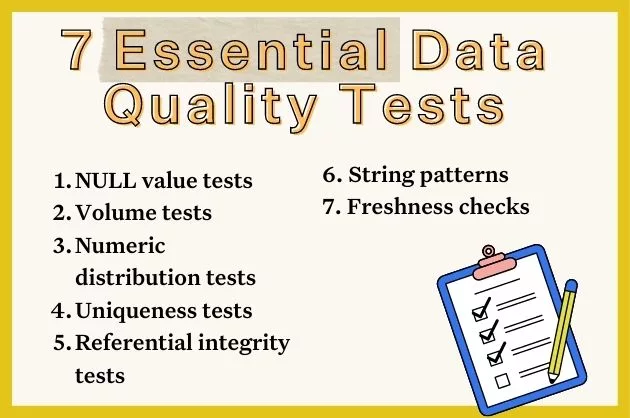
Data Quality Check: The Cornerstone of Accurate Analytics and AI
A robust Data Quality Check is not merely a technical step; it is the cornerstone of effective decision-making in any data-driven organization. This critical process ensures that raw data transforms into reliable, trustworthy information, ready to fuel insightful analysis, robust machine learning models, and strategic growth. Without diligent attention to data quality, even the most sophisticated analytical tools or AI algorithms will produce misleading or erroneous outcomes, undermining business confidence and potentially leading to significant financial and reputational damage.
Introduction: The Imperative of Data Quality in the Modern Data Landscape
In today’s fast-paced digital economy, data is often hailed as the new oil, driving innovation and competitive advantage across every industry. However, just like crude oil, raw data needs extensive refining before it can deliver true value. This refining process, known as a Data Quality Check, is paramount. It encompasses a series of activities designed to identify, assess, and rectify imperfections within data sets, ensuring their fitness for intended use. From supporting critical business intelligence dashboards to feeding complex artificial intelligence and machine learning models, the integrity of data directly impacts the validity and reliability of every outcome.
The increasing volume, velocity, and variety of data streams—often originating from disparate sources and managed across diverse platforms like data lakes, data warehouses, and streaming architectures—exacerbate the challenges of maintaining high data quality. Organizations leverage a spectrum of solutions, falling into categories such as dedicated Data Quality Tools, comprehensive Data Governance Platforms, ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tools with integrated DQ features, and emerging Data Observability Platforms. These tools utilize core technologies ranging from rules-based validation and sophisticated profiling engines to machine learning algorithms for anomaly detection, all underpinned by metadata-driven approaches for both batch processing and real-time monitoring.
This article will delve into the critical role of the Data Quality Check, exploring its fundamental components, the challenges it addresses, the advanced technologies it employs, and its profound impact on business value and competitive advantage. We will also compare modern data quality paradigms with traditional approaches and offer a forward-looking perspective on its evolution.
Core Breakdown: The Anatomy of a Robust Data Quality Check Framework
A comprehensive Data Quality Check framework is multifaceted, addressing various dimensions of data quality to ensure data is accurate, complete, consistent, timely, and relevant. It’s an ongoing process, not a one-time event, deeply integrated into the data lifecycle from ingestion to consumption.
Why Data Quality Check Matters: Foundation for Reliable Insights and Strategic Growth
The significance of a rigorous Data Quality Check cannot be overstated. Every analytical endeavor, from descriptive reporting and diagnostic analysis to predictive modeling and prescriptive AI, hinges on the integrity of its underlying data. Without a comprehensive DQ process, the derived insights can be fundamentally flawed, leading to misguided strategies and poor business decisions. For instance, customer segmentation based on inaccurate demographic data will fail to target the right audience, while financial forecasts built on inconsistent transaction records can lead to erroneous budgeting. Superior data quality builds a foundation of trust, enabling organizations to confidently leverage their data assets for competitive advantage.
Common Data Quality Issues: Navigating the Pitfalls of Imperfect Data
Data, by its very nature, is prone to imperfections. Understanding these common issues is the first step toward effective remediation:
- Inaccuracies and Inconsistencies: Data often contains typographical errors, outdated information, or conflicting entries across different sources. For example, a customer’s address might vary between the sales and billing systems. These inconsistencies distort analytical outcomes and create an unreliable data landscape.
- Missing Values and Duplicates: Gaps in data sets can skew statistical analyses and lead to biased models, while duplicate records inflate counts, waste storage, and complicate master data management. Identifying and resolving these issues is a core component of effective Data Quality Check.
- Outliers and Irrelevant Data: Extreme values that don’t represent the true data distribution (outliers) or data that serves no purpose for the intended analysis (irrelevant data) can introduce noise and compromise the accuracy of models. A thorough DQ process identifies and manages these anomalies, often through statistical methods or domain expertise.
- Timeliness Issues: Data that is not up-to-date can lead to reactive rather than proactive decisions. For example, inventory levels that aren’t refreshed in real-time can result in stockouts or overstocking.
- Non-Conformity: Data that doesn’t adhere to predefined formats, standards, or business rules (e.g., a phone number stored in an invalid format).
Key Steps in Data Quality Check: A Systematic Approach
Implementing an effective Data Quality Check involves several critical steps, often supported by key data governance features:
- Data Profiling: This initial step involves scanning data to collect statistics and information about its characteristics, such as value distributions, data types, uniqueness, completeness, and relationships. Data profiling provides a snapshot of the current state of data quality, helping to uncover hidden issues and understand data structure. It’s a foundational data governance feature, giving visibility into the data landscape.
- Data Validation Rules: Based on profiling insights and business requirements, explicit rules are defined to check data against predefined standards. Examples include checking if a date field is within a valid range, if a postal code matches a specific pattern, or if a numerical field falls within expected thresholds. Policy enforcement mechanisms ensure these rules are applied consistently.
- Data Cleansing and Standardization: Once issues are identified, data cleansing involves correcting, removing, or standardizing flawed entries. This might include parsing and reformatting data, correcting spelling errors, merging duplicate records, or imputing missing values using various techniques. Standardization ensures data conforms to a unified format across systems.
- Data Transformation: Processes format data consistently and convert it into a structure suitable for analysis and integration across different systems. This often happens in conjunction with cleansing within ETL pipelines.
- Metadata Management and Data Lineage: Maintaining accurate metadata (data about data) provides crucial context, explaining data definitions, ownership, and quality rules. Data lineage traces data’s journey from source to destination, showing transformations and aggregations, which is invaluable for understanding the root cause of quality issues and building trust. Data quality dashboards provide a centralized view of these metrics, allowing stakeholders to monitor data health.
- Master Data Management (MDM) Integration: Ensuring that core business entities (customers, products, locations) are consistent and accurate across the enterprise, often through integration with MDM platforms.
Tools and Techniques for Data Quality Check: Leveraging Automation and AI
Modern Data Quality Check initiatives leverage a blend of sophisticated tools and methodologies:
- Automated Platforms: Specialized software solutions, often integrated within Data Governance Platforms or ETL suites, can automate large parts of the DQ process. These platforms handle vast data volumes efficiently, consistently applying quality rules, and providing dashboards for monitoring. Leading tools include Informatica Data Quality, Talend Data Quality, IBM InfoSphere Information Server, and Ataccama ONE.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration: This is where the landscape is rapidly evolving. AI/ML capabilities significantly enhance DQ by:
- Anomaly Detection: ML algorithms can identify unusual patterns or outliers that might indicate data errors, even without predefined rules.
- Automated Rule Suggestion: AI can analyze data patterns and suggest potential data quality rules, reducing manual effort.
- Pattern Recognition for Data Matching and Cleansing: ML excels at identifying fuzzy matches for duplicate detection and suggesting corrections for inconsistent entries.
- Predictive Data Quality: Using historical data quality issues, AI can predict where future problems are likely to occur, allowing for proactive interventions.
- Root Cause Analysis of Data Quality Issues: ML can help trace back the likely source of data quality problems by analyzing lineage and historical changes.
- Manual Review and Expert Systems: For complex or nuanced data issues that require deep contextual understanding or subjective judgment, human oversight and expert knowledge remain invaluable. Manual reviews complement automated systems, especially in scenarios where AI still struggles with ambiguity or business-specific nuances.
- Data Observability Platforms: Newer entrants like Soda.ai and Monte Carlo offer real-time monitoring and alerting for data quality issues, akin to application performance monitoring for data pipelines. They help detect data drift, schema changes, and freshness issues proactively.
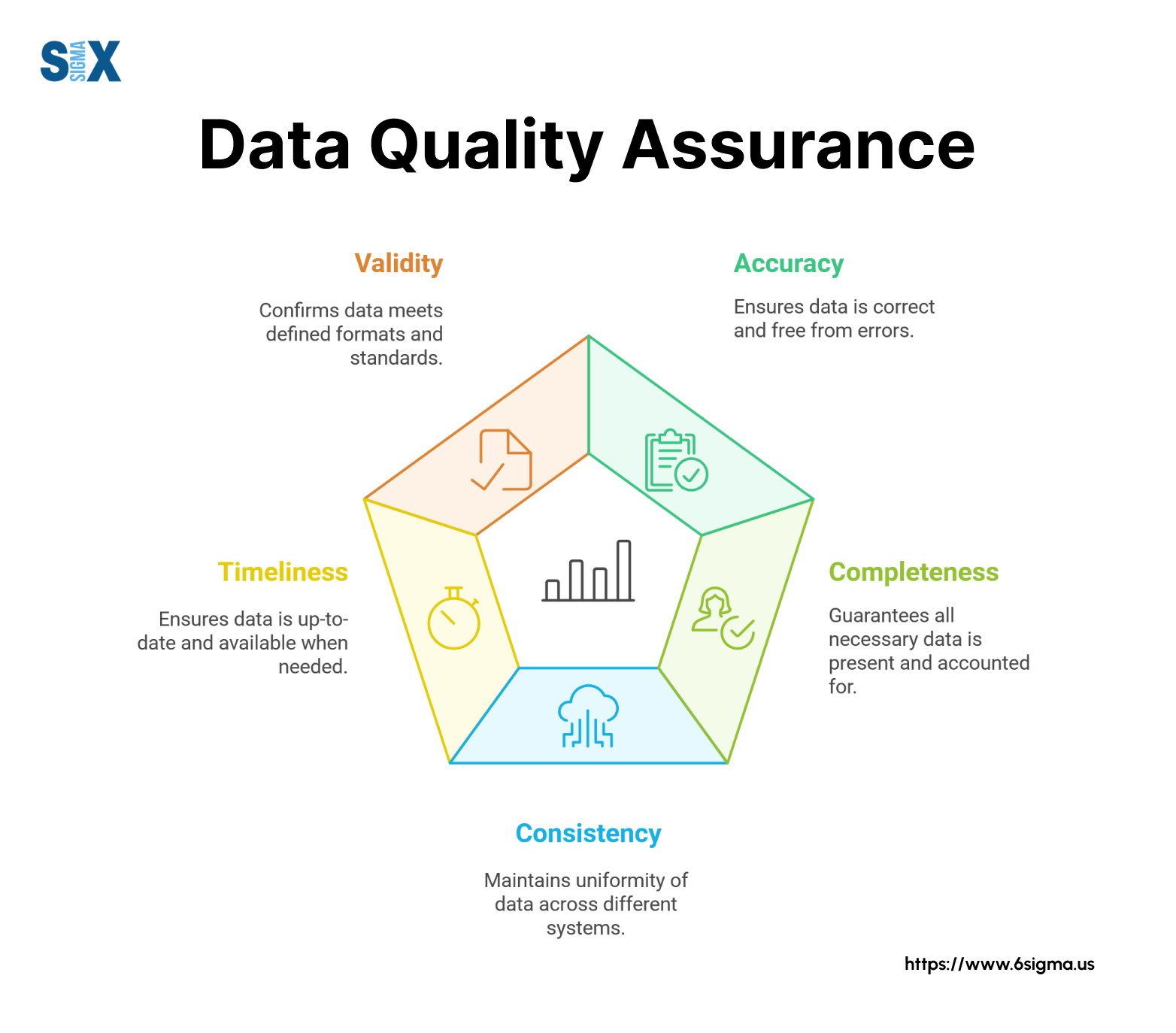
Challenges/Barriers to Adoption of Effective Data Quality Checks
Despite its critical importance, implementing and maintaining a robust Data Quality Check framework faces several significant hurdles:
- Complexity of Disparate Data Sources: Modern enterprises ingest data from hundreds, if not thousands, of sources, each with its own schema, format, and inherent quality issues. Integrating and harmonizing this diverse data for quality checks is a monumental task.
- Lack of Organizational Buy-in and Data Literacy: Without a culture that values data quality, efforts can falter. Many employees may not understand the downstream impact of poor data entry or maintenance, leading to a lack of accountability. Senior leadership support is crucial for allocating resources and establishing data quality as a strategic priority.
- Evolving Data Schemas and Data Drift: Data schemas are not static. Changes in source systems, new applications, or evolving business requirements can introduce schema changes or “data drift” that invalidate existing quality rules and pipelines, requiring continuous adaptation.
- Scalability for Big Data: Traditional data quality tools may struggle to process and validate petabytes of data in a timely and cost-effective manner. New architectures and distributed computing are essential for handling the sheer volume and velocity of big data.
- Integration with Existing MLOps Pipelines: For AI and ML initiatives, data quality is not a one-time check but a continuous process integrated into MLOps workflows. Ensuring data quality throughout feature engineering, model training, and inference, and detecting concept or data drift, adds a layer of complexity.
- Defining “Quality”: What constitutes “good” data often varies by business context and use case. Establishing universally agreed-upon definitions and metrics for data quality across an organization can be challenging.
Business Value and ROI of Superior Data Quality
The investment in a comprehensive Data Quality Check yields substantial returns:
- Enhanced Decision-Making: With high-quality data, business leaders can make more informed, confident decisions, leading to better strategic outcomes, optimized operations, and competitive advantages. The clarity provided by accurate data is invaluable.
- Increased Trust in Data Assets: Reliable data builds trust across the organization, encouraging wider adoption of data-driven approaches and fostering a culture where insights are universally respected and acted upon. This trust extends to external stakeholders, improving customer satisfaction and regulatory compliance.
- Faster Time-to-Insight and Model Deployment: By reducing the time spent cleaning and validating data, analysts and data scientists can focus more on generating insights and building models. High-quality data accelerates the entire data pipeline, leading to quicker deployment of AI/ML models and faster time-to-value.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Poor data quality leads to rework, inefficient processes, and increased error rates. For example, incorrect customer addresses lead to failed deliveries, and inaccurate product data causes inventory discrepancies. A robust DQ process minimizes these costly operational inefficiencies.
- Improved Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management: Many industries face strict regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA) regarding data privacy, accuracy, and lineage. High data quality ensures compliance, reducing the risk of fines and legal repercussions.
- Better Customer Experiences: Accurate customer data enables personalized marketing, efficient customer service, and tailored product recommendations, leading to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Comparative Insight: Evolving Beyond Traditional Data Quality Approaches
The landscape of Data Quality Check has evolved significantly from its earlier iterations, primarily driven by the demands of big data, real-time processing, and artificial intelligence. Traditionally, data quality was often a reactive process, primarily managed within ETL tools during data warehousing projects. Data quality issues were identified and addressed in batch mode, typically after data had already been ingested, often through manual review or simple rule-based validations.
In this traditional model, a data lake or data warehouse would ingest raw data, and then a series of transformations and cleansing steps would attempt to “fix” issues before the data was presented for analysis. This approach, while functional for structured, predictable data, struggles with the volume, velocity, and variety of modern data. It often lacked comprehensive metadata management, proactive monitoring, and real-time capabilities, making it difficult to detect subtle data drift or emergent quality issues rapidly.
Modern Data Quality Check platforms and methodologies represent a paradigm shift. They move from reactive, post-ingestion cleansing to proactive, continuous, and integrated quality assurance throughout the entire data lifecycle. Key differentiators include:
- Proactive vs. Reactive: Modern systems integrate DQ at the source, during ingestion, and continuously throughout data pipelines. Data observability platforms, for instance, monitor data freshness, volume, and schema changes in real-time, alerting data teams to anomalies before they impact downstream analytics or AI models.
- AI/ML-Driven Detection: Instead of relying solely on predefined rules, advanced platforms leverage machine learning for anomaly detection, automated rule suggestion, and pattern recognition. This enables the discovery of subtle quality issues that human-defined rules might miss, adapting to evolving data characteristics.
- Comprehensive Data Governance and Lineage: Modern DQ is deeply embedded within broader data governance frameworks. Solutions like Collibra and Ataccama ONE provide robust metadata management, data lineage tracking, and policy enforcement, giving full transparency into data’s origin, transformations, and quality status. This is crucial for regulatory compliance and building trust.
- Scalability and Performance: Designed for big data environments, contemporary DQ solutions leverage distributed computing and cloud-native architectures to process massive datasets efficiently, whether in batch or streaming contexts.
- Self-Service and Collaboration: Tools like Great Expectations and OpenRefine empower data analysts and engineers to define and manage data quality expectations directly, fostering a collaborative approach rather than solely relying on a centralized DQ team.
- Integration with MLOps: For AI initiatives, DQ is no longer a separate concern but an integral part of the MLOps pipeline, ensuring the quality of training data, monitoring feature stores, and detecting concept drift in production models.
This evolution means that while traditional data lakes and data warehouses remain vital, the tools and processes for ensuring data quality within and around them have become significantly more sophisticated, proactive, and intelligent. The focus has shifted from merely fixing data to preventing quality issues at the source and continuously validating data fitness for every specific use case.
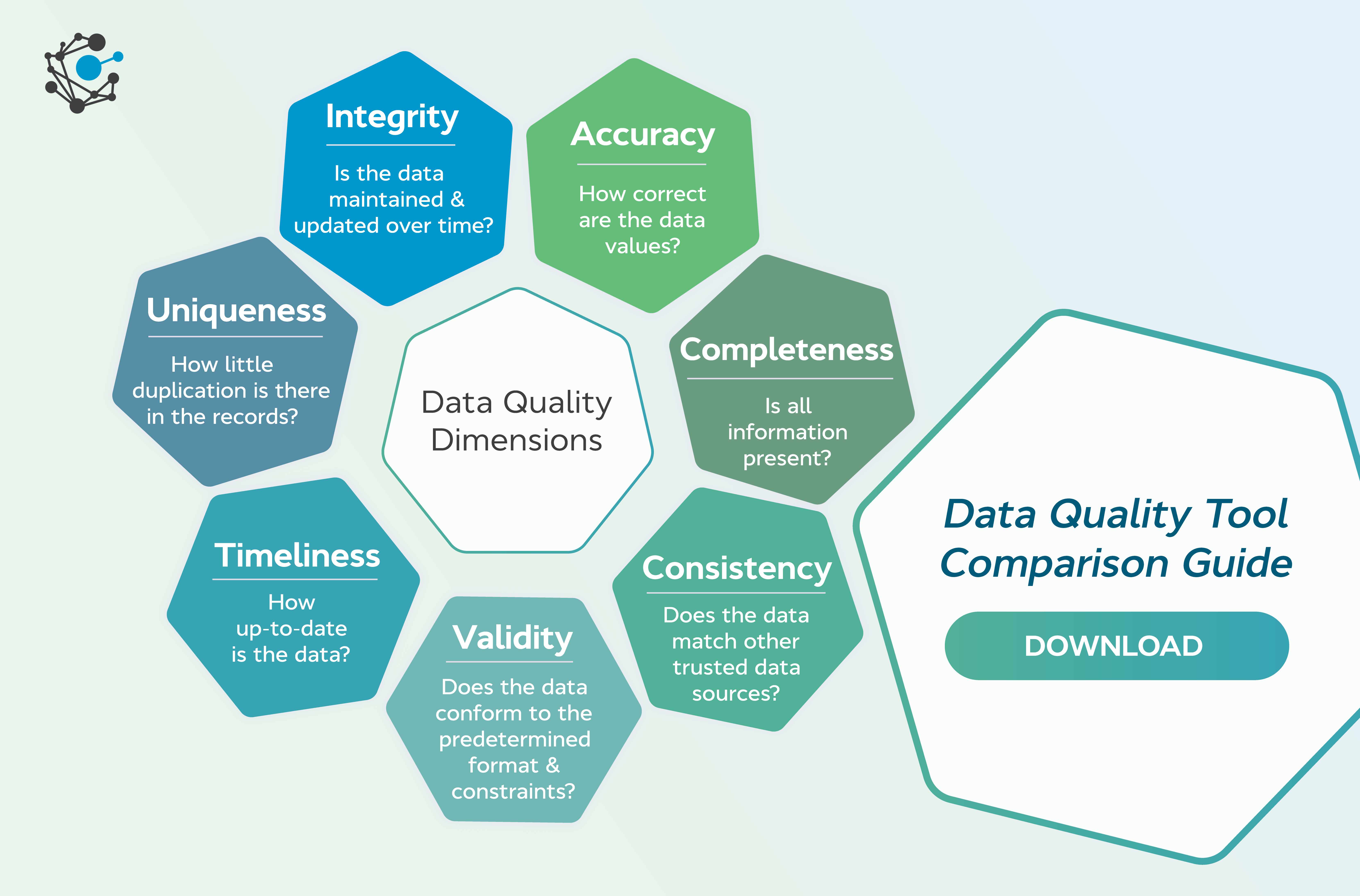
World2Data Verdict: Embracing Data Quality as a Strategic Business Imperative
The imperative for robust Data Quality Check is no longer a technical nicety but a fundamental business necessity for any organization aspiring to be data-driven. World2Data’s verdict is clear: enterprises must transcend traditional, reactive data cleansing to adopt a proactive, intelligent, and continuously integrated data quality strategy. Invest in modern data quality platforms that leverage AI/ML for automated anomaly detection, predictive quality, and seamless integration with your existing data governance and MLOps frameworks. Prioritize data literacy across all departments, establishing a culture where every data interaction contributes to data integrity. The future of competitive advantage belongs to those who view data quality not as a cost center, but as an indispensable strategic investment, directly fueling innovation, enhancing decision-making, and safeguarding long-term business resilience.