Building High-Performance Data Lakes: Mastering Scalability and Actionable Insights
1. Platform Category: Data Lake Platform
2. Core Technology/Architecture: Lakehouse Architecture using open table formats (Iceberg, Hudi, Delta Lake) on cloud object storage (S3, ADLS, GCS) with decoupled compute engines (Spark, Trino).
3. Key Data Governance Feature: Unified Data Catalog for metadata management and fine-grained access control (e.g., AWS Lake Formation, Unity Catalog).
4. Primary AI/ML Integration: Direct access for major ML platforms (SageMaker, Azure ML, Vertex AI) and frameworks (Spark MLlib, TensorFlow, PyTorch) for model training and feature engineering.
5. Main Competitors/Alternatives: Cloud Data Warehouses (Snowflake, Google BigQuery, Amazon Redshift), Managed Lakehouse Platforms (Databricks).
Building High-Performance Data Lakes is a critical endeavor for organizations seeking to harness the full potential of their vast data assets. Effective High-Performance Data Lake Construction transforms raw, disparate data into a strategic resource, enabling rapid insights and informed decision-making across various business functions. Achieving this requires a meticulous approach to architecture, implementation, and ongoing optimization, ensuring that data is not just stored, but made readily available and performant for advanced analytics and machine learning initiatives.
Introduction: The Imperative for High-Performance Data Lakes
In today’s data-driven world, the sheer volume, velocity, and variety of data pose both immense opportunities and significant challenges. Traditional data silos and even early-generation data lakes often struggle to keep pace with the demands of real-time analytics, complex AI/ML workloads, and diverse user needs. This is where the concept of High-Performance Data Lake Construction becomes paramount. An optimized data lake architecture moves beyond simple storage, focusing on delivering speed, scalability, and robust governance to unlock the true value hidden within petabytes of information. This article delves into the foundational principles, architectural choices, and operational strategies required to build and maintain data lakes that truly perform, driving innovation and competitive advantage for enterprises globally.
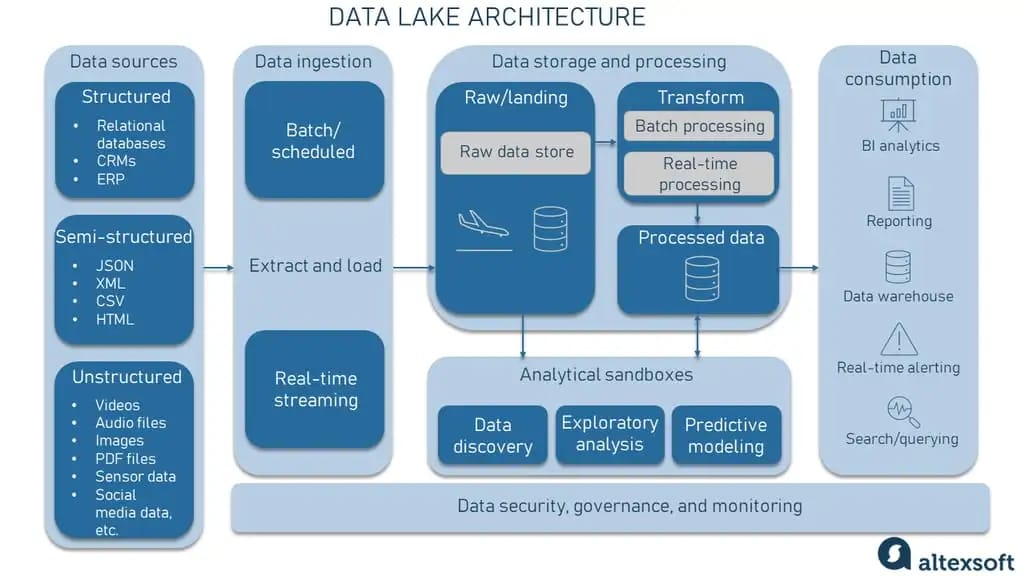
Core Breakdown: Architecture, Components, and Value of High-Performance Data Lakes
The journey to a high-performance data lake begins with a deep understanding of its core components and the strategic choices that underpin its architecture. It’s not merely about accumulating data; it’s about making that data instantly useful and accessible for a wide array of analytical applications.
Understanding the Core of High-Performance Data Lakes
Defining Performance Metrics involves establishing clear benchmarks for data ingestion speed, query latency, and concurrent user access, ensuring the lake meets operational demands. For high-performance systems, ingestion might range from sub-second latency for streaming data to minutes for large batches, while query latency for complex analytical queries should ideally be in seconds. Data Ingestion Strategies must encompass both real-time streaming (e.g., Kafka, Kinesis) and robust batch processing capabilities (e.g., Spark, Flink) to capture all relevant data efficiently from diverse sources like operational databases, IoT devices, application logs, and third-party APIs. Scalability and Flexibility Requirements dictate that the chosen architecture can seamlessly expand with increasing data volumes and adapt to new data types or analytical needs without costly overhauls. This often translates to cloud-native, serverless, or highly distributed solutions.
Architectural Foundations for Speed: The Lakehouse Paradigm
Choosing the Right Storage Layers is paramount. High-performance data lakes invariably leverage cloud object storage (e.g., AWS S3, Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2, Google Cloud Storage) as their foundational layer due to its unparalleled cost-effectiveness, scalability, durability, and serverless nature. This allows for storing vast amounts of raw, semi-structured, and structured data without upfront provisioning. Optimizing Data Formats like Parquet or ORC is crucial for reducing storage footprint and accelerating query performance. These columnar formats enable predicate pushdown and column pruning, significantly speeding up analytical queries by reading only necessary data. Leveraging Cloud-Native Solutions provides inherent scalability, managed services, and integrated security features, simplifying complex deployments and reducing operational overhead. Services like AWS Glue, Azure Data Factory, and Google Cloud Dataflow are instrumental in managing and processing data at scale.
At the heart of modern High-Performance Data Lake Construction lies the Lakehouse Architecture. This innovative paradigm blends the flexibility and cost-efficiency of data lakes with the ACID transactions, schema enforcement, and performance typically associated with data warehouses. The key enablers are open table formats such as Apache Iceberg, Apache Hudi, and Delta Lake. These formats introduce critical data warehousing capabilities directly onto cloud object storage:
- ACID Transactions: Guaranteeing data reliability and consistency, even with concurrent reads and writes.
- Schema Evolution: Allowing changes to table schemas (e.g., adding new columns) without disrupting existing queries or requiring extensive data migrations.
- Time Travel: Enabling access to historical versions of data for auditing, reproducibility, and rollback capabilities.
- Indexing and Caching: Improving query performance for frequently accessed data.
This architecture decouples compute from storage, allowing organizations to select the best-fit compute engines for specific workloads. Apache Spark remains a dominant force for large-scale data processing and transformation, while Presto/Trino excel in interactive analytics and ad-hoc queries, and tools like Flink are ideal for real-time stream processing. This flexibility ensures optimal resource utilization and cost management.
Data Ingestion and Processing Efficiency
Real-time vs. Batch Processing decisions significantly impact the freshness of data. A high-performance data lake integrates robust pipelines for both: low-latency streaming for immediate operational insights and regular batch processing for historical analysis and complex transformations. Streamlining ETL/ELT Pipelines ensures data is cleansed, transformed, and ready for analysis with minimal human intervention. This involves automated data validation, standardization, and enrichment processes. Data Governance and Quality at Scale are non-negotiable, preventing data swamps and maintaining the integrity essential for reliable business intelligence and AI models. A unified data catalog (e.g., AWS Lake Formation, Unity Catalog) is crucial for metadata management, discovery, and fine-grained access control, ensuring compliance and data security.
Query Optimization and Analytics Readiness
Indexing and Partitioning Techniques significantly enhance query speeds by reducing the amount of data scanned during analytical operations. Proper partitioning (e.g., by date, region, or customer ID) and the use of secondary indexes (e.g., min/max, bloom filters within table formats) are essential. Selecting Query Engines like Presto/Trino, Spark SQL, or Athena depends on specific workload patterns and budget considerations, each offering distinct advantages in terms of performance, cost, and SQL compliance. Facilitating Self-Service Analytics empowers business users to explore data independently, fostering a data-driven culture and accelerating insight generation through user-friendly interfaces and integrated BI tools.
Challenges and Barriers to Adoption
While the benefits of High-Performance Data Lake Construction are clear, several challenges can impede successful implementation and adoption:
- Data Quality and Governance: Maintaining high data quality across diverse sources and ensuring robust governance frameworks (metadata management, access control, lineage) can be complex, leading to “data swamps” if not meticulously managed.
- Schema Evolution Management: While open table formats help, managing rapidly evolving schemas from diverse data sources still requires careful planning and robust ETL/ELT processes to prevent data corruption or query failures.
- Cost Management: The promise of cost-effectiveness can be elusive without careful monitoring and optimization of storage tiers, compute instances, and data transfer costs in cloud environments. Over-provisioning or inefficient queries can quickly escalate expenses.
- Security and Compliance: Implementing fine-grained access control, encryption, and audit trails across a sprawling data lake to meet regulatory requirements (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) is a significant undertaking.
- Skill Gap: Building and managing a high-performance data lake requires specialized skills in distributed systems, cloud architecture, data engineering, and data science, which can be challenging to find or develop within an organization.
- Complexity of MLOps Integration: Integrating ML platforms and frameworks seamlessly, ensuring feature store consistency, and automating model training and deployment workflows on a data lake can add considerable operational complexity.
Business Value and ROI
Investing in High-Performance Data Lake Construction yields substantial business value and a strong return on investment (ROI):
- Unified Analytics Platform: Breaking down data silos to provide a single source of truth for all analytical workloads, from descriptive dashboards to predictive models.
- Enhanced Data Quality for AI/ML: By implementing robust data governance and quality processes, the data lake provides clean, consistent, and reliable data crucial for building accurate and unbiased AI/ML models. Direct integration with major ML platforms (SageMaker, Azure ML, Vertex AI) and frameworks (Spark MLlib, TensorFlow, PyTorch) accelerates feature engineering and model training.
- Faster Time-to-Insight: Optimized ingestion, processing, and query capabilities drastically reduce the time from data arrival to actionable insights, enabling quicker business responses and innovation.
- Cost Efficiency: Leveraging affordable cloud object storage and decoupled compute allows organizations to scale resources up or down as needed, leading to significant cost savings compared to traditional data warehousing for large, diverse datasets.
- Data Democratization: Empowering a broader range of users, from data analysts to business stakeholders, with self-service access to data, fostering a data-driven culture.
- New Revenue Opportunities: The ability to process and analyze vast, diverse datasets can uncover new patterns, customer behaviors, and market trends, leading to the development of new products, services, and revenue streams.
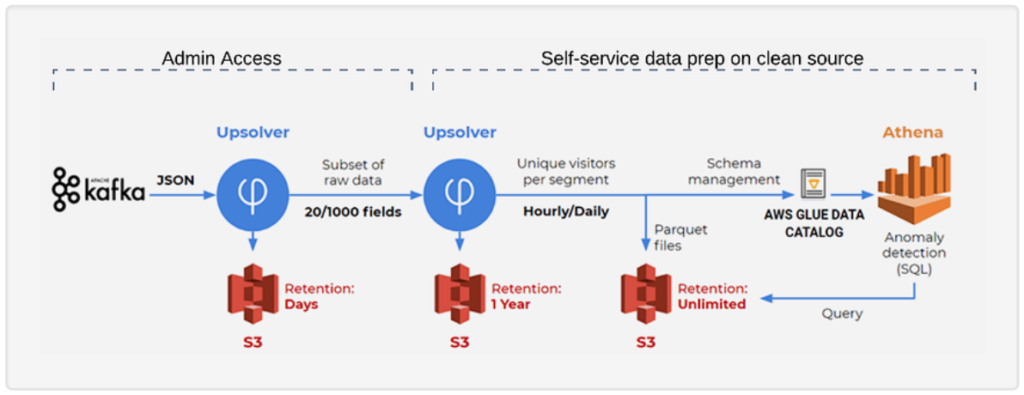
Comparative Insight: High-Performance Data Lakes vs. Traditional Models
Understanding the distinct advantages of a high-performance data lake, especially one built on a lakehouse architecture, requires a comparison with its predecessors: the traditional data lake and the conventional data warehouse.
Traditional Data Lakes
Initially envisioned as a cost-effective storage solution for all data, traditional data lakes often became “data swamps” due to a lack of schema enforcement, metadata management, and governance. While offering flexibility (schema-on-read), they struggled with data quality, discoverability, and performance for complex analytical queries. Data engineers spent significant time preparing data for specific use cases, and ACID transactions were non-existent, making concurrent updates and reliable data pipelines challenging. Security and access control were often rudimentary and difficult to implement at a granular level.
Traditional Data Warehouses
Data warehouses excel at structured data analysis, offering strong ACID guarantees, optimized query performance for relational data, and robust governance. They are ideal for reporting and business intelligence on cleansed, transformed data. However, they are typically rigid, expensive for large volumes of raw, unstructured, or semi-structured data, and struggle with schema evolution. Ingesting new data types or making schema changes can be a time-consuming and costly process. Their proprietary nature often leads to vendor lock-in, and they are generally not optimized for direct access by complex machine learning frameworks that require raw data access.
The High-Performance Data Lake (Lakehouse) Advantage
The modern, High-Performance Data Lake Construction, particularly within a lakehouse framework, bridges the gap between these two paradigms. It retains the flexibility and cost-effectiveness of storing all data types in inexpensive cloud object storage, eliminating silos. Crucially, it layers on data warehouse-like capabilities:
- ACID Transactions and Schema Enforcement: Through open table formats like Iceberg, Hudi, and Delta Lake, the lakehouse ensures data reliability and consistency, allowing for dependable ETL/ELT operations and concurrent workloads.
- Performance: Optimized data formats, indexing, and decoupled compute engines (Spark, Trino) deliver query performance often comparable to, or even exceeding, traditional data warehouses for analytical workloads, while supporting diverse query patterns.
- Unified Governance: Centralized data catalogs (e.g., AWS Lake Formation, Unity Catalog) provide comprehensive metadata management, data lineage, and fine-grained access controls, addressing the “data swamp” problem.
- AI/ML Readiness: With direct access to raw and refined data, alongside integration with major ML platforms and frameworks, the lakehouse provides an ideal environment for end-to-end MLOps workflows, supporting feature engineering, model training, and inference.
- Cost-Efficiency: By leveraging cloud object storage and pay-as-you-go compute, it offers a more cost-effective solution for managing vast, diverse datasets compared to scaling traditional data warehouses.
While cloud data warehouses (Snowflake, Google BigQuery, Amazon Redshift) remain strong competitors for structured analytics, and managed lakehouse platforms (Databricks) offer integrated solutions, the custom-built High-Performance Data Lake Construction using open source table formats provides maximum flexibility, avoiding vendor lock-in and allowing organizations to tailor their data platform precisely to their unique needs and budget constraints.
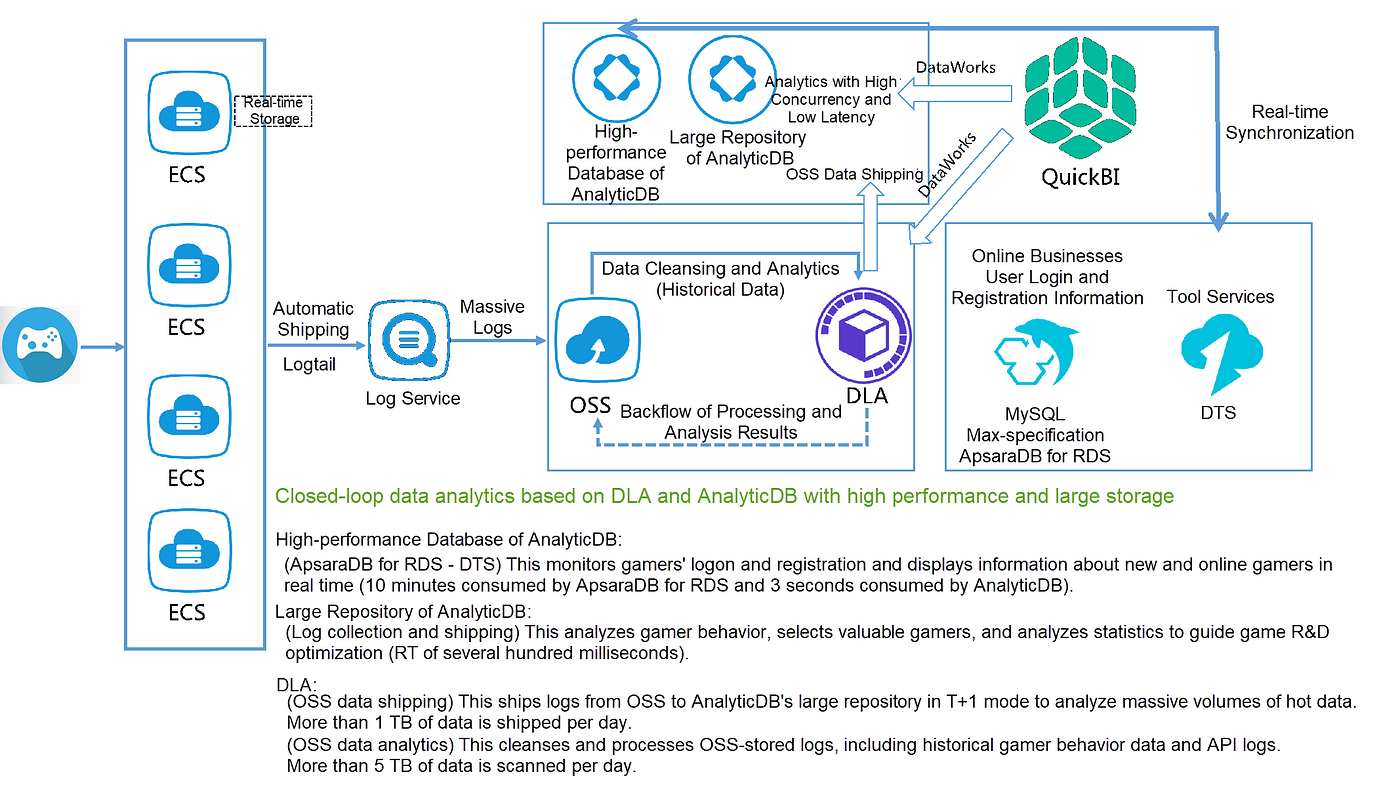
World2Data Verdict: The Strategic Imperative for a Data-Driven Future
The evolution from simple data lakes to high-performance, lakehouse-architected platforms represents a monumental shift in how organizations manage and extract value from data. World2Data.com asserts that embracing a strategy focused on High-Performance Data Lake Construction is no longer merely an option but a strategic imperative for any enterprise aiming to remain competitive and innovative in the digital age. Organizations must prioritize building a robust, scalable, and governed data foundation that leverages open table formats and decoupled compute. We recommend a phased approach, starting with a well-defined data governance framework and a clear understanding of key performance indicators. The future of enterprise analytics and AI will undoubtedly be built on these agile, cost-effective, and highly performant data platforms, providing a unified backbone for insights that drive transformational business outcomes.