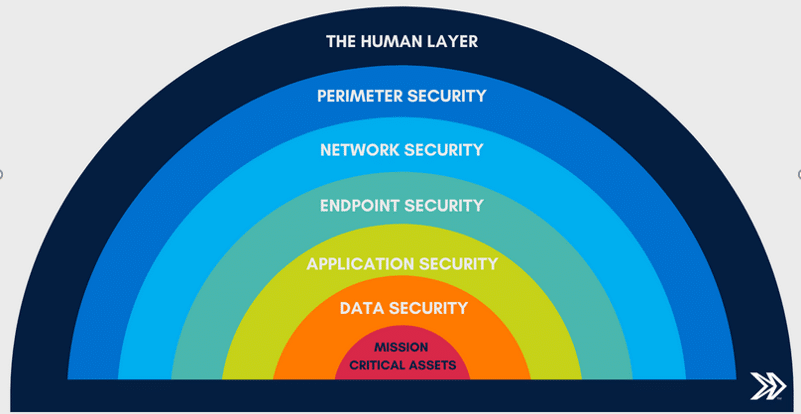
Data Security Layer: Fortifying Your Defenses for Sensitive Information Protection
Platform Category: Data Security, Data Protection, Access Control
Core Technology/Architecture: Encryption (at rest and in transit), Tokenization, Data Masking, Access Control Mechanisms (RBAC, ABAC), Data Loss Prevention (DLP), Zero Trust Architecture
Key Data Governance Feature: Data Classification, Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), Audit Logging and Monitoring, Data Minimization, Compliance Policy Enforcement
Primary AI/ML Integration: Anomaly Detection for access patterns, User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA), Automated threat detection, AI-driven data classification, Automated policy enforcement
Main Competitors/Alternatives: Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions, Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools, Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) platforms, Database Security solutions, Data Governance platforms with security modules
In today’s hyper-connected digital landscape, where information is constantly in motion, a robust Data Security Layer is no longer a luxury but an absolute necessity for safeguarding sensitive information. Organizations grapple daily with the pervasive threat of data breaches, making the strategic implementation of a comprehensive Data Security Layer paramount to their operational integrity and reputational standing. This crucial defensive stratum acts as the ultimate guardian, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data throughout its lifecycle, from creation to archival.
Introduction: Elevating Data Protection to a Strategic Imperative
The relentless expansion of data volumes, coupled with the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, has transformed data security from a purely IT concern into a strategic business imperative. Traditional perimeter-based security measures, while still important, are no longer sufficient to protect sensitive assets in an era of cloud computing, remote workforces, and pervasive data sharing. This article will delve deep into the concept of a Data Security Layer, exploring its fundamental components, the cutting-edge technologies that empower it, and its indispensable role in building resilient and compliant data ecosystems. We will uncover how a well-architected Data Security Layer provides not just protection, but also a foundation for trust, innovation, and sustained business growth.
Core Breakdown: The Multi-Faceted Architecture of a Modern Data Security Layer
A sophisticated Data Security Layer is not a single tool but an integrated framework of technologies and processes designed to shield data across its entire lifecycle. It provides an adaptable and comprehensive defense, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected regardless of its location or state.
Key Components and Technologies
- Encryption (at rest and in transit): This fundamental security measure scrambles data into an unreadable format, rendering it unintelligible to unauthorized parties.
- Encryption at Rest: Protects data stored on databases, file systems, or cloud storage. This can range from full-disk encryption to more granular column-level or cell-level encryption within databases.
- Encryption in Transit: Secures data as it moves across networks, utilizing protocols like TLS/SSL for web traffic or VPNs for secure communication channels.
- Tokenization and Data Masking: These techniques protect sensitive data by substituting it with non-sensitive equivalents.
- Tokenization: Replaces actual sensitive data (e.g., credit card numbers, PII) with a unique, randomly generated token. The original data is stored separately in a secure vault, making the token useless to an attacker even if intercepted.
- Data Masking: Creates realistic, yet fictitious, versions of sensitive data for use in non-production environments like development, testing, or training. This prevents the exposure of real sensitive information while maintaining data utility for these critical processes.
- Granular Access Control Mechanisms: Ensuring that only authorized individuals and systems can access specific data is paramount.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assigns permissions based on a user’s role within an organization, simplifying management for large user bases.
- Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC): Offers more dynamic and fine-grained control, where access decisions are made based on a combination of user attributes (e.g., department, location), resource attributes (e.g., sensitivity, creator), and environmental conditions (e.g., time of day, device).
- Privileged Access Management (PAM): Specifically manages and monitors access for accounts with elevated permissions, which are often targets for attackers.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP solutions monitor, detect, and block sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control. They can operate across various vectors:
- Endpoint DLP: Prevents data leakage from workstations and laptops.
- Network DLP: Monitors data in transit across the network.
- Cloud DLP: Secures data stored and processed in cloud environments.
- Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA): This security model operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” Every user, device, and application attempting to access data, whether inside or outside the network perimeter, must be authenticated and authorized. This approach inherently strengthens the Data Security Layer by reducing the implicit trust once granted to internal networks.
Key Data Governance Features within the Data Security Layer
Effective data security is inextricably linked with robust data governance. A comprehensive Data Security Layer integrates several governance features to maintain control and ensure compliance.
- Data Classification: Identifying and categorizing data by its sensitivity, value, and regulatory requirements (e.g., public, internal, confidential, restricted). This crucial step dictates the appropriate security controls to be applied. AI-driven data classification tools can automate and accelerate this process, especially across vast and varied datasets.
- Audit Logging and Monitoring: Comprehensive logging of all data access attempts, modifications, and security events provides an immutable record for forensic analysis, compliance audits, and proactive threat detection. Continuous monitoring helps identify suspicious activities in real-time.
- Data Minimization: Adhering to the principle of collecting and retaining only the data absolutely necessary for a specific purpose. This reduces the attack surface and the potential impact of a data breach.
- Compliance Policy Enforcement: Automatically enforcing policies derived from regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, CCPA, and industry standards. This includes retention policies, data residency requirements, and consent management.
Primary AI/ML Integration for Enhanced Security
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) is transforming the capabilities of the Data Security Layer, moving it beyond reactive measures to proactive and predictive defense.
- Anomaly Detection for Access Patterns: AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets of user and system activity to establish baselines of normal behavior. Deviations from these baselines, such as unusual login times, access to sensitive data outside typical working hours, or excessive download volumes, can trigger alerts, indicating potential insider threats or compromised accounts.
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): Building upon anomaly detection, UEBA leverages ML to understand the typical behavior of individual users and entities (e.g., servers, applications). This allows the Data Security Layer to identify subtle, yet critical, behavioral anomalies that might indicate a sophisticated attack or data exfiltration attempt.
- Automated Threat Detection and Response: AI can rapidly process threat intelligence, identify new malware signatures, phishing attempts, and zero-day exploits much faster than human analysts, enabling quicker containment and response.
- AI-driven Data Classification: As mentioned, AI can automate the classification of new and existing data, ensuring that appropriate security policies are applied consistently across dynamically growing data estates.
- Automated Policy Enforcement: ML models can learn from past policy violations and successful remediations to automatically adjust security policies, enforce access rules, and even quarantine suspicious data or users in real-time without human intervention.
Challenges and Barriers to Adoption
Despite its undeniable benefits, implementing a robust Data Security Layer presents several challenges:
- Data Sprawl and Complexity: Modern enterprises deal with data residing in diverse locations – on-premises, multiple cloud providers, SaaS applications, edge devices – making it difficult to maintain a consistent security posture.
- Integration Hurdles: Integrating new security solutions with existing legacy systems and diverse data platforms can be complex, time-consuming, and resource-intensive.
- Cost and Resource Intensiveness: Implementing advanced encryption, tokenization, and AI/ML-driven security solutions requires significant investment in technology, infrastructure, and specialized personnel.
- Skill Gap: There’s a persistent shortage of cybersecurity professionals with the expertise to design, implement, and manage sophisticated data security architectures.
- Evolving Threat Landscape: Attackers constantly innovate, developing new methods to bypass defenses, requiring continuous adaptation and updates to the Data Security Layer.
Business Value and ROI
The strategic investment in a comprehensive Data Security Layer yields substantial returns:
- Enhanced Regulatory Compliance: Proactively meeting stringent data protection regulations (GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS) reduces the risk of hefty fines and legal penalties.
- Strengthened Brand Trust and Reputation: Demonstrating a strong commitment to data protection builds invaluable trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders, safeguarding brand image in an era where data breaches can be catastrophic.
- Reduced Risk of Data Breaches: By making stolen data valueless through encryption and tokenization, and preventing unauthorized access through granular controls, the financial and reputational impact of a breach is significantly mitigated.
- Operational Efficiency and Agility: Automated security processes, AI-driven threat detection, and streamlined access controls reduce manual effort and accelerate secure data handling, enabling faster innovation.
- Enabling Secure Data Sharing and Collaboration: A well-defined Data Security Layer provides the confidence to securely share data with partners, vendors, and for analytics, fostering innovation without compromising protection.
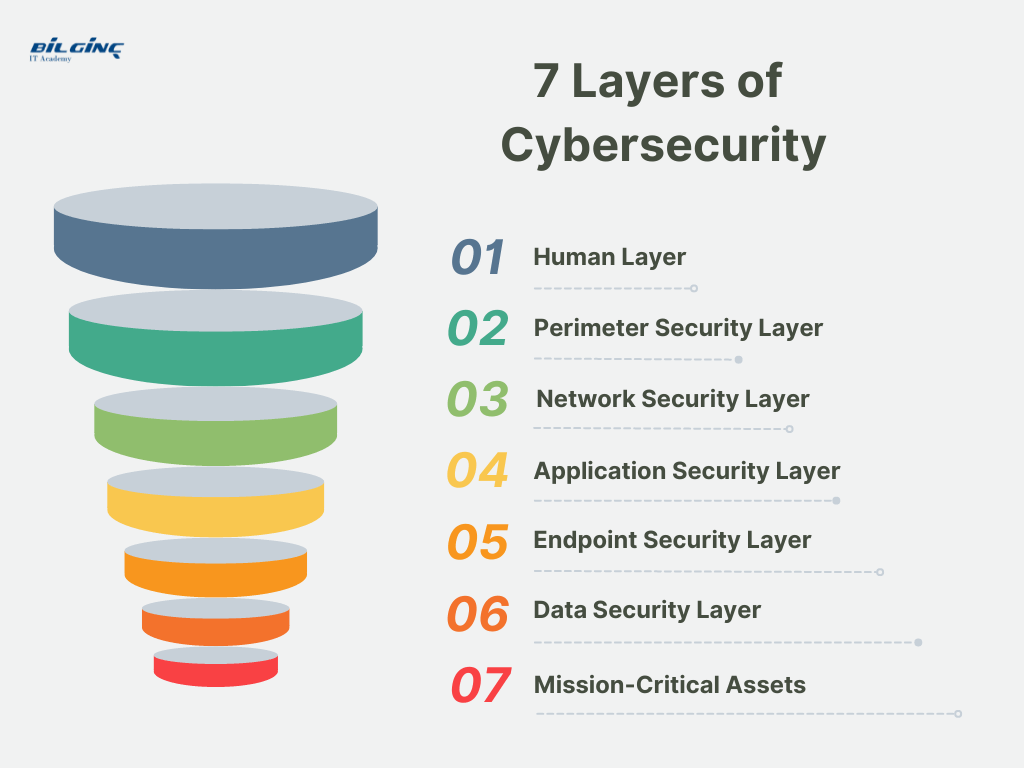
Comparative Insight: Data Security Layer vs. Traditional Data Architectures
To fully appreciate the modern Data Security Layer, it’s essential to contrast it with traditional data security approaches, often found in older Data Lake or Data Warehouse models. Historically, security was largely perimeter-focused, relying on firewalls and network segmentation to keep threats out. Once inside the network, data might have had basic access controls, but granular protection was often an afterthought. Data was centralized, but the focus was on storage and analysis, with security being a separate, often manual, process.
In traditional data lakes, for instance, raw data is ingested with minimal transformation. While this offers flexibility, securing vast quantities of unstructured, unclassified data presents immense challenges. Security might involve setting up access control lists (ACLs) at the storage level, which can be cumbersome and prone to misconfigurations. Data warehouses, with their structured and cleaned data, often had more defined security, but still typically relied on database-level security and strong network perimeters.
The modern Data Security Layer, by contrast, is fundamentally data-centric. It acknowledges that data is distributed, accessed by various users and applications, and processed in diverse environments (cloud, on-premise, hybrid). Instead of just protecting the “container” (network, server), it focuses on protecting the “content” (the data itself) wherever it resides and however it’s used. This paradigm shift means:
- Perimeter-Agnostic Protection: Security travels with the data, not just around the network. Encryption and tokenization ensure data is protected even if it leaves the traditional perimeter.
- Granular Control at the Data Element Level: Rather than just controlling access to an entire database or table, a modern Data Security Layer can apply policies down to individual rows or even specific data fields based on attributes, roles, and context.
- Proactive and Automated Defense: AI/ML integration provides real-time threat detection, anomaly identification, and automated policy enforcement, moving beyond manual, reactive security responses.
- Integrated Governance: Security is not an add-on but an integral part of data governance, with automated data classification, compliance enforcement, and audit logging built into the data lifecycle.
- Zero Trust Philosophy: Every access request is verified, eliminating the dangerous assumption of trust within the network.
This data-centric approach empowers organizations to securely leverage their data across complex architectures, enabling cloud adoption, advanced analytics, and AI/ML initiatives without compromising sensitive information. It’s a shift from protecting the walls of the castle to protecting the crown jewels inside, no matter where they are moved.
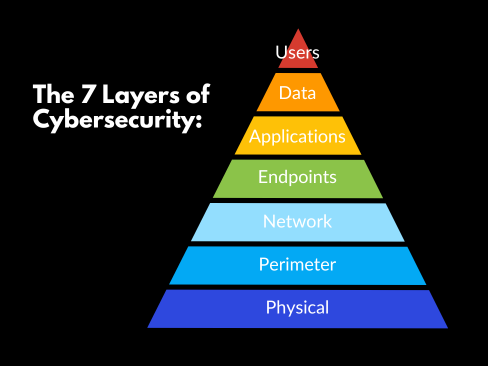
World2Data Verdict: Embracing a Data-Centric Future
The imperative for a robust Data Security Layer in today’s data-driven world cannot be overstated. It is the critical infrastructure enabling organizations to harness the power of their data while mitigating ever-present risks. World2Data.com believes that the future of data protection lies in a holistic, adaptive, and intelligent security framework, deeply integrated with data governance and powered by AI/ML. Organizations that delay this investment risk not only financial penalties and reputational damage from breaches but also stagnation in their ability to innovate and leverage data competitively. Our recommendation is clear: strategically invest in building a comprehensive Data Security Layer that emphasizes data classification, granular access controls, ubiquitous encryption, and advanced AI/ML for proactive threat detection and automated policy enforcement. The future will belong to those who can not only collect and analyze data effectively but also protect it with an impenetrable and intelligent Data Security Layer, ensuring that trust and innovation can thrive hand-in-hand.