge: data proliferation. Information resides everywhere – in cloud services, on-premise databases, SaaS applications, IoT devices, and streaming platforms. This vast and varied data estate often creates silos, hindering analytics, delaying insights, and complicating regulatory compliance. Traditional data integration methods, often reliant on manual processes and point-to-point connections, simply cannot keep pace with the velocity, volume, and variety of modern data. This is where the Data Fabric steps in as a game-changer.
The objective of a Data Fabric is not merely to connect data, but to create an intelligent, self-optimizing network that understands, governs, and delivers data to any consumer, anywhere, in real-time. It revolutionizes data integration and management by automating complex processes that traditionally required significant manual effort. By streamlining data discovery and preparation, employing AI and machine learning to identify, cleanse, and transform data from various origins, the Data Fabric ensures data quality and readiness. This innovative architecture also strengthens data governance and compliance, ensuring that data is managed according to enterprise policies and regulatory requirements without sacrificing agility, thereby laying the groundwork for a truly data-driven organization.
Deconstructing the Data Fabric Architecture and Its Transformative Capabilities
The core principles of Data Fabric architecture are centered on intelligence and automation, forming a robust and adaptive data ecosystem. It moves beyond simple connectivity to create an integrated, self-organizing system that learns and evolves. This sophisticated architecture is built upon several foundational pillars, each contributing to its ability to manage and deliver data effectively across the enterprise.
Key Pillars of the Data Fabric
- Active Metadata Management: This is perhaps the most critical component of a Data Fabric. Unlike passive metadata, which merely describes data, active metadata continuously monitors and analyzes data usage, patterns, and relationships. It employs AI and machine learning to automatically discover, classify, and enrich metadata, providing deep context and enabling intelligent automation. This constant feedback loop allows the Data Fabric to adapt, optimize data pipelines, and recommend relevant data to users, significantly improving data discoverability and understanding.
- Knowledge Graph and Semantic Layer: These components provide a rich, interconnected view of data assets and their relationships across the entire enterprise. A Knowledge Graph maps data entities and their connections, creating a powerful semantic network. The Semantic Layer then provides a business-friendly abstraction over this complex data landscape, allowing users to query data using business terms rather than technical jargon. This combination enables intelligent data discovery, advanced analytics, and facilitates contextual understanding, which is crucial for modern AI and ML applications.
- Data Virtualization: A cornerstone of the Data Fabric, data virtualization provides a unified, real-time view of disparate data sources without physically moving or replicating the data. It abstracts the underlying complexity of data locations and formats, presenting data as if it resided in a single, coherent source. This reduces data latency, minimizes storage costs, and simplifies data access for various applications and users, ensuring that insights are derived from the freshest possible data.
- Automated Data Integration: The Data Fabric leverages AI-driven automation to streamline the entire data integration lifecycle, from ingestion to transformation and delivery. This includes intelligent profiling, schema mapping, data quality checks, and pipeline generation. By automating these processes, organizations can significantly reduce the manual effort and time traditionally associated with data preparation, accelerating data availability for analytics and operational systems.
- Unified Data Catalog: Essential for discoverability and governance, the unified data catalog acts as a comprehensive inventory of all data assets within the Data Fabric. It integrates metadata from various sources, providing a single pane of glass for users to search, understand, and access data. With active metadata feeding into it, the catalog becomes dynamic, constantly updating with usage patterns, data quality scores, and policy adherence, fostering trust and self-service analytics.
Challenges and Barriers to Data Fabric Adoption
While the benefits of a Data Fabric are compelling, its implementation is not without challenges. Organizations must navigate complexities ranging from technical hurdles to organizational inertia. One significant barrier is the integration with existing legacy systems. Many enterprises operate with deeply entrenched, monolithic systems that are difficult to connect and extract data from, requiring substantial effort to normalize and integrate into the fabric.
Furthermore, organizational silos and change management pose considerable challenges. A Data Fabric, by its very nature, demands cross-functional collaboration and a unified approach to data. Resistance to change, departmental ownership of data, and a lack of understanding of the holistic benefits can impede adoption. There’s also a considerable skills gap in advanced data architectures; expertise in areas like **Knowledge Graph** construction, **Active Metadata Management**, and robust **Data Governance** frameworks is often scarce. Initial investment in the necessary tools and technologies, along with justifying the ROI, can be a hurdle for many businesses. Finally, ensuring robust **Data Governance** across a distributed and highly dynamic landscape requires continuous monitoring and automated policy enforcement, which can be complex to establish and maintain, particularly in environments prone to data drift.
Business Value and ROI of a Data Fabric
Driving business agility and innovation is a key benefit derived from implementing a robust Data Fabric. By providing a unified and consistent view of all relevant data, it empowers real-time analytics and insights, allowing companies to respond rapidly to market changes. This significantly accelerates decision-making across departments, from operations to marketing, fostering a more responsive and competitive business environment.
- Accelerated Time-to-Insight: The automation of data discovery, integration, and preparation processes drastically reduces the time it takes to get data ready for analysis. This translates into faster insights, enabling quicker responses to market demands and competitive pressures.
- Improved Data Quality and Trust: Through automated metadata management, data lineage tracking, and continuous profiling, the Data Fabric ensures higher data quality and reliability. This builds greater trust in data, which is essential for critical business decisions and regulatory compliance.
- Enhanced AI/ML Initiatives: A Data Fabric provides the consistent, high-quality, and contextualized data that advanced AI and machine learning models require to deliver meaningful business value. It enables easier access to relevant features for model training and deployment, accelerating the journey from raw data to actionable predictive insights. This seamless provision of governed data for ML models is a direct answer to the challenges of data preparation in complex **MLOps** environments.
- Increased Agility and Scalability: The adaptive nature of the Data Fabric allows it to seamlessly accommodate new data sources, technologies, and evolving business requirements without extensive re-architecture. This future-proofs the data strategy, ensuring scalability for evolving data needs and fostering innovation.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Automation of integration and governance tasks minimizes manual effort, reduces errors, and frees up valuable data engineering resources, leading to significant operational cost savings.

Data Fabric vs. Traditional Data Architectures: A Paradigm Shift
The emergence of the Data Fabric signifies a profound paradigm shift from traditional data management approaches like the **Data Warehouse** and **Data Lake**. While these traditional systems have served enterprises well for decades, they often fall short in addressing the complexities of modern, distributed, and diverse data landscapes.
A **Data Warehouse** is typically optimized for structured data, analytical reporting, and business intelligence, relying on an Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) process that physically moves and aggregates data into a centralized repository. While excellent for historical analysis and predefined reports, it struggles with semi-structured, unstructured, and real-time data, often leading to data latency and rigidity.
The **Data Lake**, introduced to handle the volume and variety of big data, stores raw, unprocessed data in its native format, often in low-cost storage. It offers flexibility for exploration and supports various data types but often suffers from becoming a “data swamp” without proper governance, metadata management, and clear semantic definitions. Data discovery and quality can be significant challenges in a pure data lake environment.
The Data Fabric, in contrast, offers a more dynamic and integrated approach. Instead of physically centralizing all data (like a data warehouse) or merely dumping it into a raw repository (like a data lake), it focuses on logical integration. It uses technologies like **Data Virtualization** to create a unified view of data wherever it resides, without requiring physical movement. Its reliance on **Active Metadata Management** and a **Semantic Layer** means that data is not just connected, but also understood, cataloged, and governed proactively, regardless of its location. This intelligence contrasts sharply with the often reactive or manual metadata processes in traditional systems.
Furthermore, while the **Data Mesh** is often discussed alongside Data Fabric, they address different, albeit complementary, aspects. Data Mesh emphasizes a decentralized, domain-oriented ownership model for data, treating data as a product. The Data Fabric, on the other hand, is an architectural and technological layer that enables the technical execution of such a decentralized vision, providing the underlying capabilities for integrated access, governance, and semantic understanding across these distributed data products. While Data Mesh focuses on organizational structure, Data Fabric focuses on the technical means to achieve seamless, intelligent data flow. The Data Fabric is designed to overcome the limitations of centralized data architectures by providing a flexible, adaptive, and intelligent layer that connects all data, enabling more sophisticated **AI Data Platform** capabilities and streamlining complex **MLOps** workflows by providing high-quality, governed data on demand.

World2Data Verdict: The Future is Woven: World2Data’s Recommendation for Data Fabric Adoption
The journey towards becoming a truly data-driven enterprise is paved with challenges, primarily stemming from data fragmentation and complexity. World2Data believes that the Data Fabric is not merely an optional upgrade but a strategic imperative for organizations aiming to unlock the full potential of their data assets, especially in an era dominated by AI and machine learning. Its ability to provide a unified, intelligent, and governed view of data across disparate sources is unparalleled, offering a distinct competitive advantage.
Our recommendation is clear: enterprises must prioritize the adoption of a Data Fabric strategy. To maximize success, start with a well-defined use case that demonstrates tangible business value, such as accelerating a critical AI initiative or improving customer 360 insights. Focus initially on implementing robust **Active Metadata Management** and a comprehensive **Unified Data Catalog** – these are the foundational intelligence layers that will enable subsequent capabilities. Embrace a phased implementation approach, iteratively building out the fabric’s reach and capabilities. Furthermore, investing in skill development related to **Knowledge Graph** construction and advanced data governance is crucial for long-term success.
Looking ahead, World2Data predicts that the Data Fabric will evolve to become the de facto standard for scalable, intelligent data ecosystems. As enterprises grapple with increasingly complex data landscapes and the demands of sophisticated **AI Data Platform** needs and intricate **MLOps** environments, the intelligent automation and logical integration offered by a Data Fabric will be indispensable. It is the architectural blueprint for a future where data is not just connected, but truly understood, empowering smarter business outcomes and fueling continuous innovation. The future of enterprise data management is woven into the fabric.