Data Observability: Monitoring the Health of Your Data Systems for Unwavering Trust
In the relentlessly data-driven landscape of modern enterprise, the integrity and reliability of data are paramount. Data Observability is no longer a luxury but a fundamental necessity, serving as the critical discipline that ensures the health, quality, and trustworthiness of your entire data ecosystem. It provides comprehensive visibility into data pipelines, proactively identifying and resolving issues before they impact business operations, ultimately fostering unwavering confidence in data-led decisions.
Introduction: The Imperative of Data Health in a Complex World
As organizations increasingly leverage vast and intricate data pipelines for everything from operational analytics to powering advanced Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) models, the risk of data issues—be it stale data, schema drift, or outright corruption—grows exponentially. Traditional monitoring tools often fall short, offering fragmented views that leave critical gaps in understanding data health. This is where Data Observability emerges as a transformative solution, bringing a holistic approach to data management akin to Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) for software infrastructure. It provides real-time insights into data quality, lineage, and performance, ensuring that the data fueling strategic decisions is accurate, timely, and reliable. The objective of this deep dive is to explore the core tenets, architectural components, business value, and strategic advantages of implementing robust Data Observability practices.
Core Breakdown: Architecting for Uncompromised Data Health
At its heart, Data Observability is a comprehensive platform category built on a suite of core technologies and architectural principles designed to give data teams unparalleled insight into their data systems. It extends beyond simple data quality checks, offering a multi-dimensional view of data health across its entire lifecycle.
Key Architectural Pillars and Technologies:
- Real-time Monitoring: This is the bedrock of any effective Data Observability solution. It involves continuously tracking data as it moves through pipelines, from ingestion to consumption. Key metrics include data freshness, volume, and schema integrity, ensuring immediate detection of deviations from expected patterns. Tools enable monitoring of data assets in motion and at rest, across diverse sources like data lakes, warehouses, and streaming platforms.
- Automated Anomaly Detection: Leveraging statistical methods and Machine Learning, Data Observability platforms automatically identify unusual patterns or outliers in data. This AI-powered anomaly detection can flag sudden drops in data volume, unexpected changes in data distribution, or deviations in critical data values. This proactive alerting mechanism is crucial for catching problems before they escalate.
- Metadata Analysis: Comprehensive metadata management is central to understanding data. This includes technical metadata (schema, data types), operational metadata (run times, job status), and business metadata (definitions, ownership). By analyzing metadata, systems can reconstruct data lineage, understand schema evolution, and provide context for detected anomalies.
- Proactive Alerting: Beyond simply detecting issues, a robust Data Observability system offers intelligent alerting. This means notifying relevant stakeholders via appropriate channels (Slack, email, PagerDuty) with contextual information, reducing alert fatigue and enabling rapid incident response. Predictive data quality issues can even be flagged before they manifest fully.
- Data Lineage: Understanding the journey of data—where it came from, how it was transformed, and where it’s being used—is indispensable. Data lineage tracking allows teams to trace the root cause of issues, assess the impact of changes, and ensure compliance. This feature is a critical component of strong data governance.
- Data Quality Monitoring: This pillar ensures that data conforms to predefined rules and expectations. It covers aspects like completeness, accuracy, consistency, validity, and uniqueness. Advanced solutions apply ML for pattern recognition in data behavior, ensuring high-quality data at all stages.
- Usage Auditing: Tracking how data is accessed and utilized provides valuable insights into data consumption patterns, helps identify stale or underutilized datasets, and supports compliance with data governance policies.
Challenges and Barriers to Adoption: Navigating the Complexities
While the benefits of Data Observability are clear, organizations often face several hurdles during its implementation and adoption:
- Legacy Infrastructure Integration: Many enterprises operate with a mix of modern cloud-based systems and on-premise legacy data infrastructure. Integrating Data Observability tools across such heterogeneous environments can be complex and resource-intensive.
- Data Volume and Velocity: The sheer scale and speed of data generated today can overwhelm traditional monitoring systems. Processing and analyzing petabytes of data in real-time requires significant computational power and sophisticated algorithms, making comprehensive observability challenging.
- Data Drift and Schema Evolution: Data schemas are rarely static. As business requirements change, so do data models. Managing and tracking schema evolution across numerous pipelines and ensuring downstream systems adapt gracefully is a continuous challenge, often leading to data quality issues if not observed effectively.
- MLOps Complexity: For organizations heavily invested in AI/ML, the complexity of MLOps pipelines adds another layer. Monitoring model inputs, outputs, feature stores, and model performance decay requires specialized observability capabilities that integrate seamlessly with ML workflows.
- Alert Fatigue and Noise: Without intelligent alerting and root cause analysis, a Data Observability platform can generate a deluge of alerts, leading to alert fatigue among data teams. Differentiating between critical issues and minor fluctuations requires sophisticated anomaly detection and prioritization.
- Skill Gap: Implementing and managing advanced Data Observability solutions requires a blend of data engineering, data science, and operations skills, which can be scarce.
Business Value and Return on Investment (ROI): The Strategic Imperative
The investment in Data Observability yields substantial returns across various business functions:
- Faster Model Deployment and Reliability for AI/ML: By ensuring the quality and freshness of data feeding AI/ML models, organizations can accelerate model development and deployment cycles. AI-powered anomaly detection and ML for root cause analysis significantly reduce the time spent debugging data issues, directly translating into faster time-to-market for AI-driven products and more reliable model performance.
- Enhanced Data Quality for AI: High-quality data is the lifeblood of effective AI. Data Observability ensures that the data used for training and inference is consistently accurate, complete, and reliable, preventing “garbage in, garbage out” scenarios that undermine AI initiatives.
- Reduced Data Downtime and Business Impact: Proactive detection of data issues prevents costly disruptions to business operations, analytics dashboards, and critical reports. By identifying and resolving data problems quickly, businesses can avoid financial losses, reputational damage, and missed opportunities.
- Increased Data Trust and Confidence: Reliable data fosters confidence among all stakeholders, from executives making strategic decisions to data scientists building models. This trust empowers better, more informed decision-making across the organization.
- Improved Operational Efficiency for Data Teams: Data professionals spend significantly less time on reactive firefighting and debugging data quality issues. This frees up valuable resources to focus on innovation, feature development, and strategic data initiatives, boosting overall productivity.
- Stronger Data Governance and Compliance: With features like data lineage tracking, data quality monitoring, and usage auditing, Data Observability provides the necessary transparency and controls to enforce data governance policies and ensure regulatory compliance (e.g., GDPR, CCPA).
- Optimized Resource Utilization: By monitoring data flow and usage, organizations can identify inefficiencies, optimize storage, and improve compute resource allocation within their data infrastructure.
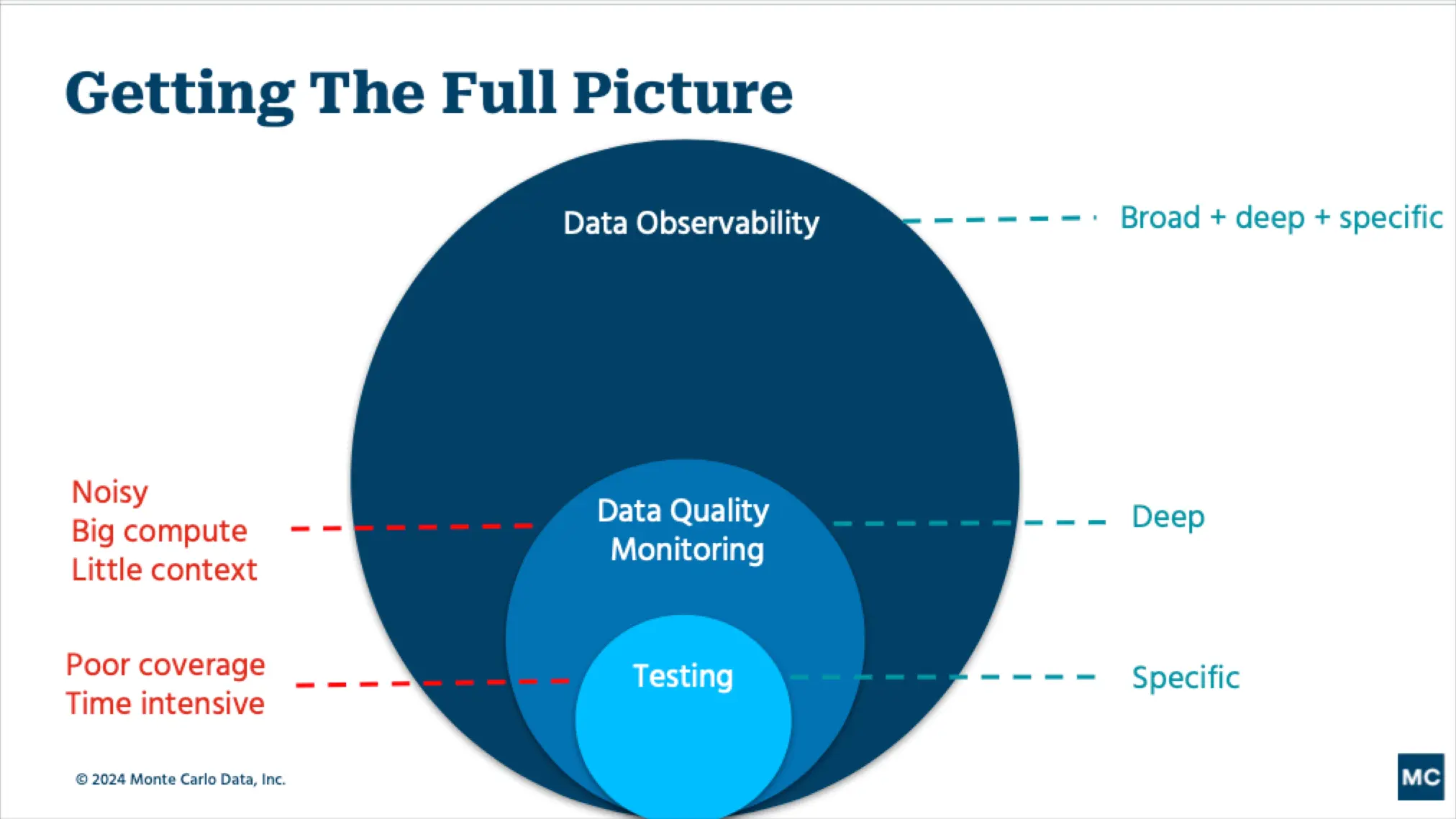
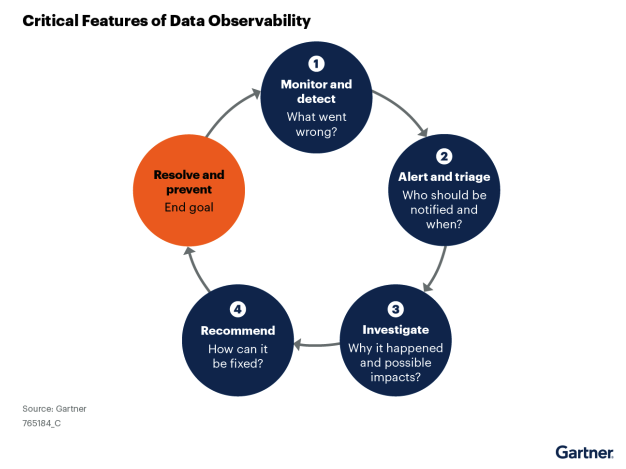
Figure 1: Visual representation of the interconnected pillars of Data Observability, highlighting real-time monitoring and data quality.
Comparative Insight: Data Observability vs. Traditional Data Monitoring
To truly appreciate the value of Data Observability, it’s essential to understand how it transcends traditional data monitoring approaches, particularly those found in older data lake and data warehouse models.
Traditional Data Lakes/Warehouses: Reactive and Fragmented
Historically, data monitoring in data lakes and warehouses often involved:
- Batch-oriented Checks: Data quality checks were typically run in batches, often after data had already been loaded into the warehouse. This meant issues were discovered hours or even days later, leading to delayed problem resolution and potentially erroneous downstream analyses.
- Manual Scripting and Custom Solutions: Monitoring often relied on custom scripts, SQL queries, or basic dashboarding, requiring significant manual effort to set up and maintain. These were often siloed, offering fragmented views of data health.
- Infrastructure-Centric: Focus was primarily on the health of the infrastructure (e.g., storage, compute, network) rather than the intrinsic quality and behavior of the data itself. A pipeline could appear “green” operationally, while producing garbage data.
- Limited Lineage: Tracing data origin and transformations was often a manual, cumbersome process, relying heavily on documentation or tribal knowledge.
- Rule-Based Quality: Data quality was enforced through a fixed set of rules, which struggled to adapt to evolving data schemas or detect novel types of anomalies.
Data Observability: Proactive and Holistic
Data Observability represents a paradigm shift:
- Real-time and Continuous: Instead of batch checks, Data Observability platforms offer continuous, real-time monitoring of data at every stage of its lifecycle. This allows for immediate detection of issues, minimizing their impact.
- Automated and AI-Powered: Leveraging AI-powered anomaly detection and ML for root cause analysis, these platforms automate the identification of issues, reducing manual effort and improving accuracy. They learn expected data patterns and flag deviations proactively.
- Data-Centric: The focus shifts from infrastructure health to data health. It’s about understanding the “what” and “why” of data anomalies, not just if a job failed. This involves deep analysis of schema, volume, freshness, distribution, and lineage.
- End-to-End Lineage: Provides automated, dynamic data lineage, offering a complete map of data flow and transformations, essential for impact analysis and debugging.
- Adaptive and Intelligent: Modern Data Observability solutions adapt to changes in data patterns and schema evolution, dynamically adjusting monitoring thresholds and rules. They use intelligent alerting to prioritize critical issues and minimize noise.
- Integrated Data Governance: Seamlessly integrates data quality monitoring, lineage, and usage auditing, providing robust support for policy enforcement and compliance, which is often an afterthought in traditional setups.
While traditional monitoring focuses on the operational status of pipelines, Data Observability delves into the semantic meaning and reliability of the data itself, offering a far more comprehensive and actionable understanding of data health. This shift is particularly crucial for organizations building on modern data stacks, which demand higher agility and reliability.
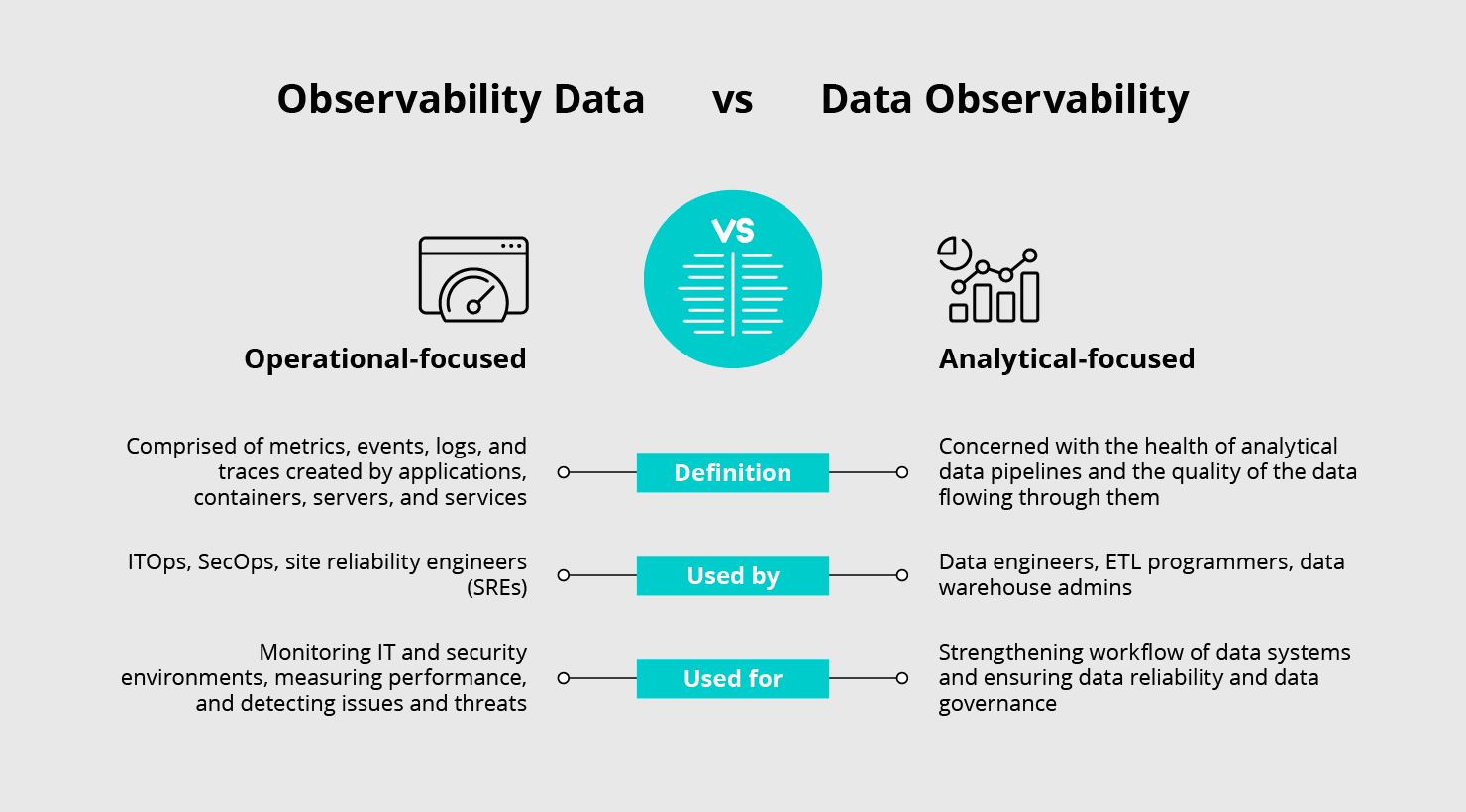
Figure 2: Distinguishing between general ‘observability data’ and the specialized practice of ‘Data Observability’ for clearer understanding.
World2Data Verdict: Embracing a Data-First Future
The accelerating pace of digital transformation and the increasing reliance on data for competitive advantage make Data Observability an indispensable component of any forward-thinking organization’s data strategy. It transcends basic monitoring, offering a proactive, intelligent, and holistic approach to ensuring data health, quality, and trustworthiness. For businesses aiming to maximize the ROI of their data investments, power reliable AI/ML initiatives, and foster an environment of data trust, adopting a robust Data Observability platform is not merely recommended—it’s critical. Leading platforms in this space, such as Monte Carlo, Acceldata, Databand (an IBM Company), Bigeye, and Lightup, are continually innovating, offering increasingly sophisticated capabilities. World2Data recommends that enterprises prioritize the integration of comprehensive Data Observability into their data stack, focusing on solutions that offer end-to-end lineage, AI-driven anomaly detection, and seamless integration with existing tools. The future belongs to organizations that can not only collect data but also flawlessly understand, trust, and leverage its full potential. Embracing Data Observability today is an investment in the reliability and success of tomorrow’s data-driven initiatives.