Prescriptive Analytics: Turning Insights into Smarter Decisions for Business Optimization
- Platform Category: Advanced Analytics Platform, Decision Support System
- Core Technology/Architecture: Optimization Algorithms, Simulation Modeling, Machine Learning, Operations Research
- Key Data Governance Feature: Model Governance, Data Lineage, Data Quality Management
- Primary AI/ML Integration: Built-in AI/ML for predictive modeling and optimization; Reinforcement Learning
- Main Competitors/Alternatives: IBM Decision Optimization, SAS Optimization, FICO Xpress Optimization, Gurobi, CPLEX
In today’s data-rich environment, simply understanding what happened or predicting what might occur is no longer enough to maintain a competitive edge. This is where Prescriptive Analytics emerges as a critical differentiator, representing the pinnacle of data analysis. It moves beyond retrospective insights and future forecasts to actively recommend the optimal course of action. By leveraging sophisticated data models and algorithms, prescriptive analytics empowers organizations to not only anticipate outcomes but also to proactively suggest the best decisions to achieve specific business goals, ensuring superior results and strategic advantage.
The Pinnacle of Data-Driven Strategy: An Introduction to Prescriptive Analytics
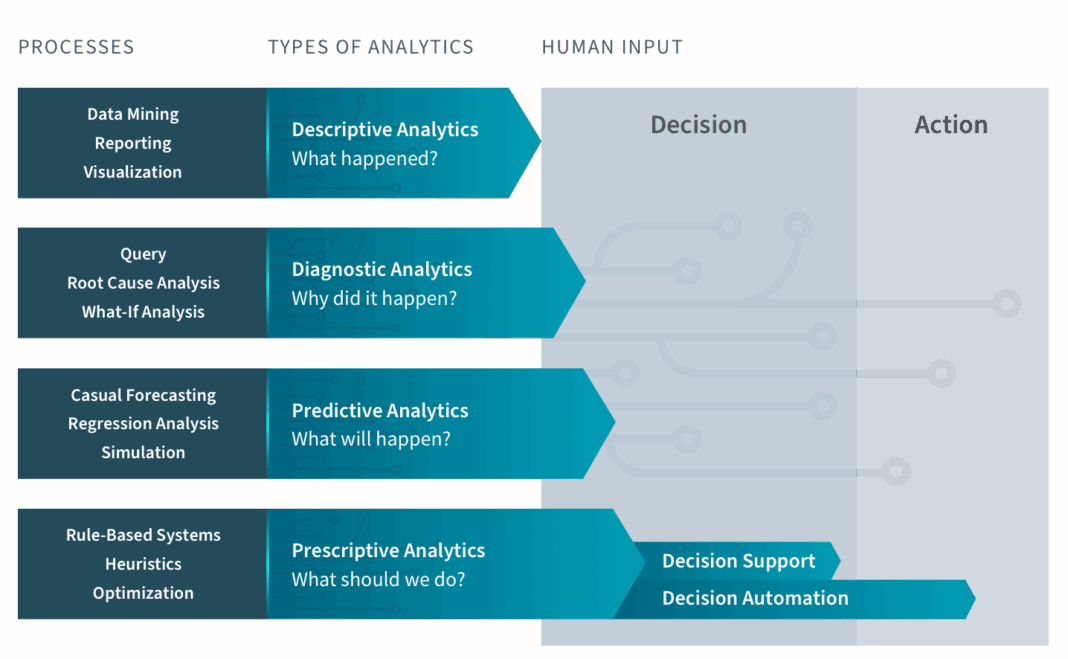
The journey of data analytics has evolved significantly over the years, typically progressing through distinct stages, each building upon the capabilities of the last. It begins with descriptive analytics, which answers the fundamental question of “what happened?” by summarizing historical data to reveal patterns and trends. This provides valuable hindsight into past performance and operational metrics. The next stage is predictive analytics, which addresses “what will happen?” by employing statistical models and machine learning algorithms to forecast future events, probabilities, and trends. While predictive analytics offers foresight, it still leaves the decision-making process to human interpretation.
Prescriptive Analytics stands as the most advanced and impactful stage in this analytical continuum. It fundamentally shifts the paradigm by answering the crucial question of “what should we do?” Unlike its predecessors, prescriptive analytics doesn’t just present data or forecasts; it provides actionable recommendations and optimal solutions to achieve desired outcomes. By integrating historical data, real-time information, business rules, and powerful computational techniques, prescriptive analytics guides decision-makers towards the most effective path forward. This proactive approach transforms passive insights into definitive actions, enabling organizations to optimize processes, mitigate risks, and capitalize on opportunities with unprecedented precision. For any organization striving for true data-driven excellence, understanding and implementing Prescriptive Analytics is no longer optional but a strategic imperative.
Unpacking the Mechanisms of Prescriptive Analytics: Core Breakdown and Components
At its heart, Prescriptive Analytics is a complex orchestration of advanced analytical models and computational techniques designed to identify the best possible actions. It synthesizes a wide array of inputs, from historical performance data and real-time operational feeds to external market intelligence and inherent business rules. The core technologies driving this sophisticated decision support system include optimization algorithms, simulation modeling, machine learning, and operations research methodologies.
Core Technologies and Architecture
- Optimization Algorithms: These are the engines of prescriptive analytics, designed to find the best possible solution among a set of alternatives, given specific constraints and objectives. Techniques such as linear programming, integer programming, dynamic programming, and non-linear programming are commonly used. Industry leaders like Gurobi and CPLEX offer robust solvers for these complex optimization problems, enabling businesses to maximize profits, minimize costs, or optimize resource allocation across intricate systems like supply chains or workforce scheduling.
- Simulation Modeling: Before recommending an action, prescriptive systems often simulate various scenarios to understand potential outcomes and risks. Monte Carlo simulations, discrete-event simulations, and agent-based modeling allow analysts to test different strategies under uncertainty, providing a probabilistic view of what might happen if certain decisions are made. This helps in stress-testing recommendations and building more resilient strategies.
- Machine Learning (ML): ML algorithms, particularly advanced techniques like Reinforcement Learning, are integral to building predictive models that feed into the prescriptive process. ML helps in identifying complex patterns, making accurate forecasts, and even learning optimal policies through trial and error in simulated environments. It can predict demand fluctuations, equipment failures, or customer behavior, all of which become critical inputs for the optimization algorithms to act upon.
- Operations Research (OR): OR provides the foundational mathematical and analytical tools for solving complex decision problems. It encompasses a broad range of techniques, including queuing theory, network analysis, and decision trees, which are applied to model and analyze systems for optimal performance. The principles of OR are deeply embedded in the design of prescriptive models, ensuring that solutions are mathematically sound and operationally feasible.
- Big Data and Real-time Data Processing: To fuel these complex models, a robust data infrastructure capable of handling vast volumes of historical and real-time data is essential. This includes data lakes, data warehouses, and streaming analytics platforms that ensure timely and accurate data ingestion and processing.
Challenges and Barriers to Adoption
Despite its immense potential, the successful adoption of Prescriptive Analytics is not without its hurdles. Organizations often face several significant challenges:
- Data Quality and Availability: The efficacy of any prescriptive model hinges on the quality and completeness of its input data. Poor data hygiene, silos, or insufficient historical records can lead to flawed recommendations, eroding trust in the system. Robust Data Quality Management frameworks are paramount.
- Complexity of Models and Skill Gap: Designing, implementing, and maintaining sophisticated optimization and machine learning models requires a highly specialized skill set in mathematics, statistics, computer science, and domain expertise. A significant talent gap often exists within organizations, making it difficult to build in-house capabilities.
- Computational Resources: Solving complex optimization problems and running extensive simulations can be computationally intensive, demanding significant processing power and memory. This often necessitates substantial investment in advanced computing infrastructure, including cloud-based solutions.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Seamlessly integrating prescriptive models and their recommendations into existing operational systems, ERPs, CRMs, and decision-making workflows can be a major technical and organizational challenge, requiring intricate API development and robust data pipelines.
- Model Governance and Interpretability: Ensuring that prescriptive models are ethical, fair, transparent, and compliant with regulatory standards is critical. Model Governance frameworks are essential for tracking model performance, managing versions, and explaining how recommendations are generated, especially in highly regulated industries. The “black box” nature of some advanced ML models can be a barrier to trust and adoption.
- Change Management and Trust: Shifting from human-led decision-making to algorithm-driven recommendations requires a significant cultural change. Building trust among stakeholders and demonstrating the tangible value of prescriptive insights are crucial for widespread acceptance and utilization.
Business Value and Return on Investment (ROI)
Despite the challenges, the ROI of successfully implementing Prescriptive Analytics can be transformative, yielding significant competitive advantages:
- Optimized Resource Allocation: Whether it’s managing inventory levels, scheduling workforce shifts, allocating marketing spend, or optimizing logistics routes, prescriptive analytics ensures that resources are utilized in the most efficient and effective manner, directly translating to cost savings and improved service levels.
- Cost Reduction: By eliminating inefficiencies, reducing waste, and streamlining operations, businesses can achieve substantial reductions in operational expenses. This includes optimizing energy consumption, minimizing material costs in manufacturing, and cutting down on transportation expenses.
- Revenue Enhancement: Prescriptive models can identify opportunities for revenue growth, such as dynamic pricing strategies that maximize profit based on real-time demand, personalized product recommendations, and optimized cross-selling/up-selling strategies.
- Risk Mitigation: Proactively identifying and mitigating potential risks, from supply chain disruptions to financial market volatility or equipment failures, allows businesses to avoid costly setbacks and maintain operational continuity. This capability is enhanced through robust Data Lineage tracking and comprehensive risk models.
- Enhanced Decision-Making Speed and Quality: By providing immediate, data-backed recommendations, prescriptive analytics drastically shortens the decision-making cycle and improves the quality of choices, enabling organizations to respond more agilely to market changes and emerging threats.
- Proactive Problem Solving: Instead of reacting to problems after they occur, prescriptive analytics empowers companies to anticipate challenges before they materialize. For example, predicting machine breakdowns and scheduling preventative maintenance, or identifying potential customer churn and deploying targeted retention campaigns.
Comparative Insight: Prescriptive Analytics vs. The Analytical Continuum
To fully appreciate the transformative power of Prescriptive Analytics, it is crucial to understand its position within the broader analytical continuum and how it fundamentally differs from its predecessors: descriptive and predictive analytics. While all three are vital for a comprehensive data strategy, they serve distinct purposes and offer varying levels of actionable insight.
Descriptive Analytics: What Happened?
This is the most basic form of analytics, focusing on summarizing past events to provide a clear picture of what has already occurred. Tools include dashboards, reports, and basic aggregations. It answers questions like “What were our sales last quarter?” or “Which product sold the most?” While essential for understanding historical performance and setting benchmarks, descriptive analytics is purely reactive. It tells you about the past but offers no guidance on future actions.
Predictive Analytics: What Will Happen?
Building upon descriptive insights, predictive analytics uses historical data and statistical models to forecast future outcomes. Techniques range from regression analysis to advanced machine learning algorithms. It answers questions such as “What will our sales be next quarter?” or “Which customers are likely to churn?” Predictive models help organizations anticipate future trends and probabilities, enabling them to prepare for potential scenarios. However, predictive analytics stops short of telling you what to do. It provides foresight but doesn’t dictate the optimal action, leaving that interpretation to human decision-makers who must weigh various forecasted possibilities against business objectives.
Prescriptive Analytics: What Should We Do?
Prescriptive Analytics transcends both descriptive and predictive capabilities by not only forecasting what might happen but also recommending the best course of action to achieve a specific objective. It integrates the insights from both descriptive and predictive models with business rules, constraints, and optimization techniques. Instead of just knowing that sales might drop or customers might churn, prescriptive analytics suggests concrete steps: “To maximize sales next quarter, adjust pricing on product A by 5% and increase marketing spend on channel B by 10%,” or “To prevent customer churn, offer a specific discount package to these identified high-risk customers.”
The key differentiator is the focus on actionable intelligence. While traditional data lakes and data warehouses store vast amounts of data for descriptive and predictive analysis, they typically don’t inherently possess the algorithms or intelligence to generate optimal decisions. Prescriptive analytics leverages these data foundations but adds a sophisticated layer of computational power, AI/ML (including Reinforcement Learning), and operations research to transform raw data and predictions into concrete, optimized strategies. It shifts the analytical focus from understanding and forecasting to actively influencing and shaping future outcomes, making it a true decision support system that moves beyond passive insights to active recommendations.
World2Data Verdict: Charting the Future with Prescriptive Power
The trajectory of business intelligence is undeniably moving towards greater autonomy and precision, with Prescriptive Analytics leading the charge. Our analysis at World2Data indicates that organizations that strategically invest in and successfully implement prescriptive capabilities will not merely adapt to market changes but actively shape their future. The power to transform data insights into concrete, optimal actions offers an unparalleled competitive advantage, driving efficiencies, maximizing revenue, and significantly de-risking complex operational environments.
However, the journey requires more than just technological adoption. It demands a holistic approach encompassing robust Data Quality Management, sophisticated Model Governance frameworks, and a cultural shift towards trusting algorithm-driven recommendations. The future of decision-making lies in intelligent automation, where human expertise is augmented by prescriptive systems that can navigate complex trade-offs and identify optimal paths at scale. World2Data’s recommendation is clear: organizations must prioritize building their prescriptive analytics capabilities, starting with clear business objectives and a phased implementation. This involves investing in the right mix of talent, technologies (especially those leveraging advanced AI/ML like Reinforcement Learning), and a commitment to continuous model refinement. Those who embrace this shift will not just make smarter decisions; they will redefine what it means to be strategically agile and operationally excellent in the digital age.