Managing the Full Data Lifecycle: A Practical Guide to Data Management Excellence
1. Platform Category: Integrated Data Management Platform
2. Core Technology/Architecture: DataOps, Data Mesh, Cloud-Native Architecture
3. Key Data Governance Feature: Data Catalog, Data Lineage, Data Quality Management
4. Primary AI/ML Integration: MLOps, AI-powered Data Quality, Predictive Analytics
5. Main Competitors/Alternatives: AWS Data Services, Azure Data Platform, Google Cloud Data Analytics, Informatica, IBM Data and AI
Managing the Full Data Lifecycle: A Practical Guide is crucial in today’s data-driven world. Effectively handling your data lifecycle from inception to disposal isn’t just good practice; it’s fundamental to operational efficiency and strategic decision-making. This guide delves into the intricacies of each stage, providing a comprehensive understanding of how to optimize your organization’s data assets. From acquisition to secure disposal, mastering the data lifecycle ensures data integrity, compliance, and maximizes its strategic value across the enterprise.
Introduction: Mastering the Data Lifecycle in a Dynamic World
In an era where data is often hailed as the new oil, its effective management throughout its entire existence is not merely an operational task but a strategic imperative. The concept of the Data Lifecycle describes the sequence of stages that data goes through from its initial generation or capture to its eventual archival or deletion. For businesses aiming for sustained growth, innovation, and competitive advantage, a robust framework for managing the data lifecycle is indispensable. This article provides a comprehensive deep dive into each phase of the data lifecycle, offering practical insights and exploring how modern integrated data management platforms, leveraging technologies like DataOps and Data Mesh, are revolutionizing this critical discipline. We will examine the architectural components, key governance features, and the profound business value derived from expertly navigating the complexities of data from creation to secure disposal.
Core Breakdown: Deconstructing the Data Lifecycle and its Modern Management Paradigms
The full data lifecycle is a complex, multi-stage journey that demands meticulous attention at every turn. Understanding and optimizing each phase is critical for harnessing data’s true potential. An effective integrated data management platform acts as the central nervous system for this entire process, ensuring continuity, security, and maximum utility.
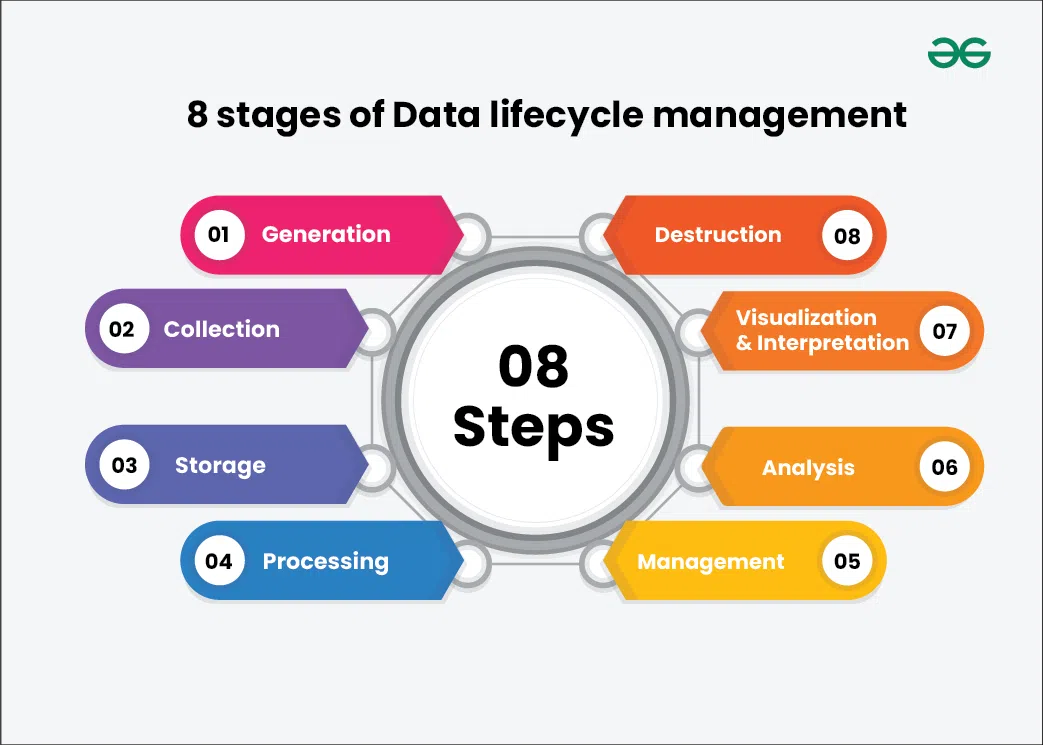
Defining Data Stages: From Inception to Oblivion
The data lifecycle typically encompasses distinct, yet interconnected, phases:
- Data Creation/Acquisition: This initial stage involves gathering or generating data from various internal and external sources. Whether it’s transactional data, sensor readings, social media feeds, or scientific measurements, accuracy and relevance at this point are paramount. Modern platforms often employ sophisticated connectors and APIs to streamline data ingestion from diverse endpoints, setting the foundation for the entire data lifecycle.
- Data Storage: Once acquired, data needs to be securely stored in accessible repositories. This can range from traditional databases and data warehouses to more flexible data lakes, and increasingly, cloud-native object storage solutions. The choice of storage depends on data volume, velocity, variety, and the specific access patterns required for processing and analysis, always balancing cost with accessibility.
- Data Processing and Transformation: Raw data is rarely in a usable state for analytics or machine learning. This phase involves cleaning, validating, transforming, and integrating data to ensure its quality, consistency, and readiness for downstream applications. ETL/ELT pipelines, often powered by DataOps principles, automate and orchestrate these complex transformations, ensuring data integrity and timeliness as it moves through its lifecycle.
- Data Usage and Analysis: This is where data’s value is truly realized. Analysts, data scientists, and business users leverage processed data for reporting, business intelligence, predictive analytics, and machine learning model training. Effective data catalogs, a key data governance feature, become invaluable here, allowing users to discover, understand, and trust available data assets for informed decision-making.
- Data Retention and Archiving: Data that is no longer actively used but must be retained for compliance, historical analysis, or potential future use is moved to cost-effective, long-term storage solutions. While less frequently accessed, archived data must remain discoverable and retrievable, often requiring robust data lineage capabilities to track its origin and transformations for auditing purposes.
- Data Disposal: The final, yet often overlooked, stage involves the secure and irreversible deletion of data when it has served its purpose and is no longer legally or operationally required. This is crucial for mitigating security risks, preventing data breaches, and ensuring compliance with privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA, thus completing the data lifecycle responsibly.
The Importance of a Structured Flow with Modern Architectures
A well-managed data lifecycle, orchestrated by an Integrated Data Management Platform, ensures data integrity, security, and accessibility throughout its entire journey. Core technologies like DataOps emphasize automation, collaboration, and continuous delivery across the data lifecycle, accelerating the journey from raw data to actionable insights. Similarly, Data Mesh architectures promote decentralized data ownership and consumption, treating data as a product and empowering domain teams to manage their data assets across the lifecycle, fostering higher quality and usability. The underlying Cloud-Native Architecture provides the scalability, flexibility, and resilience necessary to handle the ever-increasing volumes and varieties of data, facilitating seamless progression through each lifecycle stage. Key data governance features such as a Data Catalog provide a comprehensive inventory of data assets, enabling efficient discovery and understanding. Meanwhile, Data Lineage tracks data transformations from source to destination, crucial for auditing, troubleshooting, and ensuring compliance. Data Quality Management tools, often AI-powered, proactively identify and rectify inaccuracies, ensuring that data at every stage is fit for purpose and maximizing its utility for predictive analytics and MLOps integrations.
Challenges and Barriers to Comprehensive Data Lifecycle Adoption
Despite the clear benefits, organizations frequently encounter significant hurdles in implementing and maintaining a holistic data lifecycle strategy:
- Data Silos and Fragmentation: Data often resides in disparate systems across an enterprise, leading to inconsistent formats, redundant storage, and difficulty in obtaining a unified view. This fragmentation complicates data integration and governance efforts across the lifecycle, hindering a comprehensive approach.
- Lack of Data Governance and Ownership: Without clear policies, standards, and accountability for data assets, managing their lifecycle becomes chaotic. Ambiguity around who is responsible for data quality, security, and compliance at each stage can lead to critical gaps and increased risk.
- Compliance and Regulatory Complexity: Navigating the myriad of industry-specific regulations (e.g., HIPAA, PCI DSS, GDPR) and geographical data residency requirements adds immense complexity, particularly in data retention, archiving, and disposal phases, demanding specialized expertise.
- Data Quality Issues: Poor data quality — inaccuracies, inconsistencies, or incompleteness — can undermine the value derived from data at any stage of the lifecycle. Remedying these issues retrospectively is often costly and time-consuming, impacting downstream analytics and AI/ML model performance.
- Scalability and Performance Concerns: As data volumes explode, traditional infrastructure struggles to cope with the demands of storage, processing, and rapid analysis, especially for real-time applications or large-scale machine learning, creating bottlenecks in the data flow.
- MLOps Complexity: Integrating machine learning models into the data lifecycle introduces further complexities. Managing data versions, model training pipelines, feature stores, and continuous model deployment (MLOps) requires specialized tools and expertise to ensure reproducibility, reliability, and ethical AI practices.
- Cost Management: Balancing the costs associated with storage (hot vs. cold), processing, data transfer, and specialized tooling across the entire lifecycle can be challenging, particularly for large-scale data environments where efficient resource allocation is paramount.
Business Value and ROI of Effective Data Lifecycle Management
Investing in a robust data lifecycle management strategy, underpinned by an Integrated Data Management Platform, yields substantial returns and strategic advantages:
- Enhanced Data Quality and Trust: By implementing stringent data quality management throughout the lifecycle, organizations ensure data accuracy, consistency, and reliability. This builds trust in data, leading to more confident decision-making and more effective AI/ML models.
- Improved Regulatory Compliance and Risk Reduction: A structured approach to data retention, archiving, and secure disposal significantly reduces the risk of non-compliance fines, legal penalties, and reputational damage. Data Lineage and Data Catalogs provide auditable trails essential for regulatory scrutiny.
- Faster Time-to-Insight and Innovation: Streamlined data processing and analysis, often automated with DataOps principles, accelerate the journey from raw data to actionable insights. This enables quicker responses to market changes and fosters a culture of data-driven innovation.
- Optimized Resource Utilization and Cost Efficiency: Intelligent data tiering (moving data to appropriate storage based on access frequency), efficient processing, and timely disposal of unnecessary data can lead to significant cost savings in storage, compute, and data management overheads across the entire data lifecycle.
- Accelerated MLOps and AI/ML Model Deployment: With high-quality, well-governed data flowing through the lifecycle, organizations can train, deploy, and monitor machine learning models more efficiently. Features like AI-powered Data Quality and seamless integration with MLOps pipelines lead to faster model iterations and more accurate predictive analytics.
- Empowered Data Consumers: A comprehensive Data Catalog and well-defined Data Mesh structures empower business users and data scientists to easily discover, access, and understand relevant data, reducing dependency on central IT and fostering self-service analytics and data product creation.

Comparative Insight: Modern Data Lifecycle Platforms vs. Traditional Data Architectures
The landscape of data management has evolved dramatically. Understanding how modern Integrated Data Management Platforms, driven by concepts like DataOps and Data Mesh, differentiate from traditional Data Lakes and Data Warehouses is crucial for effective data lifecycle management.
Traditional Data Warehouses were designed primarily for structured, historical data analysis, focusing on business intelligence and reporting. They excel at serving aggregated data for known queries, but often struggle with the variety, velocity, and volume of modern data sources, particularly unstructured and semi-structured data. Managing the full data lifecycle within a traditional data warehouse can be rigid, with lengthy ETL processes and limited flexibility for real-time data needs or experimental AI/ML workloads. Data governance, while present, often relies on manual processes and is less integrated across the entire data journey. Competitors like IBM Data and AI, while offering robust solutions, sometimes carry the legacy of these more structured approaches.
Traditional Data Lakes emerged to address the limitations of data warehouses, offering a scalable repository for raw, unformatted data of any type. While providing flexibility for storing diverse data, data lakes often suffered from becoming “data swamps” – vast repositories where data was ingested without proper governance, metadata, or quality controls. This made data discovery, understanding, and ensuring data quality across its lifecycle incredibly challenging. The “garbage in, garbage out” problem was rampant, hindering effective data usage and analysis, particularly when compared to the structured management ethos of an Integrated Data Management Platform.
In contrast, Integrated Data Management Platforms, built on Cloud-Native Architectures and embodying principles of DataOps and Data Mesh, offer a holistic approach to the data lifecycle that significantly outperforms traditional models:
- Unified Governance and Discovery: Unlike fragmented traditional systems, modern platforms integrate features like a comprehensive Data Catalog, robust Data Lineage tracking, and continuous Data Quality Management across all data stages. This ensures discoverability, trustworthiness, and compliance from ingestion to disposal, a capability often disparate in traditional data environments.
- Agility and Automation: DataOps automates data pipelines, testing, and deployment, drastically reducing the time it takes to deliver high-quality data products. This contrasts with the often manual and slow processes found in traditional setups, making the data lifecycle far more dynamic and responsive to business needs.
- Support for Diverse Workloads: These platforms are designed to handle both structured and unstructured data, supporting a wide array of workloads from traditional BI to advanced analytics, streaming data, and complex AI/ML applications. Their cloud-native foundation, common to services like AWS Data Services, Azure Data Platform, and Google Cloud Data Analytics, provides elastic scalability on demand.
- Decentralized Ownership (Data Mesh): Data Mesh architecture shifts ownership of data domains to specialized teams, treating data as a product. This empowers domain experts to manage their data’s lifecycle, ensuring higher data quality, better understanding, and faster delivery of data products, a significant departure from centralized IT bottlenecks inherent in older models.
- Seamless AI/ML Integration: With dedicated MLOps capabilities, AI-powered Data Quality, and robust infrastructure for predictive analytics, these platforms are purpose-built to support the entire lifecycle of machine learning models, from feature engineering to deployment and monitoring. This proactive integration contrasts sharply with the often retrospective or add-on nature of AI/ML in traditional architectures.
While competitors like Informatica offer powerful tools, the strength of an integrated platform lies in its cohesive approach to managing every phase of the data lifecycle, unifying diverse data capabilities under a single, well-governed umbrella that maximizes efficiency and value.
World2Data Verdict: The Imperative for an Integrated Data Lifecycle Strategy
The future of data management is undeniably integrated, automated, and governed by intelligent systems that span the entire data lifecycle. Organizations that continue to grapple with fragmented data strategies, manual processes, and siloed data initiatives will increasingly find themselves at a severe competitive disadvantage. World2Data.com believes that the imperative for enterprises moving forward is not just to collect more data, but to master its journey from inception to disposal. Embracing an Integrated Data Management Platform, fueled by DataOps and Data Mesh principles and built on a cloud-native architecture, is no longer an option but a strategic necessity. This approach promises not only enhanced compliance and reduced risk but also unlocks unprecedented opportunities for innovation, faster time-to-market for data products and AI/ML models, and ultimately, a more intelligent and resilient enterprise. Prioritize a unified vision for your data lifecycle; the rewards in efficiency, insight, and competitive edge are profound and indispensable for any modern enterprise.