AI Generating Synthetic Data for Training Models: Revolutionizing ML Workflows
Platform Category: Synthetic Data Generation Platform
Core Technology/Architecture: Generative AI (e.g., Generative Adversarial Networks – GANs, Variational Autoencoders – VAEs, Transformers, Diffusion Models)
Key Data Governance Feature: Privacy Preservation (e.g., Differential Privacy, K-anonymity, L-diversity)
Primary AI/ML Integration: Generation of tabular, image, text, and time-series data for direct use in ML model training pipelines, data augmentation, and testing.
Main Competitors/Alternatives: Gretel.ai, Mostly.ai, Tonic.ai, Datagen, SDV (Open Source Library), Hazy, Synthpop
AI Generating Synthetic Data for Training Models is rapidly transforming the landscape of machine learning, marking a pivotal shift in how data challenges are addressed. The profound power of Synthetic Data Generation for ML lies in its ability to overcome traditional data hurdles such as scarcity, privacy concerns, and bias, paving the way for the development of more robust, ethical, and performant AI systems. This innovative approach promises to unlock new frontiers in model development, allowing organizations to innovate faster and with greater confidence.
Introduction: The Dawn of Data Autonomy with Synthetic Data
The quest for high-quality, diverse, and privacy-compliant data has long been a bottleneck in the advancement of artificial intelligence. Real-world data is often expensive to acquire, difficult to label, fraught with privacy regulations, and frequently contains biases that can perpetuate inequalities in AI systems. It’s within this challenging context that AI Generating Synthetic Data for Training Models emerges as a transformative solution. By leveraging advanced generative AI techniques, synthetic data platforms create artificial datasets that statistically resemble real data without containing any actual sensitive information. This capability ensures unparalleled privacy and security for sensitive information during model development, enabling a new era of responsible AI innovation.
This article provides a deep dive into the technical and strategic implications of synthetic data. We will explore its core mechanisms, dissect the business value it delivers, and critically compare it against conventional data paradigms. Our objective is to illuminate how Synthetic Data Generation for ML not only accelerates model training cycles but also addresses fundamental ethical and practical concerns, making advanced solutions more accessible and sustainable for World2Data’s clients and the broader data science community.
Core Breakdown: Architecture, Applications, and Impact of Synthetic Data Generation
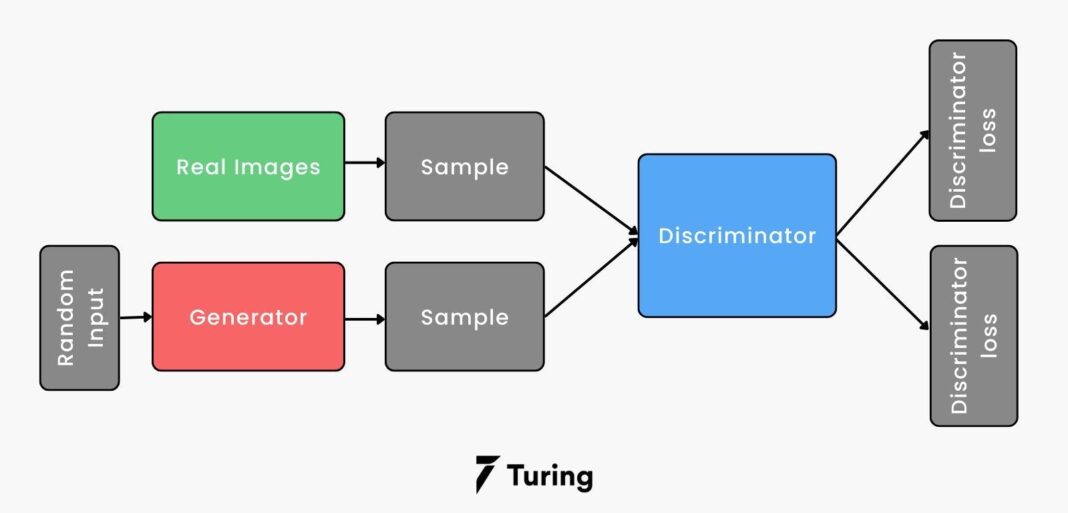
At its heart, the process of AI Generating Synthetic Data for Training Models relies on sophisticated generative artificial intelligence algorithms. These include Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), autoregressive models, and more recently, diffusion models. These technologies learn the underlying patterns, distributions, and relationships within real datasets and then use this learned knowledge to produce entirely new, artificial data points. The generated data maintains the statistical properties, correlations, and structural integrity of the original, but each record is novel and untraceable to any real individual or entity.
The impact of this technology is multifaceted. Firstly, it directly addresses the critical issue of data scarcity, especially for niche applications or rare events where real data is either non-existent or extremely limited. For instance, in fraud detection, synthetic data can simulate novel attack vectors that haven’t yet occurred in the real world, preparing models for future threats. Secondly, synthetic data ensures unparalleled privacy and security for sensitive information during model development. By replacing real data with synthetic versions, organizations can comply with stringent regulations like GDPR and HIPAA, mitigating privacy risks without compromising the quality of their AI models. Consequently, AI teams can significantly accelerate their model training cycles, bringing advanced solutions to market faster and with greater confidence in their ethical deployment.
Enhancing Model Robustness and Data Quality for AI
The generation of diverse datasets through synthetic means expands the variety of training examples available to machine learning models. This process is crucial for mitigating inherent biases often found in real-world data, leading to fairer and more equitable AI systems. For example, if a real dataset disproportionately represents certain demographics, synthetic data can be generated to balance these representations, thereby reducing algorithmic bias. Furthermore, synthetic data excels at simulating rare or difficult-to-capture scenarios, providing invaluable training material for critical situations in domains like autonomous driving (simulating complex road conditions) or medical diagnostics (simulating rare disease manifestations). This capability profoundly improves the generalization capabilities of machine learning models across varied conditions, playing a vital role in reducing the risks of overfitting and leading to more reliable and deployable AI systems. Developers can efficiently validate new algorithms against comprehensive, controlled synthetic environments before real-world implementation.
In the context of data platforms, Synthetic Data Generation for ML can significantly streamline operations related to Feature Stores and Data Labeling. Instead of waiting for large volumes of real, labeled data to populate a feature store, synthetic data can be used to quickly create diverse feature sets for prototyping and initial model training. This capability drastically reduces the dependency on manual data labeling efforts, which are often time-consuming and expensive. For scenarios requiring specific data augmentations or variations, synthetic data generators can produce millions of labeled examples that mimic human annotations, ensuring a consistent and scalable supply of high-quality training data.
Challenges and Barriers to Adoption in Synthetic Data
Despite its immense promise, the widespread adoption of AI Generating Synthetic Data for Training Models faces several challenges. A primary concern is ensuring the statistical fidelity and utility of the generated data. While synthetic data aims to replicate the statistical properties of real data, achieving perfect fidelity, especially for complex, high-dimensional datasets, remains a research frontier. Inaccurate synthesis can lead to models that perform poorly in real-world scenarios, exhibiting issues like data drift when deployed. Validation methodologies for synthetic data are still evolving, requiring sophisticated statistical tests and expert judgment to confirm its suitability for specific ML tasks.
Another barrier is the computational cost and complexity associated with state-of-the-art generative models. Training GANs or diffusion models, especially on large datasets, demands significant computational resources and expertise in model architecture and hyperparameter tuning. Integrating synthetic data generation into existing MLOps pipelines also presents complexities. Organizations need robust frameworks for generating, validating, versioning, and deploying synthetic datasets alongside real data, ensuring a seamless workflow from data creation to model deployment and monitoring. Furthermore, ethical considerations surrounding the generation of synthetic data, particularly regarding the potential for “synthetic bias” (where biases from the original data are inadvertently amplified or new biases are introduced), require careful governance and oversight.
Business Value and ROI from Synthetic Data Generation
The return on investment (ROI) from adopting Synthetic Data Generation for ML is substantial and multifaceted. For businesses, the primary value propositions include:
- Accelerated Model Development: By overcoming data scarcity and labeling bottlenecks, teams can develop and iterate on models much faster, reducing time-to-market for new AI products and features.
- Enhanced Data Privacy and Compliance: Synthetic data allows organizations to innovate with sensitive information while maintaining strict privacy compliance, opening up new opportunities in highly regulated industries like healthcare and finance without legal or reputational risk.
- Cost Reduction: Significantly reduces the costs associated with data acquisition, anonymization, and manual labeling, freeing up resources for other critical tasks.
- Improved Model Performance: Access to larger, more diverse, and less biased synthetic datasets leads to more robust, generalizable, and fairer AI models, ultimately boosting business outcomes.
- Innovation Enablement: Facilitates experimentation and research by providing developers with on-demand data, fostering a culture of innovation even in data-constrained environments. This includes testing edge cases, stress-testing models, and exploring “what-if” scenarios that are impractical with real data.
Figure 1: Illustrative workflow of a typical Synthetic Data Lifecycle, from generation to deployment.
Comparative Insight: Synthetic Data Platforms vs. Traditional Data Lakes/Warehouses
To fully appreciate the paradigm shift brought by AI Generating Synthetic Data for Training Models, it’s crucial to compare it with traditional data management infrastructures like data lakes and data warehouses. These established systems are primarily designed for storing, processing, and analyzing real, often raw, data. Data lakes, with their schema-on-read flexibility, are excellent for storing vast amounts of diverse, unstructured data, while data warehouses excel at structured data for business intelligence and reporting, offering high performance for analytical queries.
However, both traditional data lakes and warehouses inherently deal with real data, which comes with its own set of challenges regarding privacy, security, and accessibility. Accessing sensitive data in these environments often requires complex anonymization processes, strict access controls, and compliance audits, slowing down development cycles and increasing operational overhead. Furthermore, if real data is scarce or biased, these systems merely reflect those limitations in the downstream AI applications.
Synthetic data platforms, in contrast, operate on a different principle. While they may draw statistical insights from data residing in lakes or warehouses, their core function is *creation* rather than mere storage or processing of real data. They are purpose-built for Synthetic Data Generation for ML, addressing the specific needs of AI model training. This includes:
- Privacy by Design: Synthetic data is intrinsically privacy-preserving, eliminating the need for complex anonymization techniques or granting direct access to sensitive real data for development and testing.
- Data Augmentation and Scarcity: Synthetic platforms can generate virtually infinite amounts of data, overcoming scarcity issues prevalent in real-world datasets and providing diverse examples for robust model training.
- Bias Mitigation: Unlike traditional systems that passively store existing biases, synthetic data generators can be designed to actively identify and correct biases during the generation process, leading to fairer models.
- Flexibility and Agility: Developers can quickly generate specific datasets tailored for particular experiments, allowing for rapid prototyping and hypothesis testing without waiting for real data collection or access approvals.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Long-term costs associated with data acquisition, storage of petabytes of raw sensitive data, and stringent compliance measures can be significantly reduced by relying on high-quality synthetic data for many use cases.
While data lakes and warehouses remain indispensable for storing organizational knowledge and facilitating traditional analytics, synthetic data platforms serve as a complementary, yet distinct, layer essential for modern AI development. They act as “data factories” for AI, providing a continuous, secure, and customizable supply of data specifically optimized for machine learning models, thereby greatly enhancing the efficiency and ethical posture of AI initiatives.

Figure 2: An overview of various tools and techniques employed in Generative AI for Synthetic Data, highlighting its diverse applications.
World2Data Verdict: The Imperative for Synthetic Data in Future AI Ecosystems
The trajectory of AI innovation is inextricably linked to the quality, quantity, and accessibility of data. World2Data believes that AI Generating Synthetic Data for Training Models is not merely an optional enhancement but an essential component of any forward-looking data strategy. The capability to create statistically representative, privacy-preserving, and bias-mitigated datasets on demand will fundamentally redefine the agility and ethical foundation of AI development. For organizations grappling with data scarcity, regulatory constraints, or the prohibitive costs of real-world data acquisition and labeling, synthetic data offers an unparalleled solution.
Our recommendation is clear: enterprises must strategically invest in and integrate Synthetic Data Generation for ML into their core MLOps and data governance frameworks. This includes allocating resources for research into advanced generative models, developing robust validation methodologies for synthetic data quality, and establishing clear policies for its responsible use. The future of AI is not solely about larger models or more powerful compute; it’s equally about smarter, more ethical, and more sustainable data practices. Synthetic data stands as a cornerstone of this future, empowering innovators to build better, fairer, and more robust AI systems that truly serve humanity without compromising privacy or perpetuating existing biases. Early adopters of this technology will gain a significant competitive advantage, unlocking new possibilities for innovation and responsible growth in the data-driven economy.